U m i, H u n t – Datatek UMI User Manual
Page 60
U N I V E R S A L M E D I A T I O N I N T E R F A C E ( U M I ) U S E R M A N U A L
04/30/09
60
1 2 A P P E N D I X
E :
U M I
H U N T
G R O U P
D E M O N S T R A T I O N
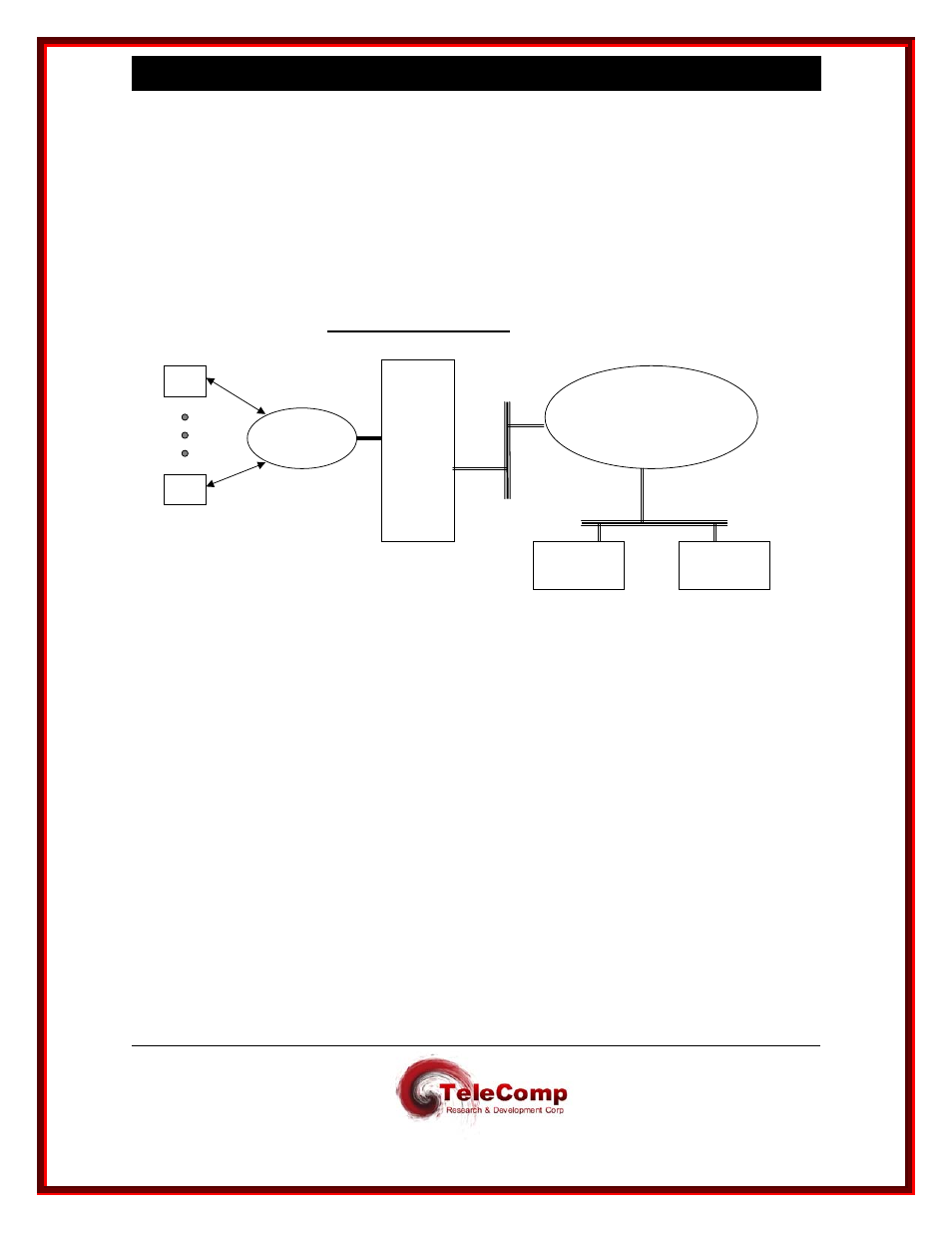
A UMI Hunt Group is a set of virtual ports arranged to receive calls at a common TCP port
number. These calls may in turn be directed to a Predefined Destination (PDD) in the BNS
network. Consider the following diagram:
Modem
Modem
UMI
IP Network
10BaseT
Host “A”
Host “B”
UMI Hunt Group Demonstration
BNS
Network
Suppose both
Host A and Host B need to share a common BNS resource, such as a bank of
modems. If each modem were individually addressed (with a PDD), the hosts would need to
search through a list of UMI virtual ports (i.e., TCP ports), and attempt to call each one until a
connection is successfully established. Since TCP connection timeouts are rather large, this
would probably result in unacceptable performance.
This is solved with the UMI by assigning a common TCP port number to a hunt group of virtual
ports from which the modems are automatically dialed in the BNS network. Multiple distinct banks
of modems may be dialed in the BNS network from a single UMI hunt group. The command
sequence to configure the UMI for the desired operation was shown in section 4.3.2.
When a host calls the correct IP address and TCP port, it is connected to the next available
virtual port in the hunt group. (A TCP connection timeout will take place only if no virtual ports are
available.) When this connection is made, a BNS PDD directs the call to the address specified
(by node administration) for the corresponding SAM504 port. This destination may actually be a
BNS hunt group of ports, hence the ability to have a UMI hunt group act like a group of hunt
groups.