Short circuit hoods – Greenheck Waterwash (458292) User Manual
Page 34
34
April 2005
®
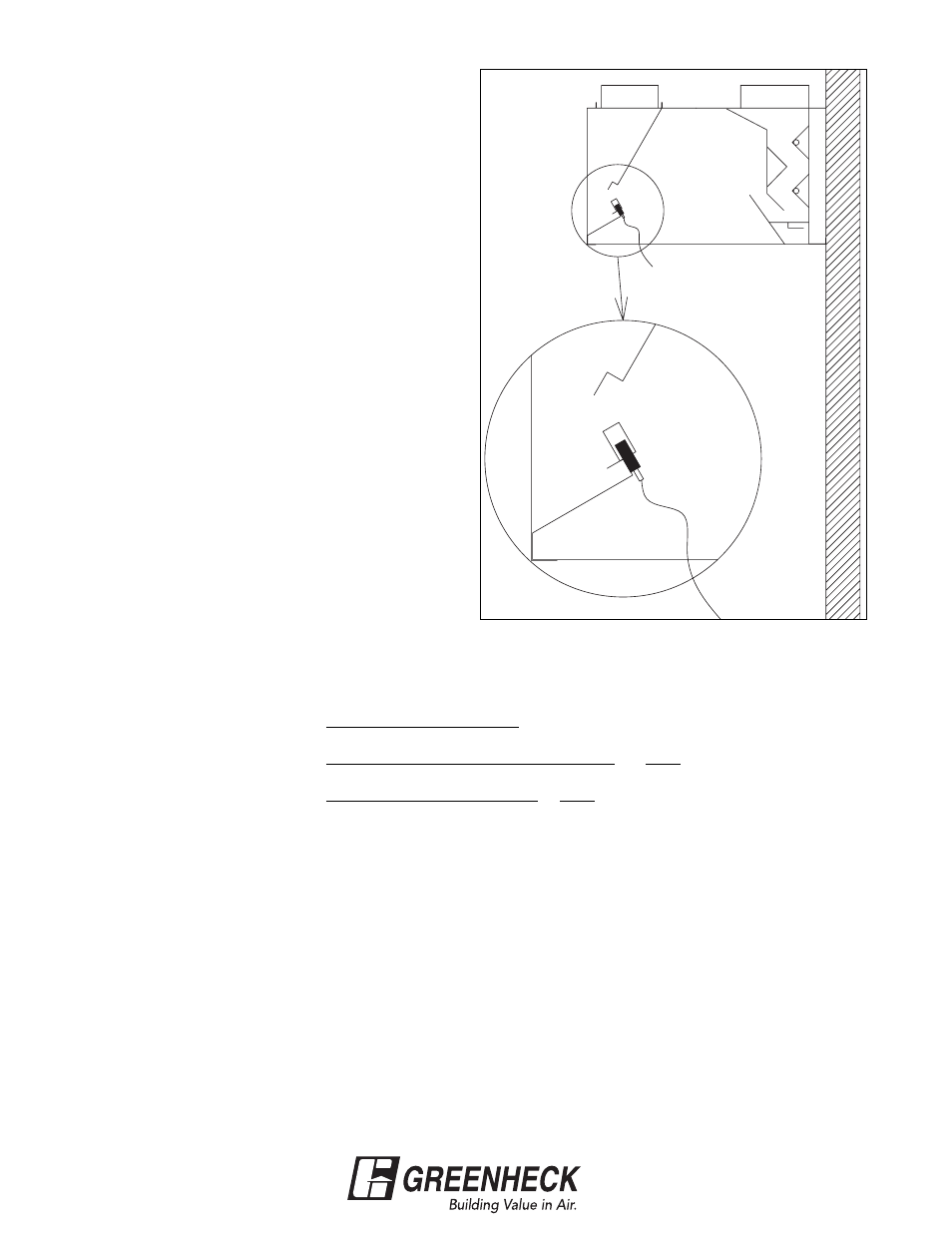
TESTING HOOD AIR VOLUME
Short Circuit Hoods
Supply
All cooking equipment should be off. The hood exhaust
should also be off.
1.
Measuring Velocities
•
Velocity measurements should be made with
a digital 2-3/4 in. rotating vane anemometer
or its equivalent.
•
One velocity measurement should be taken
for every 8 in. of short circuit opening length,
starting tight against one edge of the
opening, and finishing tight against the other
edge. The anemometer should be placed at
the bottom edge of the opening, flush with
the bottom lip as shown in Fig. 26. Both
squareness and placement are important for
accuracy.
2.
Calculate the average slot velocity.
3.
Calculate the CFM per linear foot by dividing the
average velocity by a conversion factor of 5.52.
4.
Calculate the hoods exhaust volume by
multiplying the CFM per linear foot by the total
hood length.
Example: 4 ft. short circuit hood (36 in. short circuit opening).
1.
Number of Readings
= 36 in. / 8 in. => 6 readings
2.
Average Slot Velocity
=
(Sum of Velocity Readings)
(Number of Readings)
=
786 + 900 + 1126 + 1048 + 1111 + 1115 = 6086 = 1014 FPM
6
6
3 .
CFM per Linear Foot
= Average Slot Velocity in FPM = 1014 = 184 CFM / Linear Foot
5.52
5.52
4.
Hood Supply Volume
=
(CFM/Linear Foot) x (Total Hood Length in Feet)
= 184 x 4 = 736 CFM
Fig. 26