Ipv4 over ipv4 tunnel, Introduction to ipv4 over ipv4 tunneling protocol, Encapsulation and decapsulation – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 162
15-5
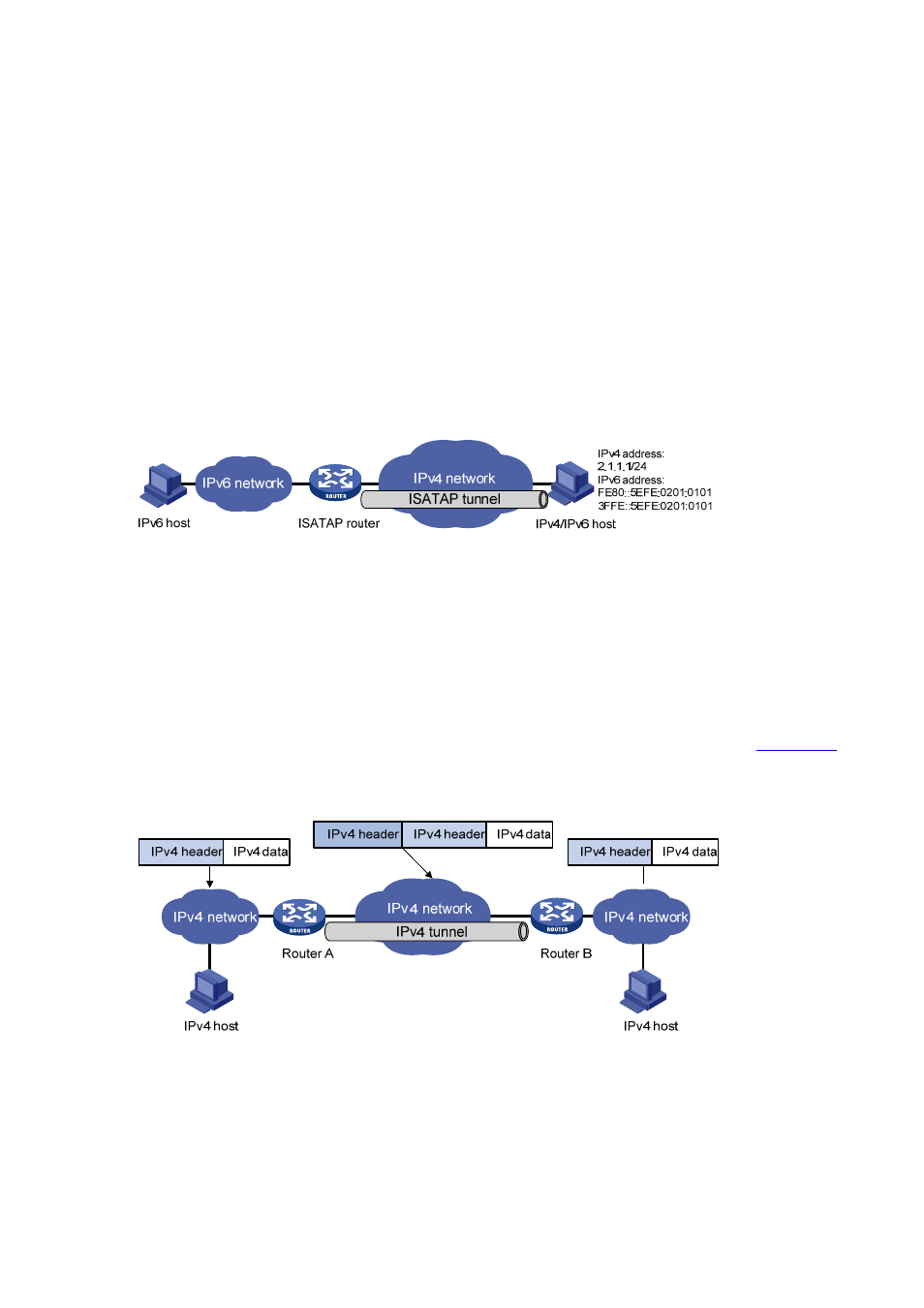
With the application of the IPv6 technology, there will be more and more IPv6 hosts in the existing IPv4
network. The ISATAP tunneling technology provides a satisfactory solution for IPv6 application. An
ISATAP tunnel is a point-to-point automatic tunnel. The destination of a tunnel can automatically be
acquired from the embedded IPv4 address in the destination address of an IPv6 packet.
When an ISATAP tunnel is used, the destination address of an IPv6 packet and the IPv6 address of a
tunnel interface both adopt special ISATAP addresses. The ISATAP address format is
prefix(64bit):0:5EFE:ip-address. The 64-bit prefix is the prefix of a valid IPv6 unicast address, while
ip-address is a 32-bit source IPv4 address in the form of a.b.c.d or abcd:efgh, which need not be
globally unique. Through the embedded IPv4 address, an ISATAP tunnel can automatically be created
to transfer IPv6 packets.
The ISATAP tunnel is mainly used for connection between IPv6 routers or between a host and an IPv6
router over an IPv4 network.
Figure 15-2 Principle of ISATAP tunnel
IPv4 over IPv4 Tunnel
Introduction to IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling protocol
The IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling protocol (RFC 1853) is developed for IP data packet encapsulation so
that data can be transferred from one IPv4 network to another IPv4 network.
Encapsulation and decapsulation
Packets traveling through a tunnel undergo an encapsulation and decapsulation process.
shows these two processes.
Figure 15-3 Principle of IPv4 over IPv4 tunnel
z
Encapsulation
The encapsulation process is as follows:
1) The interface of Router A connecting to an IPv4 host receives an IP packet and submits it to the IP
protocol stack for processing.