4 dhcp overview, Introduction to dhcp, Dhcp address allocation – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 36: Allocation mechanisms, Dhcp overview
4-1
4
DHCP Overview
Introduction to DHCP
The fast expansion and growing complexity of networks result in scarce IP addresses assignable to
hosts. Meanwhile, as many people need to take their laptops across networks, the IP addresses need
to be changed accordingly. Therefore, related configurations on hosts become more complex. The
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) was introduced to solve these problems.
DHCP is built on a client-server model, in which a client sends a configuration request and then the
server returns a reply to send configuration parameters such as an IP address to the client.
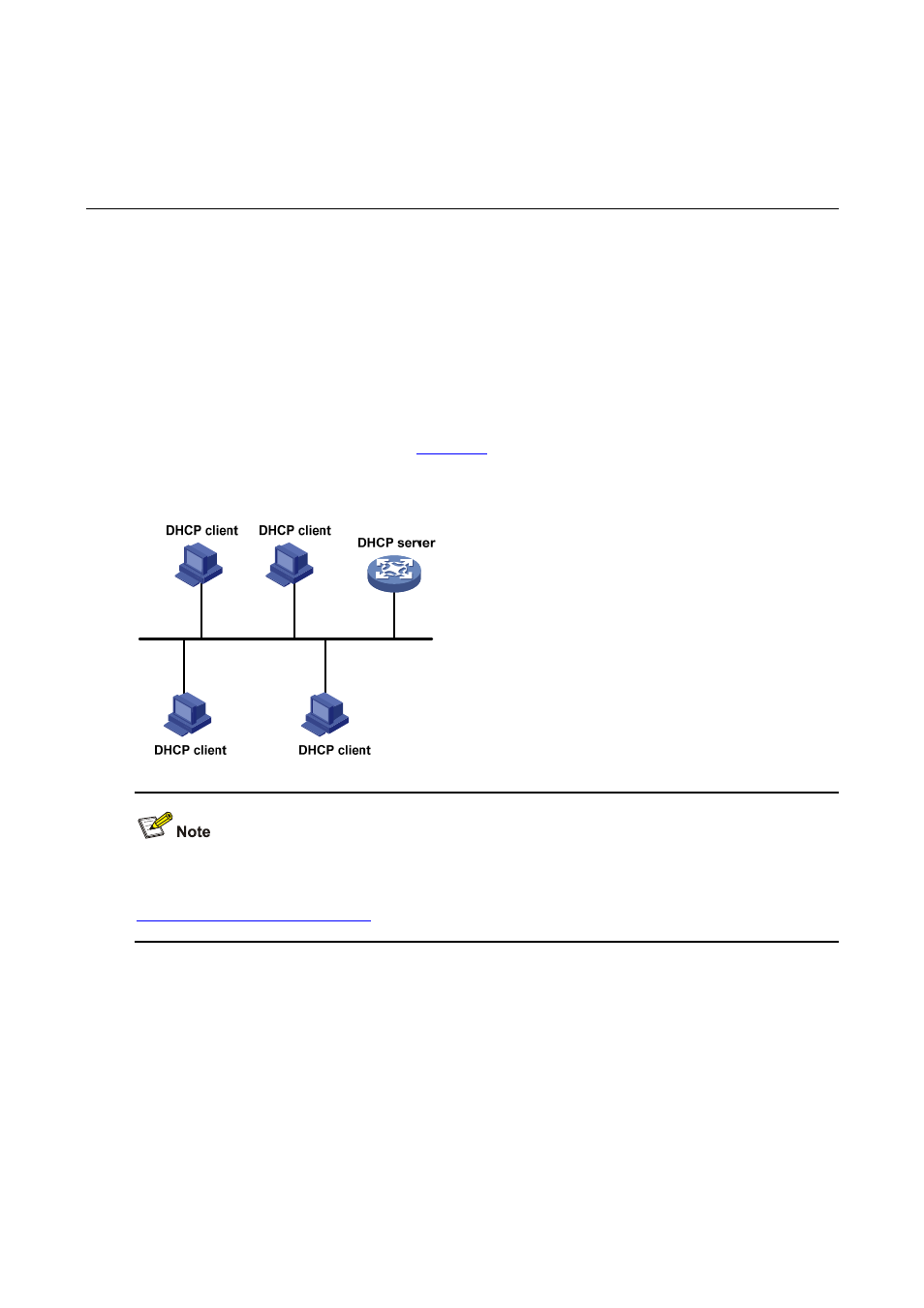
A typical DHCP application, as shown in
, includes a DHCP server and multiple clients (PCs
and laptops).
Figure 4-1 A typical DHCP application
A DHCP client can get an IP address and other configuration parameters from a DHCP server on
another subnet via a DHCP relay agent. For information about the DHCP relay agent, refer to
Introduction to DHCP Relay Agent
.
DHCP Address Allocation
Allocation Mechanisms
DHCP supports three mechanisms for IP address allocation.
z
Manual allocation: The network administrator assigns an IP address to a client like a WWW server,
and DHCP conveys the assigned address to the client.
z
Automatic allocation: DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a client.