Specifications, Hypertransport technology overview, Chapter 3. specifications – Altera HyperTransport MegaCore Function User Manual
Page 27: Hypertransport technology overview –1
© November 2009
Altera Corporation
HyperTransport MegaCore Function User Guide
Preliminary
3. Specifications
HyperTransport Technology Overview
HyperTransport technology (HT) is packet-based point-to-point link that is designed
to deliver a scalable, high-performance interconnect between the CPU, memory, and
I/O devices on a circuit board. The HT link uses low-swing differential signaling with
differential termination to achieve high data rates from 400 Megabytes per second
(Mbytes/s) to 1.6 Gigabytes per second (Gbytes/s) per direction, assuming an 8-bit
interface.
The HT link provides significantly more bandwidth than competing interconnect
technologies; it uses scalable frequency and data width to achieve scalable
bandwidth. Designers can use HT in networking, telecommunications, computer, and
high-performance embedded applications, and in applications that require high
speed, low latency, and scalability.
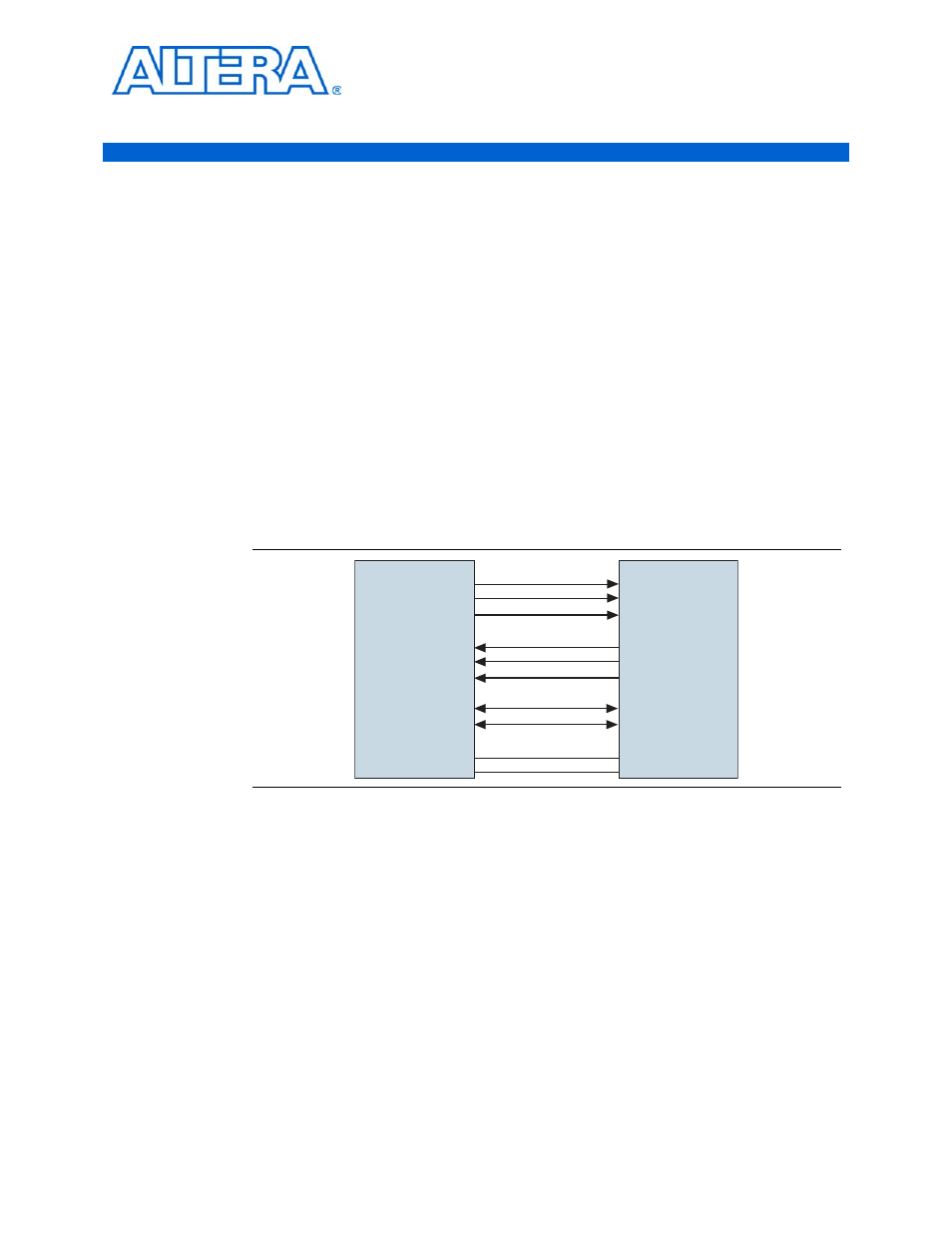
The HT link consists of two independent, source-synchronous, clocked, and
unidirectional sets of wires, as illustrated in
f
For additional information, refer to the HyperTransport I/O Link Specification Revision
1.03.
HT systems consist of two or more HT devices. The HyperTransport specification
includes the following device types:
■
Host Bridge—A host bridge is the HT interface that provides connectivity to the
system’s host processor. Because all communication within an HT chain is
between individual devices and the host bridge, the host bridge includes
additional functionality such as managing peer-to-peer packets and handling error
conditions.
Figure 3–1. HT Link
HyperTransport
Device A
Control Pair
Clock Pair
2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Data Pairs
Clock Pair
Control Pair
2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Data Pairs
RESET_L
PWROK
V
HT
GND
HyperTransport
Device B