Clocking options, Clocking options –7, Clocking options” on – Altera HyperTransport MegaCore Function User Manual
Page 33: R to, Csr module
Chapter 3: Specifications
3–7
HyperTransport MegaCore Function Specification
© November 2009
Altera Corporation
HyperTransport MegaCore Function User Guide
Preliminary
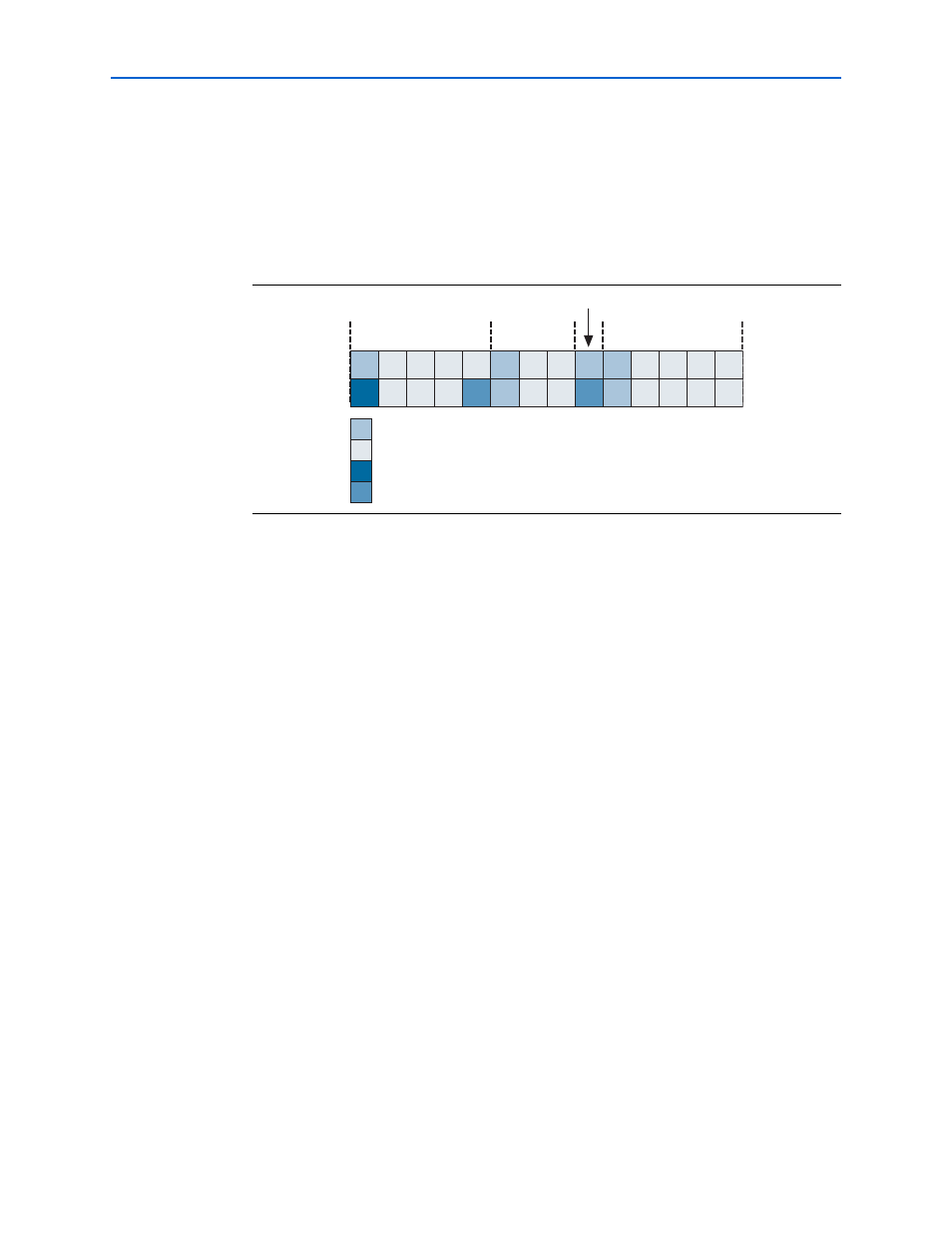
shows example transmitter traffic. This example assumes that each square
represents one DWORD. The top square is the low DWORD and the bottom square is
the high DWORD. In
, the leftmost information transmits first. The vertical
dashed lines delineate packets. The idle NOP packets are NOP packets inserted to
align data and never contain flow control information. Flow control NOP packets are
read from the NOP generator and may or may not contain flow control information,
depending on the buffer release status generated by the Rx claimed buffers.
CSR Module
The CSR module reads packets from the non-posted buffer and checks whether they
are CSR access packets. This process allows the HyperTransport MegaCore function
to use the same buffers for the CSR interface that it uses for general non-posted traffic,
reducing the size of the MegaCore function variation. If a packet is a CSR access (read
or write request) it is routed to the CSR interface module instead of the user interface.
Normal non-posted traffic is provided directly to the local user interface.
The CSR module contains all of the CSR registers and provides read/write capability
to them. It also generates the appropriate response to CSR accesses in the Tx response
buffer.
Clocking Options
The HyperTransport MegaCore function has three distinct clock domains:
■
Protocol interface clock domain
■
Rx alignment clock domain
■
Tx alignment clock domain
The MegaCore function has three clocking options that link clock domains together to
reduce overall latency and resource usage. Due to the HT protocol flow control
mechanism, the clocking option you choose results in different latency for the flow
control information inside the HyperTransport MegaCore function, which can affect
your overall system performance.
Figure 3–4. Example Transmission in the Tx Interface
32-Bit Command
Followed by 28-Byte Data
64-Bit Command
Followed by
16-Byte Data
32-Bit Command
64-Bit Command
Followed by
32-Byte Data
Command
Data
Idle NOP
Flow Control NOP