Mstp features, Mstp basic concepts – H3C Technologies H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 73
62
MSTP features
Developed based on IEEE 802.1s, MSTP overcomes the limitations of STP, RSTP, and PVST. In addition to
supporting rapid network convergence, it also provides a better load sharing mechanism for redundant
links by allowing data flows from different VLANs to be forwarded along separate paths.
MSTP provides the following features:
•
Divides a switched network into multiple regions, each of which contains multiple spanning trees
that are independent of one another.
•
Supports mapping VLANs to spanning tree instances by means of a VLAN-to-instance mapping
table. MSTP can reduce communication overheads and resource usage by mapping multiple
VLANs to one instance.
•
Prunes a looped network into a loop-free tree, which avoids proliferation and endless cycling of
packets. In addition, it supports load balancing of VLAN data by providing multiple redundant
paths for data forwarding.
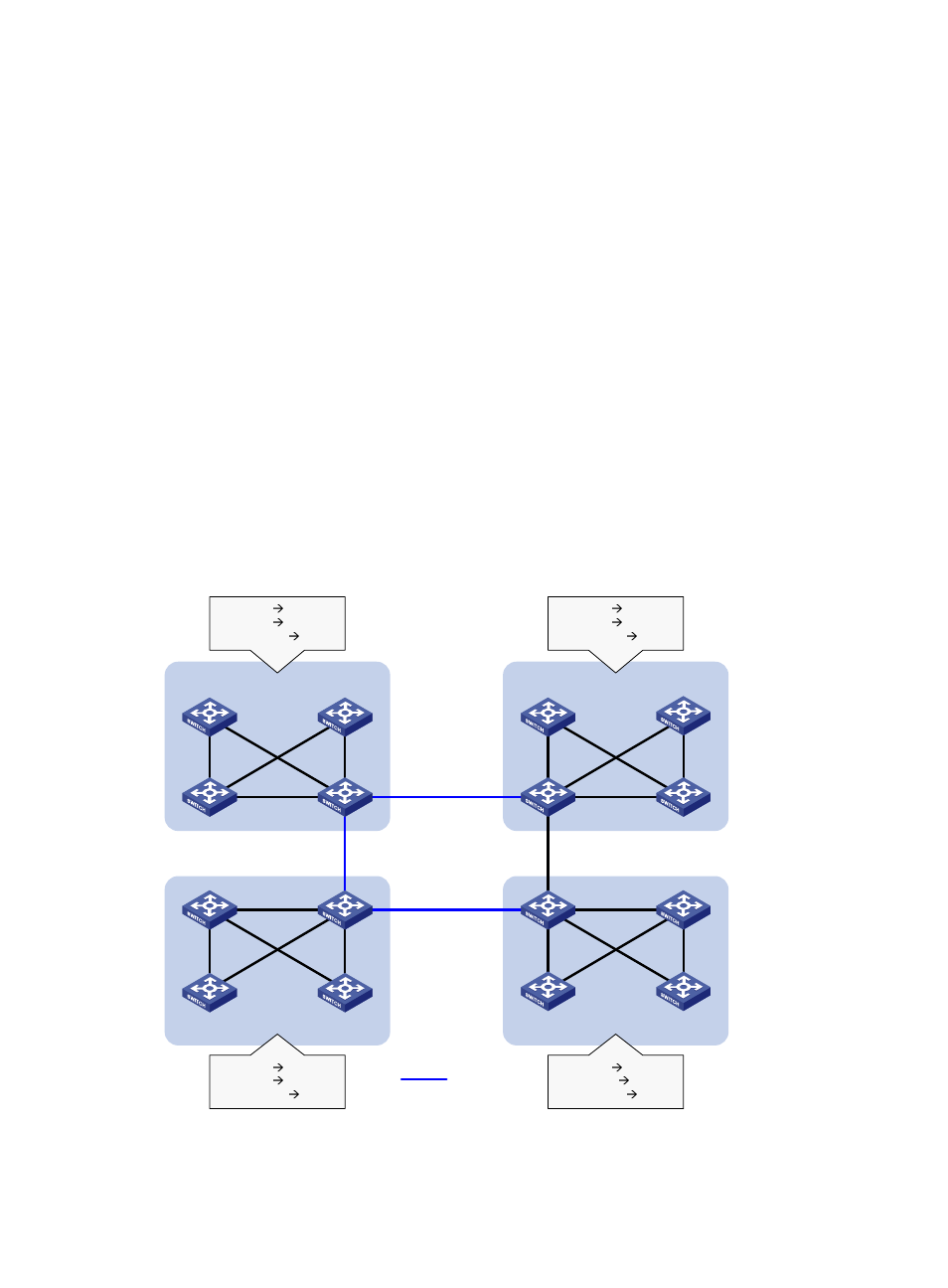
MSTP basic concepts
shows a switched network that comprises four MST regions, with each MST region comprising
shows the network topology of MST region 3.
Figure 17 Basic concepts in MSTP
MST region 1
MST region 2
MST region 3
MST region 4
VLAN 1
MSTI 1
VLAN 2
MSTI 2
Other VLANs
MSTI 0
VLAN 1
MSTI 1
VLAN 2
MSTI 2
Other VLANs
MSTI 0
VLAN 1
MSTI 1
VLAN 2
MSTI 2
Other VLANs
MSTI 0
VLAN 1
MSTI 1
VLAN 2&3
MSTI 2
Other VLANs
MSTI 0
CST