Grid-tie inverter, Acld-40 controller – Magnum Energy AC Load Diversion Controller (ACLD-40) User Manual
Page 9
©
2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 2
Introduction
Traditionally, when a battery-based inverter is used, the renewable energy system is connected
or ‘coupled’ to the battery (or DC) side of the inverter. In a DC coupled system, the renewable
energy is wired at a lower voltage to better match the battery bank, and a DC controller is used to
manage the energy to prevent the battery from being overcharged. This type of system is usually
more costly and complex to install because of more components; and because the voltage is lower,
there are more effi ciency losses as a whole (when compared to a grid-tie inverter-only system).
However, using a concept known as AC Coupling, a four quadrant (bi-directional) battery-based
inverter (such as Sensata’s MS-PAE Series) can be installed that utilizes the renewable energy to
power the home’s critical loads during a power outage from the AC side. With the addition of a
battery bank, a critical-loads sub-panel, and a diversion controller with load, coupling a MS-PAE
Series inverter on the AC side can be very advantageous. The existing renewable energy system
does not need to be rewired to the DC side, and the high conversion effi ciency of the grid-tie
inverter is maintained while the utility power is available.
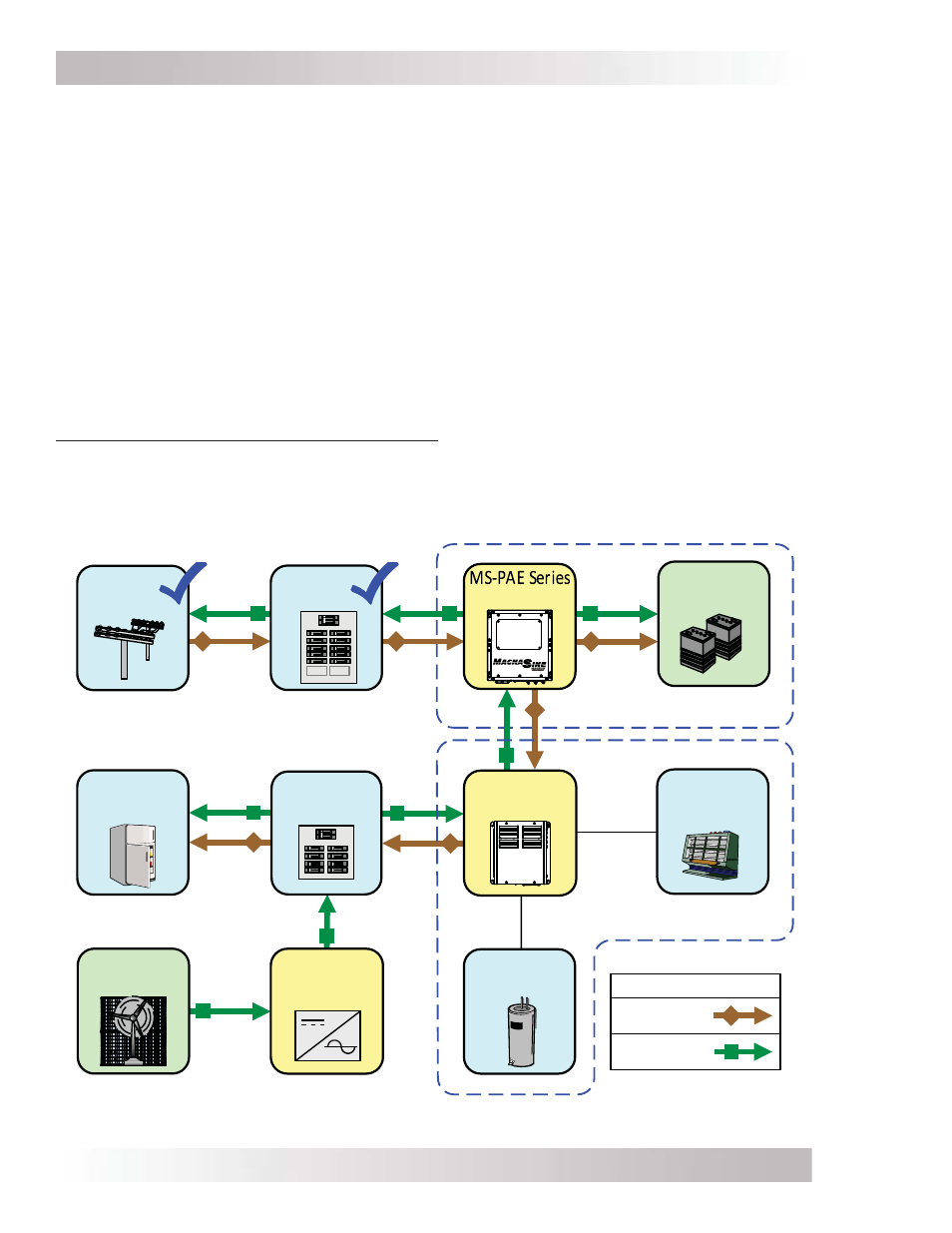
1.3 How an AC Coupled System Works
Described below is how an AC-Coupled system works when utility power is available, and when
there is an utility power outage.
When utility power is available (see Figure 1-1): Normally, when utility power is available and a
MS-PAE Series inverter is installed, the grid-tie inverter converts the renewable energy to work in
parallel with the utility to power the loads in the home (main-panel and critical loads sub-panel),
charge the battery system, and feed any surplus renewable energy back into the utility grid.
Figure 1-1, ACLD Inactive (Utility Power Available)
Battery Back-up Section
AC Load
(Primary)
ACLD Section
Main
Panel
Utility
Grid
Inverter
Battery
Bank
Grid-Tie
Inverter
Critical
Loads
Sub-
Panel
ACLD-40
Controller
AC Load
(Secondary)
Renewable
Energy
Power Flow
Renewable
Energy
Utility Grid