ProSoft Technology MVI69-DFNT User Manual
Page 84
Reference
MVI69-DFNT ♦ CompactLogix or MicroLogix Platform
User Manual
EtherNet/IP Client/Server Communication Module
Page 84 of 167
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 14, 2014
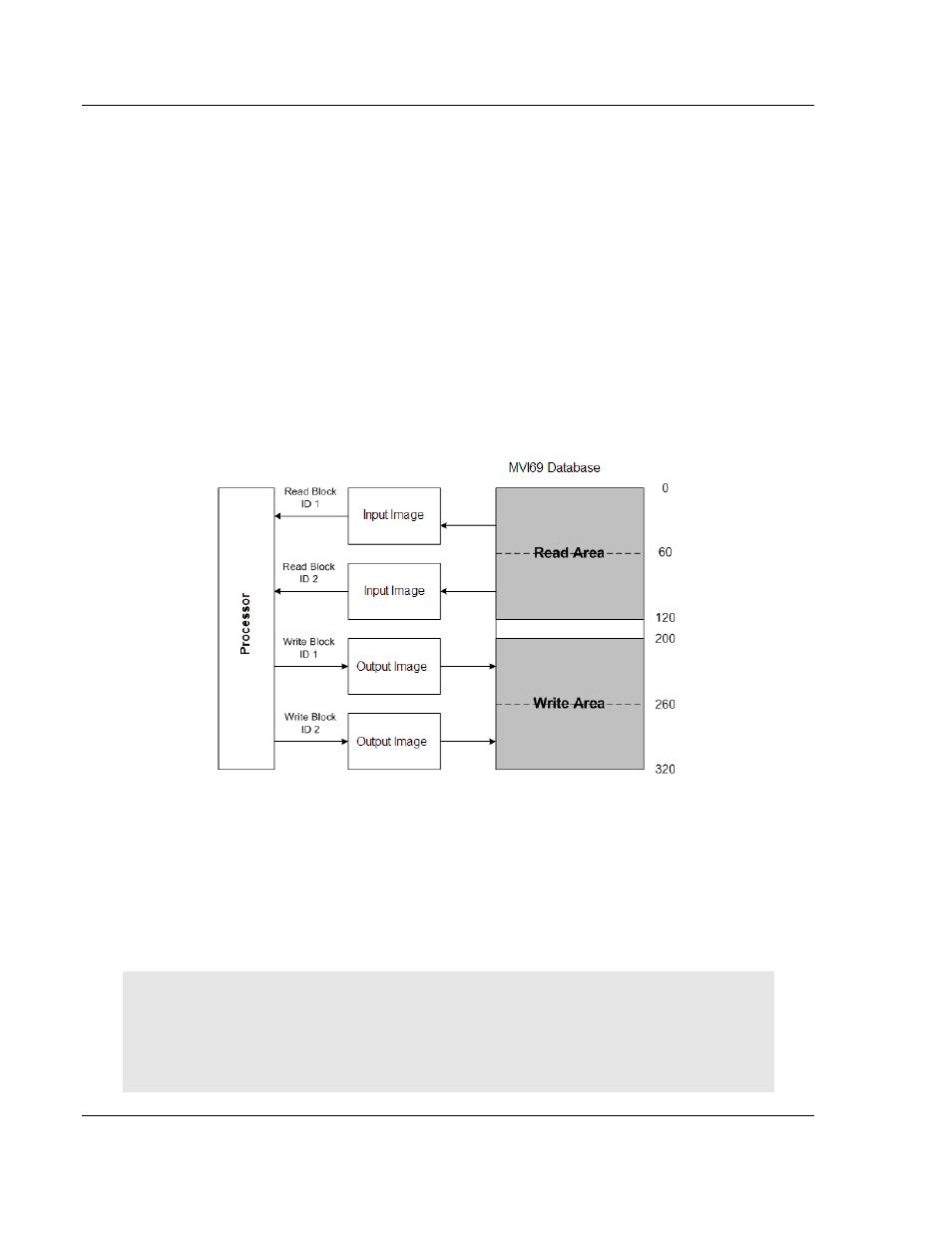
The module’s available database space can be divided into Read Data and Write
Data Areas, as well as used to hold module hardware, driver status and
application status data. These areas are defined by the user when the module
configuration is created. The following is one example of how configuration
parameters can be used to define Read and Write Data areas.
Read Register Start = 0
Read Register Count = 120
Write Register Start = 200
Write Register Count = 120
Let us also assume that the configuration parameter, Block Transfer Size is set
to 60.
In this case, backplane data transfers will hold only 60 16-bit words per block; so,
each area will be broken down into blocks of 60 words.
The following example shows the resulting data flow:
Notice that the number of read or write blocks that will need to be transferred
depends on the Read Register Count and Write Register Count values and may
be calculated using the formulas:
Read Register Count divided by the Block Transfer Size = Total number of Read
Blocks
Write Register Count divided by the Block Transfer Size = Total number of Write
Blocks
Note: Any fractional portion of a block will be rounded up to the next larger whole block number,
that is, 100 divided by 60 would result in 2 blocks to transfer; 500 divided by 60 would result in 9
blocks to transfer, 500 divided by 240 would result in 3 block to transfer, and so on. Therefore, it
would be a good idea to enter the Read Register Count and Write Register Count parameters in
multiples of the configured Block Transfer Size.