9 assembly of pump – Flowserve M-series PolyChem User Manual
Page 47
USER INSTRUCTIONS PolyChem M-SERIES ENGLISH 71569218 07-11
flowserve.com
Page 47 of 60
®
will need to replace either the inner (most likely)
or outer magnet assembly.
6.8.4
Power End
a)
Inspect the outer magnet for wear and condition
of potting compound that exists between the
magnet poles.
b)
Inspect the anti-friction bearings for scoring,
pitting, scratches or rust. If any of these
conditions exists or if the bearings have been
removed from the shaft the bearings should be
replaced.
c)
In order to ensure proper bearing fits, the shaft
(OD), bearings (ID and OD), and bearing
housing (ID) should be checked. A micrometer
can be used to check the OD dimensions and an
inside caliper the ID dimensions. See Figure 6-
39.
Figure 6-39
PolyChem M-series
Feature mm (in)
Group A and 1
Group B and 2
Bearing
OD
79.992/79.987
(3.1493/3.1491)
110.000/109.985
(43304/43301)
ID
35.000/34.989
(1.3780/1.3775)
50.000/49.987
(1.9685/1.9680)
Shaft OD
35.014/35.004
(1.3785/1.3781)
50.013/50.003
(1.9690/1.9686)
Housing ID
80.020/80.005
(3.1504/3.1498)
110.023/110.007
(4.3316/4.3310)
Fit
Bearing/Housing
0.033L/0.013L
(0.0013L/0.0005L)
0.038L/0.008L
(0.0015L/0.0003L)
Fit
Bearing/Shaft
0.025T/0.004T
(0.0010T/0.0001T)
0.026T/0.003T
(0.0010T/0.0001T)
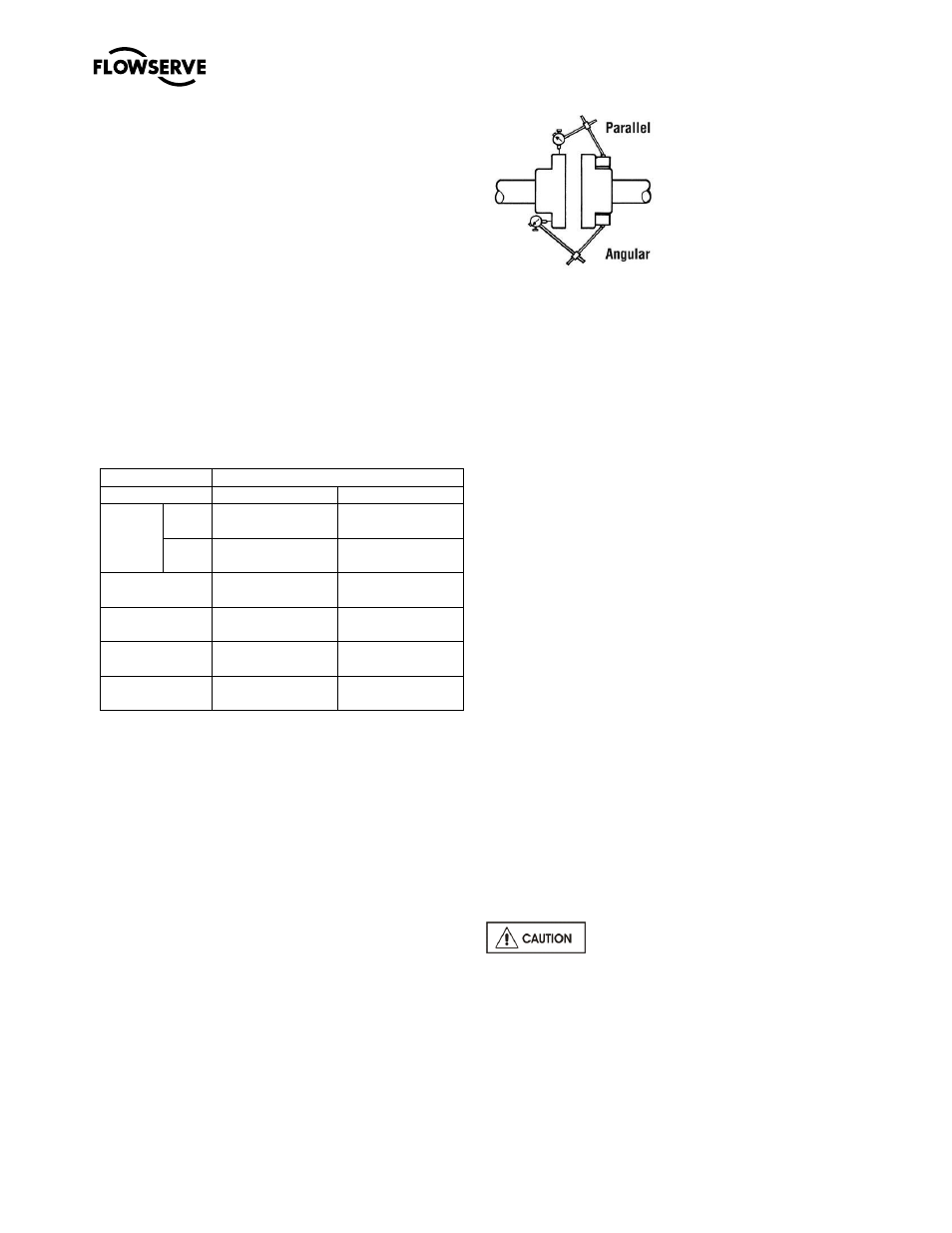
6.8.4.1
Alignment
Misalignment of the pump and motor shafts can
cause the following problems:
Failure of the motor and/or pump bearings
Failure of the coupling
Excessive vibration/noise
The schematics below show the technique for a
typical rim and face alignment using a dial indicator.
It is important that this alignment be done after the
flanges are loaded, and at typical operating
temperatures. If proper alignment cannot be
maintained a close coupled arrangement and/or
stilt/spring mounting should be considered.
Alignment
Many companies today are using laser alignment
which is a more sophisticated and accurate
technique. With this method a laser and sensor
measure misalignment. This is fed to a computer with
a graphic display that shows the required adjustment
for each of the motor feet.
See section 4.8 for recommended final shaft
alignment limits.
6.8.4.2
Vibration analysis
Vibration analysis is a type of condition monitoring
where a pump’s vibration “signature” is monitored on
a regular, periodic basis. The primary goal of
vibration analysis is extension on MTBPM. By using
this tool Flowserve can often determine not only the
existence of a problem before it becomes serious, but
also the root cause and possible solution.
Modern vibration analysis equipment not only detects
if a vibration problem exists, but can also suggest the
cause of the problem. On a centrifugal pump, these
causes can include the following: unbalance,
misalignment, defective bearings, resonance,
hydraulic forces, cavitation and recirculation. Once
identified, the problem can be corrected, leading to
increased MTBPM for the pump.
Flowserve does not make vibration analysis
equipment; however Flowserve strongly urges
customers to work with an equipment supplier or
consultant to establish an on-going vibration analysis
program.
6.9 Assembly of pump
It is important that all pipe threads be
sealed properly. Flowserve does not recommend the
use of PTFE tape as a thread sealant.
Flowserve has investigated and tested alternate
sealants and has identified two that provide an
effective seal and have the same chemical resistance
as the tape. These are La-co Slic-Tite and Bakerseal.
Both products contain finely ground PTFE particles in