Yamaha CVP-705B User Manual
Page 60
Creating/Editing Styles (Style Creator)
CVP-709/CVP-705 Reference Manual
60
NTR/NTT
(Note
Transposition
Rule/Note
Transposition
Table)
NTT
Type
Arpeggio
Suitable for arpeggio-played sound of the guitar, resulting in beautiful
four-note arpeggio sounds.
NTT
Bass
The channel for which this is set to “On” will be played back by the bass root note, when
the on-bass chord is recognized by the instrument. When NTR is set to Guitar and this
parameter is set to “On,” only the note which is assigned to bass will be played back by the
bass root note.
NTR/NTT Settings for the Rhythm Channels
Since the Rhythm channels should not be affected by Chord change, make sure to make the
following settings.
• NTR = Root Fixed
• NTT = Bypass
• NTT Bass = Off
With the above settings, the “Source Root” and “Source Chord” parameters are changed to “Play
Root” and “Play Chord,” respectively.
High Key/Note
Limit
Adjusts the Octave of the notes converted via the NTT and NTR.
High Key
This sets the highest key (upper octave limit) of the note transposition
for the chord root change. Any notes calculated to be higher than the
highest key are transposed down to the next lowest octave. This setting is
available only when the NTR parameter (
) is set to “Root Trans.”
Note Limit Low
These set the note range (highest and lowest notes) for Voices recorded
to the Style channels. By judicious setting of this range, you can ensure
that the Voices sound as realistic as possible — in other words, that no
notes outside the natural range are sounded (e.g., high bass sounds or
low piccolo sounds).
Note Limit High
RTR
(Retrigger
Rule)
These settings determine whether notes stop sounding or not and how they change pitch in
response to chord changes.
Stop
The notes stop sounding.
Pitch Shift
The pitch of the note will bend without a new attack to match the type of
the new chord.
Pitch Shift to Root
The pitch of the note will bend without a new attack to match the root of
the new chord. However, the octave of the new note remains the same.
Retrigger
The note is retriggered with a new attack at a new pitch corresponding to
the next chord.
Retrigger To Root
The note is retriggered with a new attack at the root note of the next
chord. However, the octave of the new note remains the same.
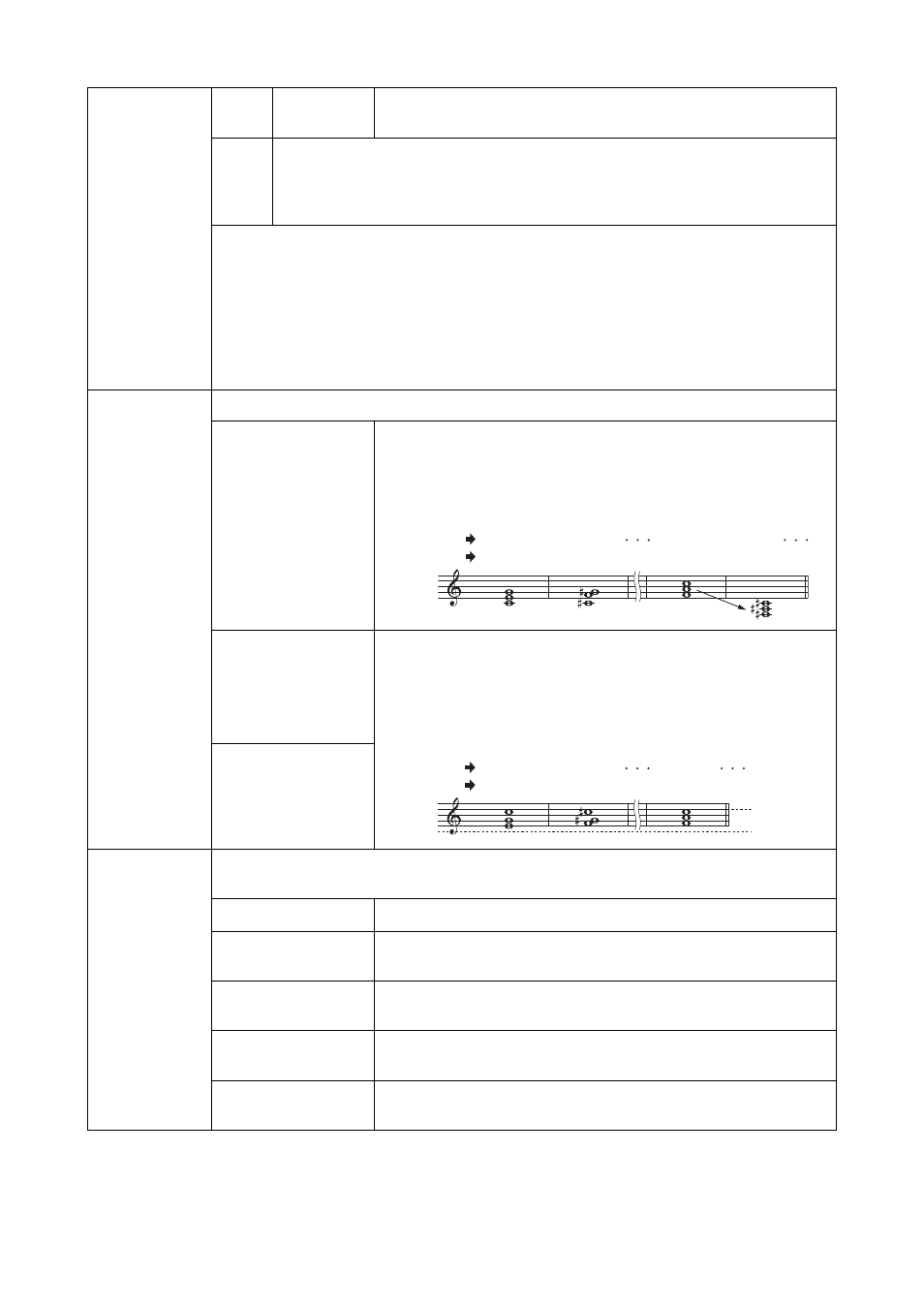
CM
C3-E3-G3
FM
F3-A3-C4
FᅊM
Fᅊ2-Aᅊ2-Cᅊ3
CᅊM
Cᅊ3-F3-Gᅊ3
Root changes
Notes played
Example — When the highest key is F
CM
E3-G3-C4
FM
F3-A3-C4
C
ᅊM
F3-G
ᅊ3-Cᅊ4
Root changes
Notes played
Example — When the lowest note is C3 and the highest is D4
High Limit
Low Limit