Operation, 3 operation scenarios - utility connected – Magnum Energy AC Load Diversion Controller (ACLD-40) User Manual
Page 33
©
2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 26
Operation
Relay
PWM
Switch
Grid-Tie
Inverter
ACLD Controller
(Inactive)
Renewable
Energy
MS-PAE Series
Inverter
Battery
Bank
Battery
Full
Critical
Loads
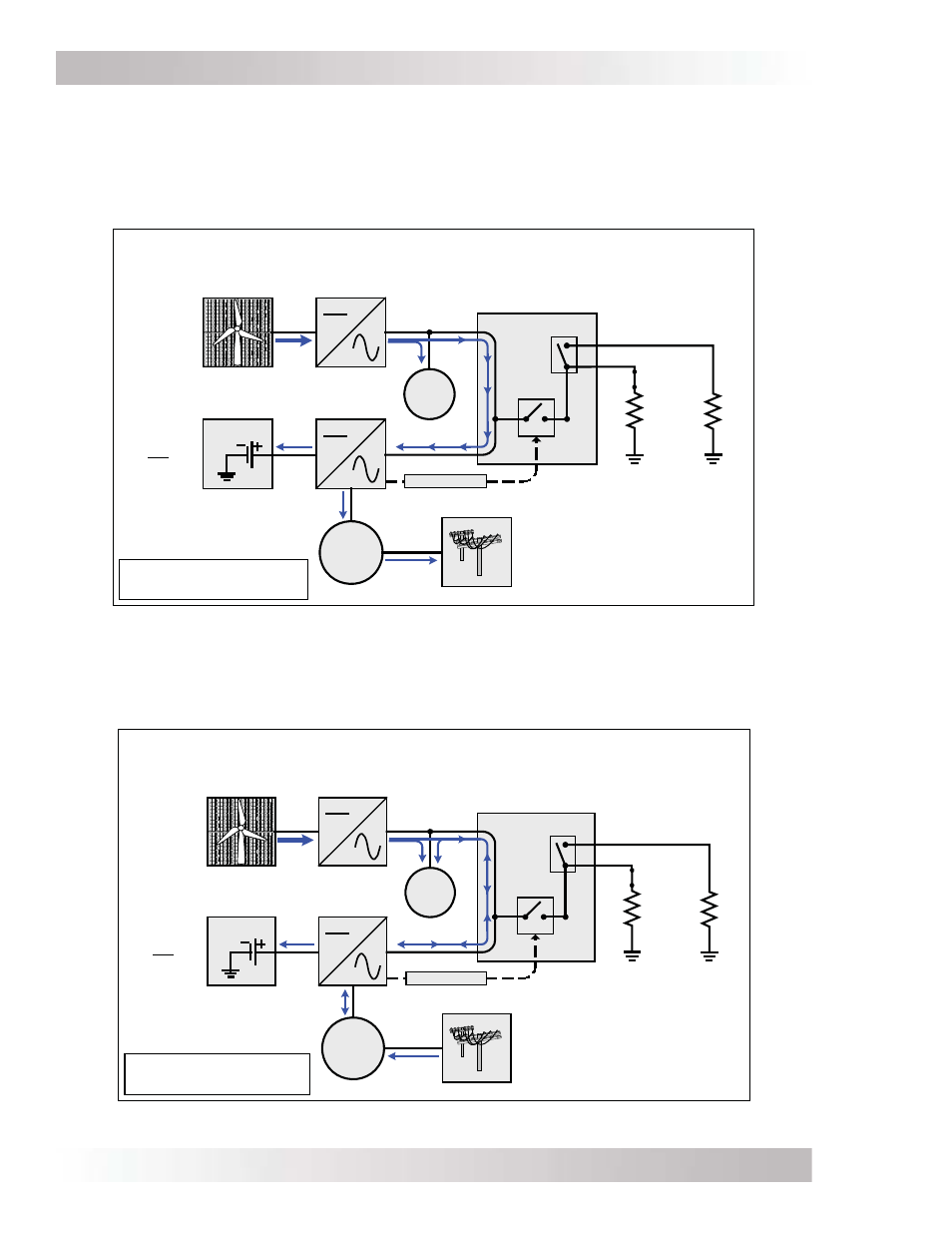
Utility Connected – Surplus Power Fed to the Utility Grid
(Renewable Energy greater than Household and Critical Loads)
Note: When the MS-PAE Series inverter
is connected to the utility and charging
the battery, the ALCD is Inactive.
Main
Household
Loads
Utility
Grid Power
Secondary
Load
(Not powered)
Primary
Load
(Not powered)
MagNet Control
Relay
PWM
Switch
Grid-Tie
Inverter
ACLD Controller
(Inactive)
Renewable
Energy
MS-PAE Series
Inverter
Battery
Bank
Battery
Full
Critical
Loads
Utility Connected – Additional Power Provided by the Utility Grid
(Renewable Energy less than Household and Critical Loads)
Main
Household
Loads
Utility
Grid Power
Secondary
Load
(Not powered)
Primary
Load
(Not powered)
Note: When the MS-PAE Series inverter
is connected to the utility and charging
the battery, the ALCD is Inactive.
MagNet Control
Figure 3-2, Utility Connected - Surplus Power Fed to the Utility Grid
Figure 3-3, Utility Connected - Additional Power Provided by the Utility Grid
During occasions when the renewable energy is less than the power required by the loads in the
home (i.e., PV system on a cloudy day), the additional power is provided by the utility to continue
powering the household and critical loads (see Figure 3-3).
3.3 Operation Scenarios - Utility Connected
When utility power is connected, the grid-tie inverter synchronizes to the utility grid and converts
the renewable energy to work in parallel with the utility grid to power the main and critical loads in
the home. Some of this power is used by the battery charger inside of the MS-PAE Series inverter
to keep the battery bank charged in case of a power failure. If there is any surplus renewable
energy after satisfying the loads in the home, it is fed back into the utility grid (see Figure 3-2).