Traffic shaping – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 44
36
•
Dropping the packet if the evaluation result is “excess”
•
Forwarding the packet with its precedence (which can be 802.1p priority, DSCP, and local
precedence) re-marked if the evaluation result is “conforming”
Traffic shaping
NOTE:
Traffic shaping shapes the outbound traffic.
Traffic shaping provides measures to adjust the rate of outbound traffic actively. A typical traffic shaping
application limits the local traffic output rate according to the downstream traffic policing parameters.
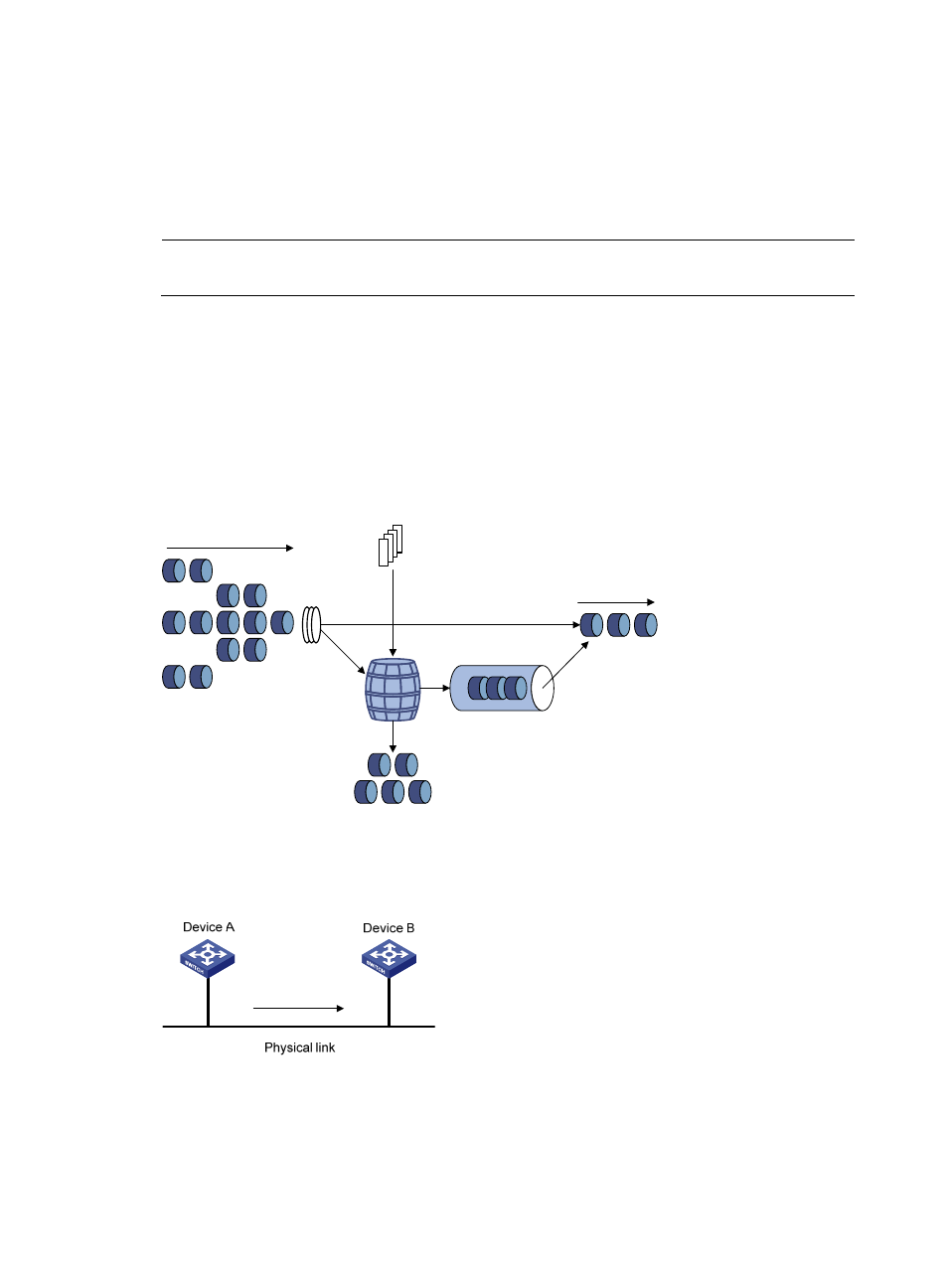
The difference between traffic policing and GTS is that packets to be dropped with traffic policing are
retained in a buffer or queue with GTS, as shown in
. When enough tokens are in the token
bucket, the buffered packets are sent at an even rate. Traffic shaping can result in additional delay and
traffic policing does not.
Figure 10 Schematic diagram for GTS
Token
bucket
Packets dropped
Packet
classification
Packets to be sent
through this interface
Packets sent
Tokens are put into the
bucket at the set rate
Queue
For example, in
, Device A sends packets to Device B. Device B performs traffic policing on
packets from Device A and drops packets exceeding the limit.
Figure 11 GTS application
You can perform traffic shaping for the packets on the outgoing interface of Device A to avoid
unnecessary packet loss. Packets exceeding the limit are cached in Device A. Once resources are
released, traffic shaping takes out the cached packets and sends them out. In this way, all of the traffic
sent to Device B conforms to the traffic specification defined in Device B.