K-Patents PR-01-S User Manual
Page 9
INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR K-PATENTS PR-01-S (-AX/FM/CS)
DOCUMENT/REVISION No. INM 1/14
Effective: May 15, 2009
7
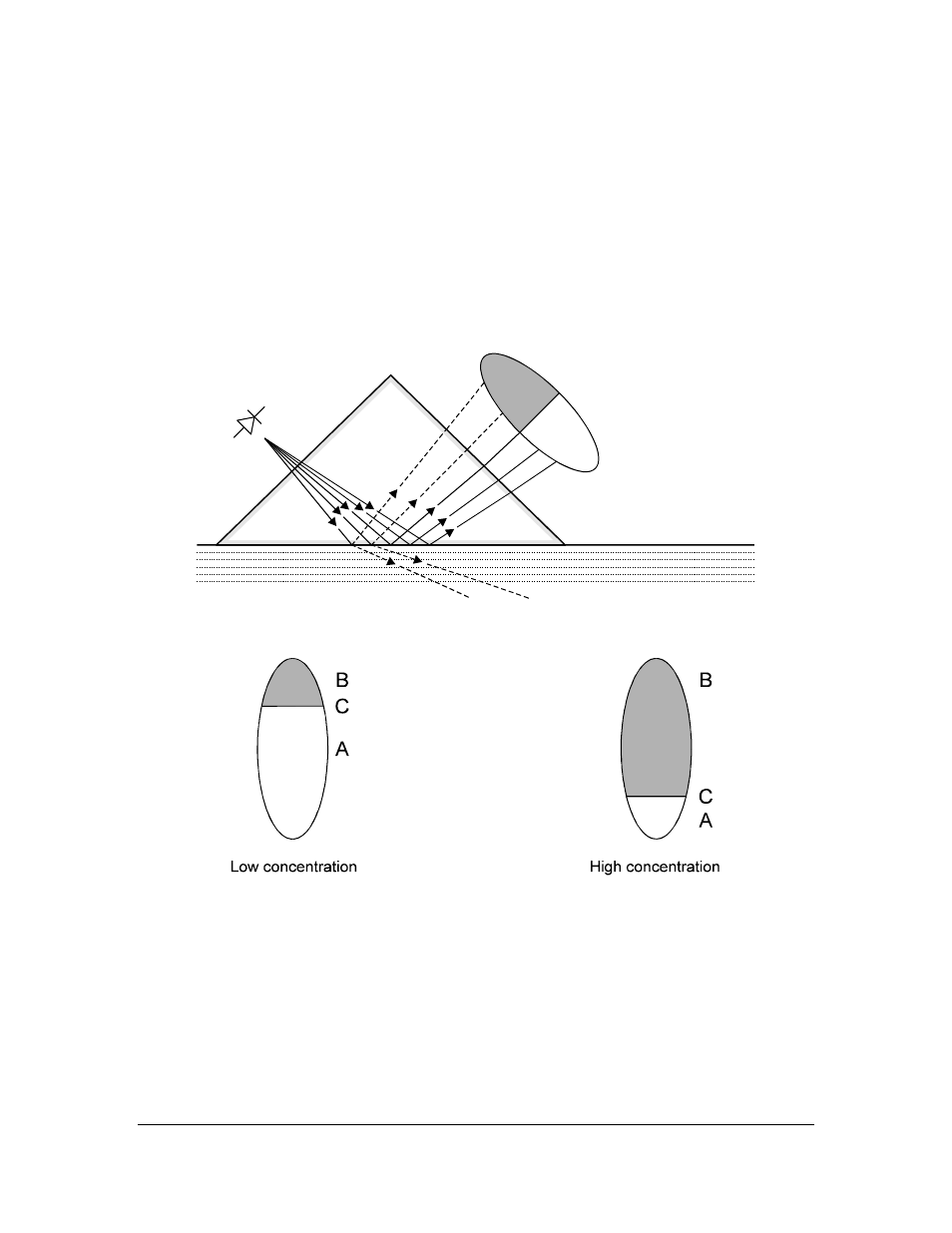
2.3. PRINCIPLE OF MEASUREMENT
The K-Patents Process Refractometer determines the refractive index (R.I) of the process solution by
measuring the critical angle of refraction. The light from a light source (L) (Figure 2.30) is directed against
the interface between a prism (P) and the process solution (S). The light rays meet this surface at different
angles. The reflected rays form an image (ACB), where (C) is the position of the critical angle ray. The
rays at (A) are totally reflected at the interface, the rays at (B) are partially reflected and partially refracted
into the process solution. In this way the optical image is divided into a light area (A) and a dark area (B).
The position of the borderline (C) between the areas shows the value of the critical angle and thus of the
refractive index of the process solution. The refractive index normally increases with increasing
concentration.
B
C
A
S
P
L
Figure 2.30
Refractometer principle.
Figure 2.31
Optical images.
From this follows that the optical image changes with the process solution concentration as shown in
Figure 2.31. The optical image is converted to an electric signal by an image detector.
By this method the concentration of the solution is measured. The color of the solution, gas bubbles or
undissolved particles do not interfere with the result.