Amprobe AMB-110 Insulation-Resistance-Tester User Manual
Page 14
9
DC vs. AC testing voltage
Testing with a DC voltage is widely accepted as being useful as testing with AC and / or pulsed
voltages. DC voltages can be used for breakdown tests especially where high capacitive leakage
currents interfere with measurements using AC or pulsed voltages. DC is mostly used for insulation
resistance measurement tests. In this type of test, the voltage is defined by the appropriate product
application group. This voltage is lower than the voltage used in the withstanding voltage test so
the tests can be applied more frequently without stressing the test material.
Typical insulation tests
In general, insulation resistance tests consist of the following possible procedures:
• Simple insulation resistance measurement also called a spot test;
• Measurement of the relationship between voltage and insulation resistance;
• Measurement of the relationship between time and insulation resistance
• est of residual charge after the dielectric discharge.
The results of this test can indicate whether the replacement of the insulation system is required.
Typical examples of where testing insulation resistance and its diagnosis are recommended are
transformer and motor insulation systems, cables and other electrical equipment.
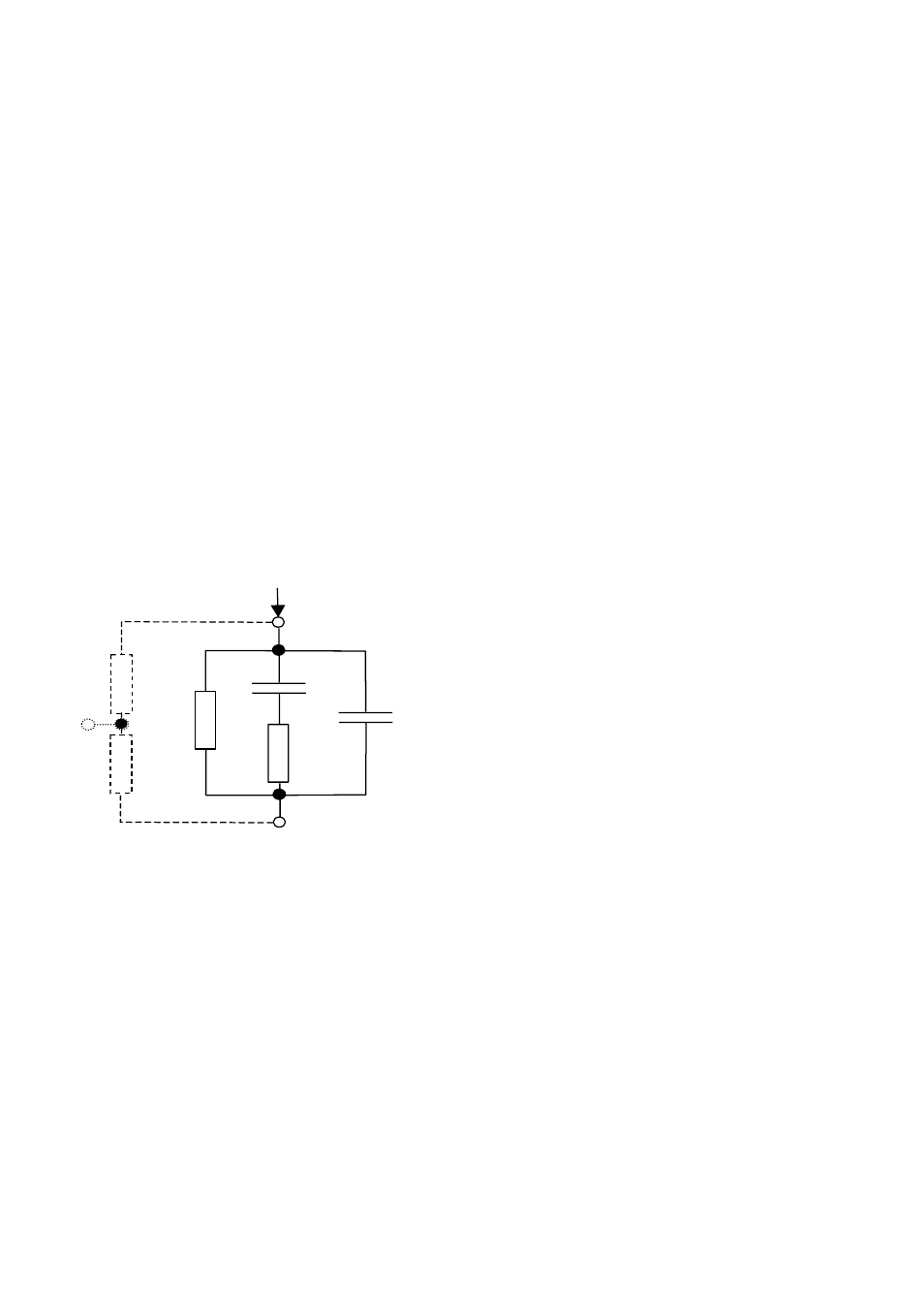
Electrical representation of insulating material
The Fig. 5 represents the equivalent electrical circuit of an insulating material.
Riso
Cpi
Rpi
Ciso
Riss1
Riss2
material
surface
Itest
+
-
Guard
Fig. 5
R
iss1
and R
iss2
- the surface resistivity (position of optional guard connection)
R
iso
– the actual insulation resistance of material
C
iso
– capacitance of material
C
pi
, R
pi
- represents polarization effects.