2 displaying source status (example), 1 detecting source signals, Displaying source status (example) – IDK GF-100 User Manual
Page 21: Detecting source signals, P.21)
GF-100 User’s Guide
21
6.2 Displaying source status (example)
6.2.1 Detecting source signals
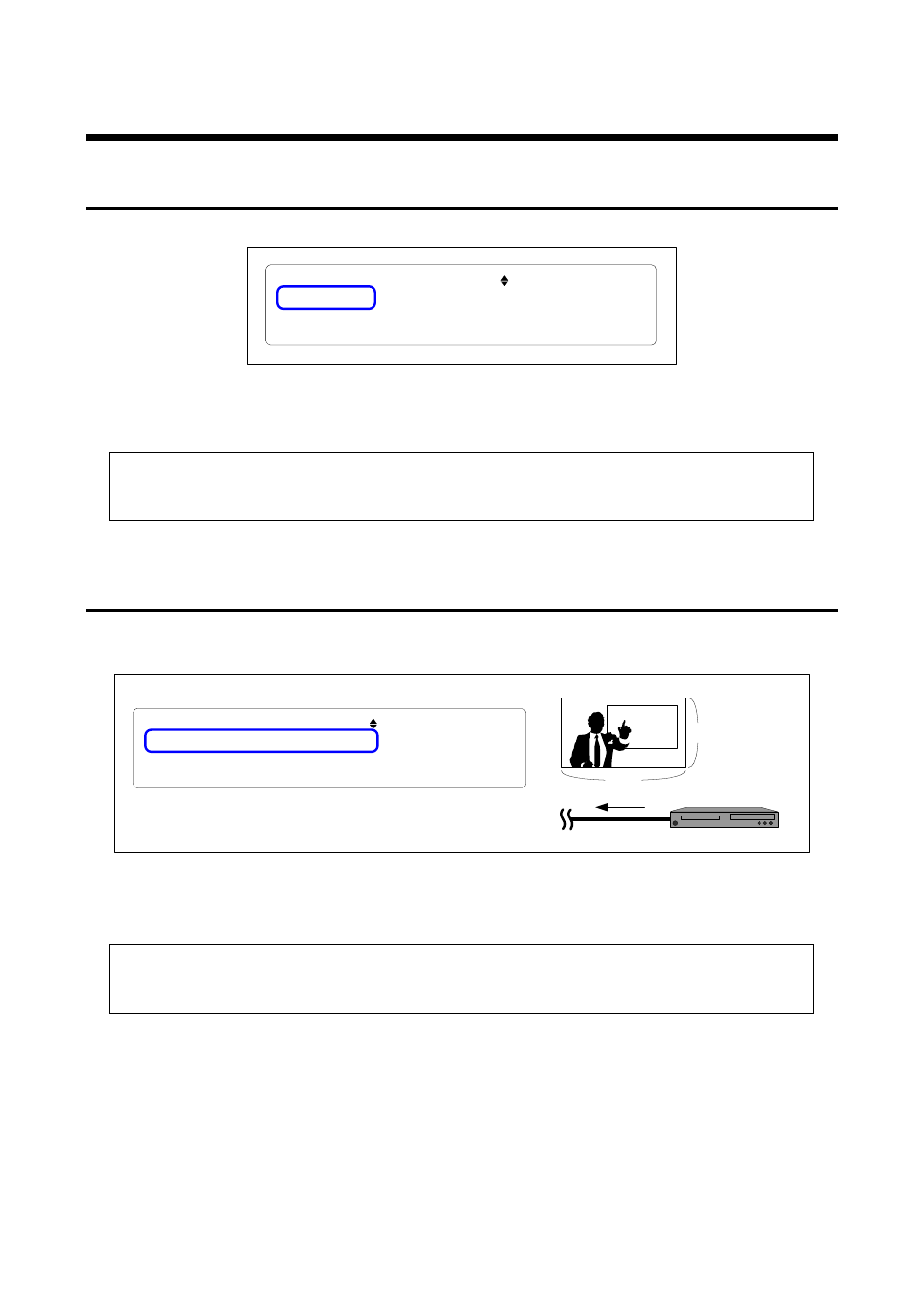
If the GF-100 does not detect source signals, “NO SIGNAL” is displayed.
T O P > S O U R C E S T A T E [ 1 / 9 ] S U M M A R Y
N O S I G N A L
D D C = 0 . 2 6 V
[Fig. 6.4] Signals are not detected
<Recommended actions>
● Check the connection, power supply of the source device, and external output settings (laptop)
● Perform the cable test (P.48)
● Replace the cable.
6.2.2 Video timing (Resolution/scanning method/frame rate/aspect ratio)
Displaying resolution, scanning method, frame rate, and aspect ratio of the source signals.
For the scanning method: “p” means progressive while “i” means interlace.
T O P > S O U R C E S T A T E [ 1 / 9 ] S U M M A R Y
1 9 2 0 x 1 0 8 0 p , 5 9 . 9 4 H z , 1 6 : 9 , V I C = 1 6
H D M I , H D C P , R G B , 8 b i t C O L O R , D D C = 5 . 0 0 V
P C M , 2 C H , 4 8 k H z , 2 4 b i t , N O T H I - B I T
1920
1080
[Fig. 6.5] Video timing
<Recommended actions for when the image cannot be displayed on the sink device>
● Sink device: Check the power supply, input switching (if there are some inputs), supported
resolution (P.38), and operation using test patterns (P.39).
● Source device: Change the output resolution.