BECKHOFF EL9xxx User Manual
Page 56
Basics communication
Different CoE parameter types are possible, including string (text), integer numbers, Boolean values or larger
byte fields. They can be used to describe a wide range of features. Examples of such parameters include
manufacturer ID, serial number, process data settings, device name, calibration values for analog
measurement or passwords.
The order is specified in 2 levels via hexadecimal numbering: (main)index, followed by subindex. The value
ranges are
• Index: 0...65535
• SubIndex: 0...255
A parameter localized in this way is normally written as x8010:07, with preceding "x" to identify the
hexadecimal numerical range and a colon between index and subindex.
The relevant ranges for EtherCAT fieldbus users are:
• x1000: This is where fixed identity information for the device is stored, including name, manufacturer,
serial number etc., plus information about the current and available process data configurations.
• x8000: This is where the operational and functional parameters for all channels are stored, such as
filter settings or output frequency.
Other important ranges are:
• x4000: In some EtherCAT devices the channel parameters are stored here (as an alternative to the
x8000 range).
• x6000: Input PDOs ("input" from the perspective of the EtherCAT master)
• x7000: Output PDOs ("output" from the perspective of the EtherCAT master)
Note
Availability
Not every EtherCAT device must have a CoE list. Simple I/O modules without dedicated
processor usually have no variable parameters and therefore no CoE list..
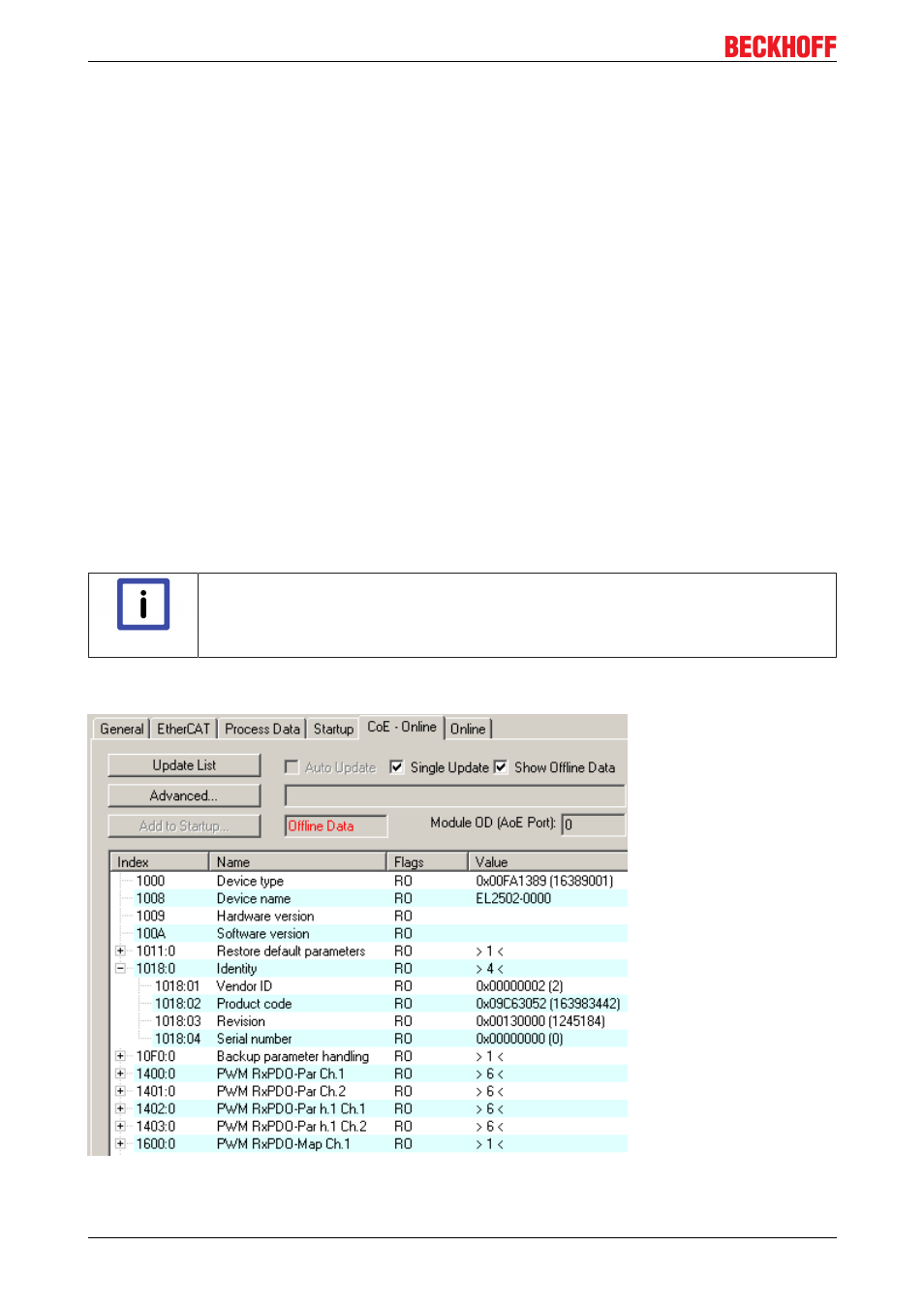
If a device has a CoE list, it is shown in the TwinCAT System Manager as a separate tab with a listing of the
elements:
Fig. 43: "CoE Online " tab
EL9xxx
56
Version 3.1