Introduction to ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 125
13-6
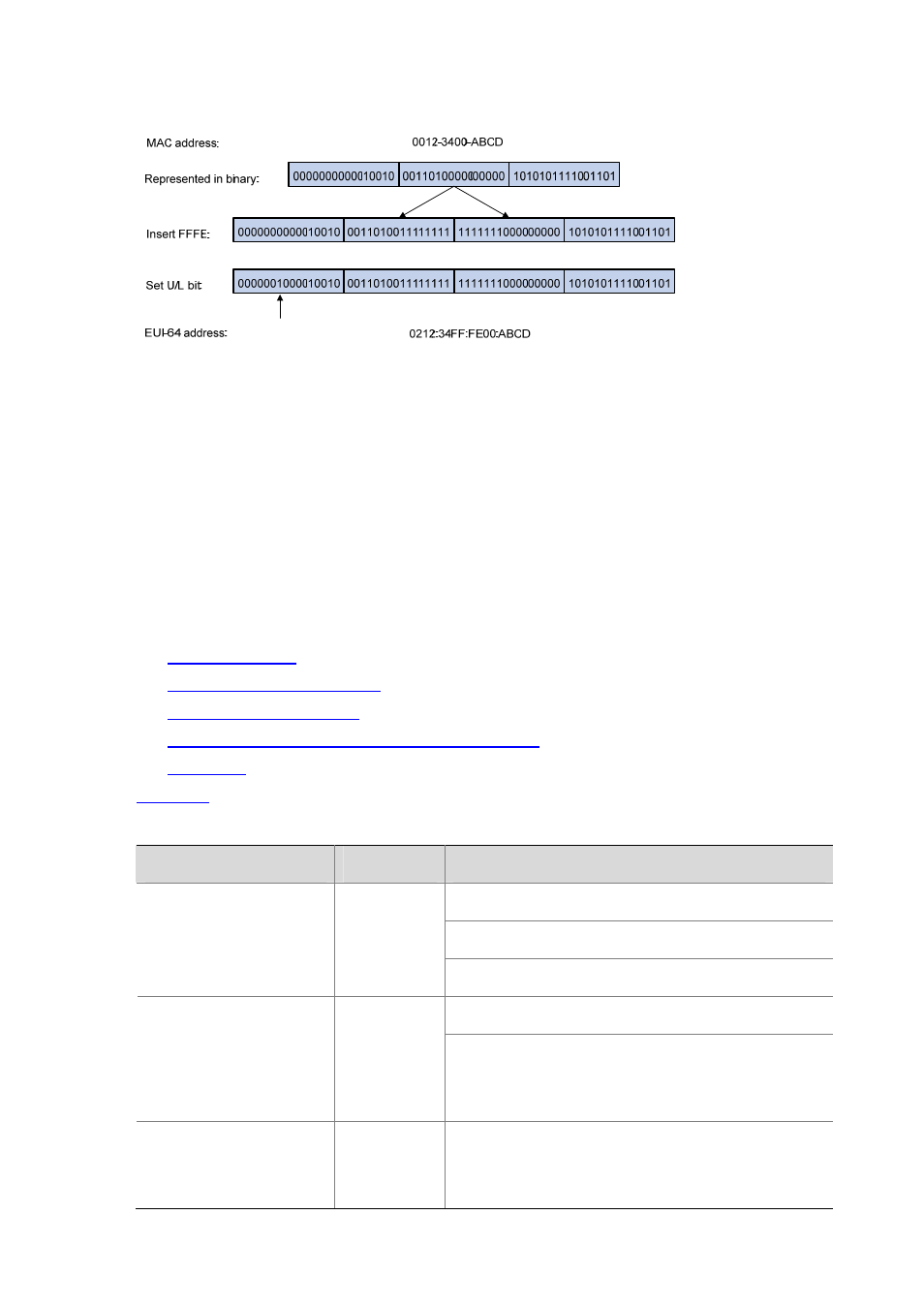
Figure 13-2 Convert a MAC address into an EUI-64 interface identifier
z
Tunnel interfaces: The lower 32 bits of the interface identifier are the source IPv4 address of the
tunnel interface. The higher 32 bits of the interface identifier of an ISATAP tunnel interface are
0000:5EFE, while those of other tunnel interfaces are all zeros. For more information about
tunnels, refer to Tunneling Configuration in the Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration Guide.
z
Other interfaces (such as serial interface): The interface identifier is generated randomly by the
device.
Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol
The IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) uses five types of ICMPv6 messages to implement the
following functions:
z
z
Neighbor reachability detection
z
z
Router/prefix discovery and address autoconfiguration
lists the types and functions of ICMPv6 messages used by the NDP.
Table 13-3 Types and functions of ICMPv6 messages
ICMPv6 message
Number
Function
Used to acquire the link-layer address of a neighbor
Used to verify whether the neighbor is reachable
Neighbor solicitation (NS)
message
135
Used to perform a duplicate address detection
Used to respond to an NS message
Neighbor advertisement (NA)
message
136
When the link layer changes, the local node initiates an NA
message to notify neighbor nodes of the node information
change.
Router solicitation (RS)
message
133
After started, a node sends an RS message to request the
router for an address prefix and other configuration
information for the purpose of autoconfiguration.