2 ddns server – PLANET NVR-3250 User Manual
Page 38
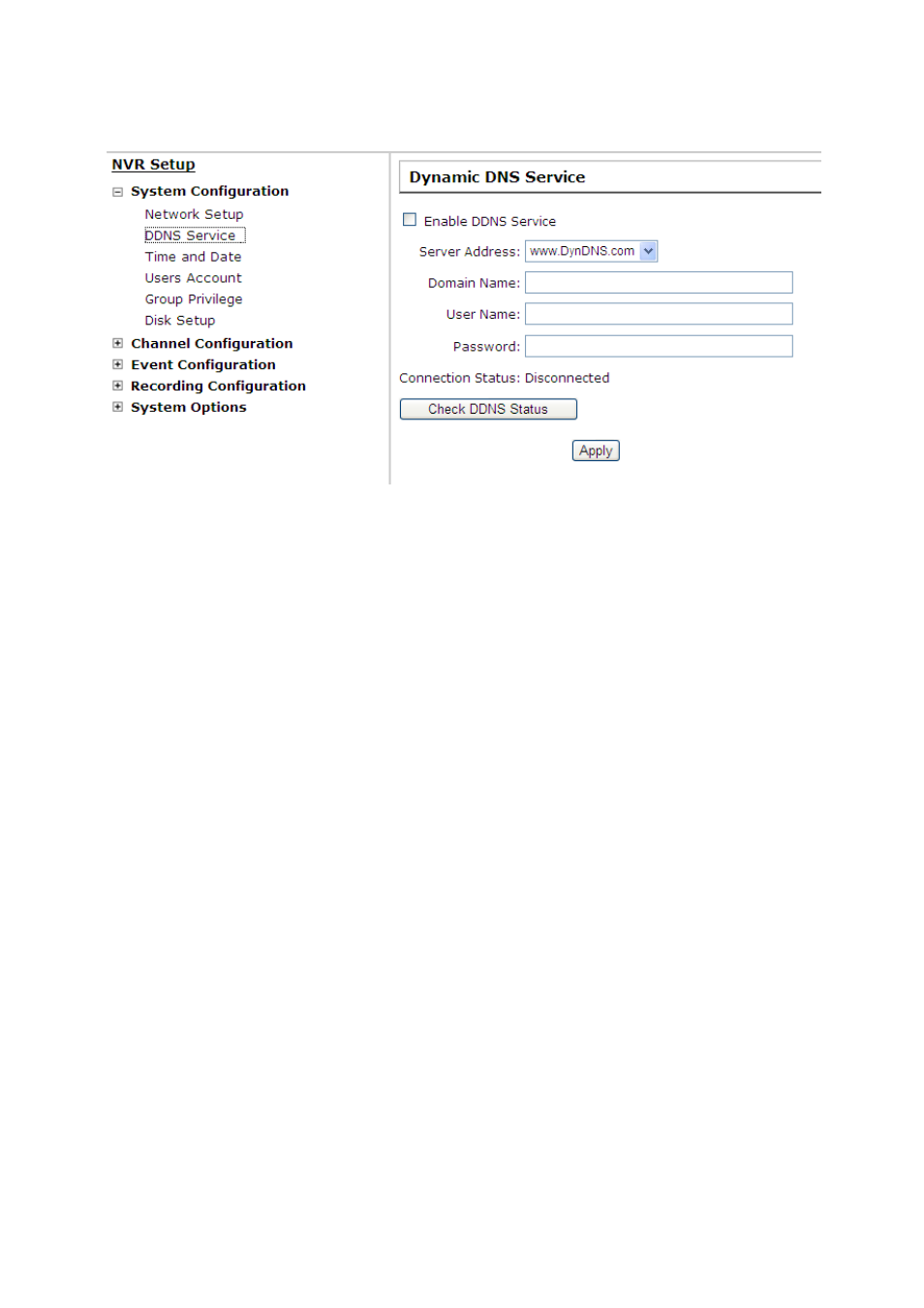
6.1.2 DDNS Server
DNS, which stands for “Dynamic DNS”, is a method, protocol, or network service that provides the
capability for a networked device, such as a router or computer system (in this case, the NVR) using the
Internet Protocol Suite, to notify a domain name server to change, in real time, the active DNS
configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses or other information stored in DNS.
A popular application of dynamic DNS is to provide a residential user’s Internet gateway that has a
variable, often changing, IP address with a well known hostname resolvable through standard DNS
queries.
This is useful if the NVR is placed on the Internet with a dynamic public IP, which once the DDNS is
properly setup, users can access the NVR remotely with the DDNS domain name without worrying if the
IP has changed or not.
*Please make sure a valid DNS server has been configured under the “Network Setting” page in order
for this function to work properly.
*The NVR currently only works with free DDNS service provided by “DynDNS”. For more information,
please go to www.dyndns.com
*If the NVR is placed behind a router or Internet gateway, please make sure port forwarding for port 80
is configured on the router or the gateway in order for the DDNS function to properly register with the
service. It’s often suggested to use the DDNS function in the router / gateway for such case instead.
*Once you have the DDNS function successfully up and running, please DO NOT forget to configure
port forwarding for the NVR web port (default 80) and the streaming port (default 9877) in the
router/gateway for remote viewing. You can then type in http://yourddnsdomain in the browser to access
the NVR remotely for live view.
38