Foxconn Q67M-S User Manual
Page 77
5
70
RAID 0 (Stripe)
RAID 0 reads and writes sectors of data interleaved among multiple drives. If any disk
mem�er fails, it affects the entire array. The disk array data capacity is equal to the
num�er of drive mem�ers times the capacity of the smallest mem�er. The striping
block size can be set from 4KB to 128KB. RAID 0 does not support fault tolerance.
RAID 1 (Mirror)
RAID 1 writes duplicate data onto a pair of drives and reads �oth sets of data in
parallel. If one of the mirrored drives suffers a mechanical failure or does not respond,
the remaining drive will continue to function. Due to redundancy, the drive capacity of
the array is the capacity of the smallest drive. Under a RAID 1 setup, an extra drive
called the “spare drive” can �e attached. Such a drive will �e activated to replace a
failed drive that is part of a mirrored array. Due to the fault tolerance, if any RAID 1
drive fails, data access will not �e affected as long as there are other working drives in
the array.
RAID 5 (Parity)
RAID 5 provides data striping at the byte level and also stripes error correction
information. This results in excellent performance and good fault tolerance. Level 5 is
one of the most popular implementations of RAID.
RAID 10 (0+1)
RAID 10 is a combination of striping and mirroring. This configuration provides optimal
speed and relia�ility, �ut you need four SATA hard disks.
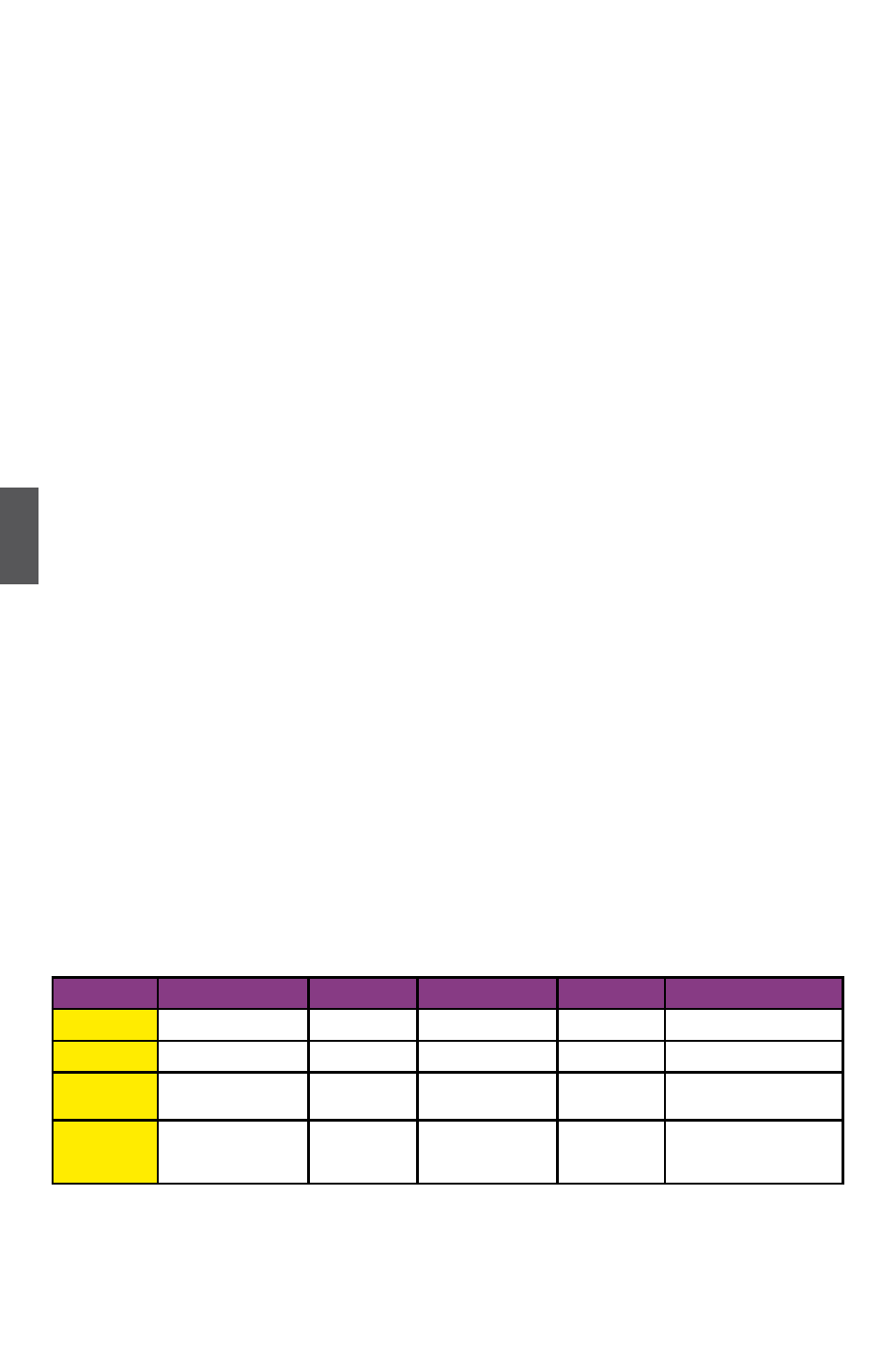
Comparison Table :
Solution
Hard Disks No.
Capacity
Performance
Relia�ility
Application
RAID0
>=2
All
Highest
Dangerous
Look for speed
RAID1
2
50%
Read faster
Excellent
100% Data backup
RAID5
>=3
N-1
Read faster
Write slower
Good
Limited �udget
RAID10
>=4
(Even num�er)
Smallest
*2
High
Excellent
Unlimited �udget