Mpls l3vpn packet forwarding – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 114
103
2.
From the ingress PE to the egress PE:
The ingress PE adds RD and route target attributes to these standard IPv4 routes to create VPN-IPv4
routes, saves them to the routing table of the VPN instance created for the CE, and advertises the
VPN-IPv4 routes to the egress PE through MP-BGP.
3.
From the egress PE to the remote CE:
After receiving the VPN-IPv4 routes, the egress PE compares their export target attribute with the
local import target attribute, and, if they match, adds the routes to the routing table of the VPN
instance. Then the egress PE restores the VPN-IPv4 routes to the original IPv4 routes and advertises
those routes to the connected CE over a static route, RIP route, OSPF route, IS-IS route, EBGP route,
or IBGP route.
MPLS L3VPN packet forwarding
In a basic MPLS L3VPN (within a single AS), a PE adds the following information into VPN packets:
•
Outer tag—Identifies the public tunnel from the local PE to the remote PE. The public tunnel can be
an LSP or an MPLS TE tunnel. Based on the outer tag, a VPN packet can be forwarded along the
public tunnel to the remote PE. The outer tag is an MPLS label.
•
Inner label—Identifies the remote VPN site. The remote PE uses the inner label to forward packets
to the target VPN site. MP-BGP advertises inner labels for VPN routes among PEs.
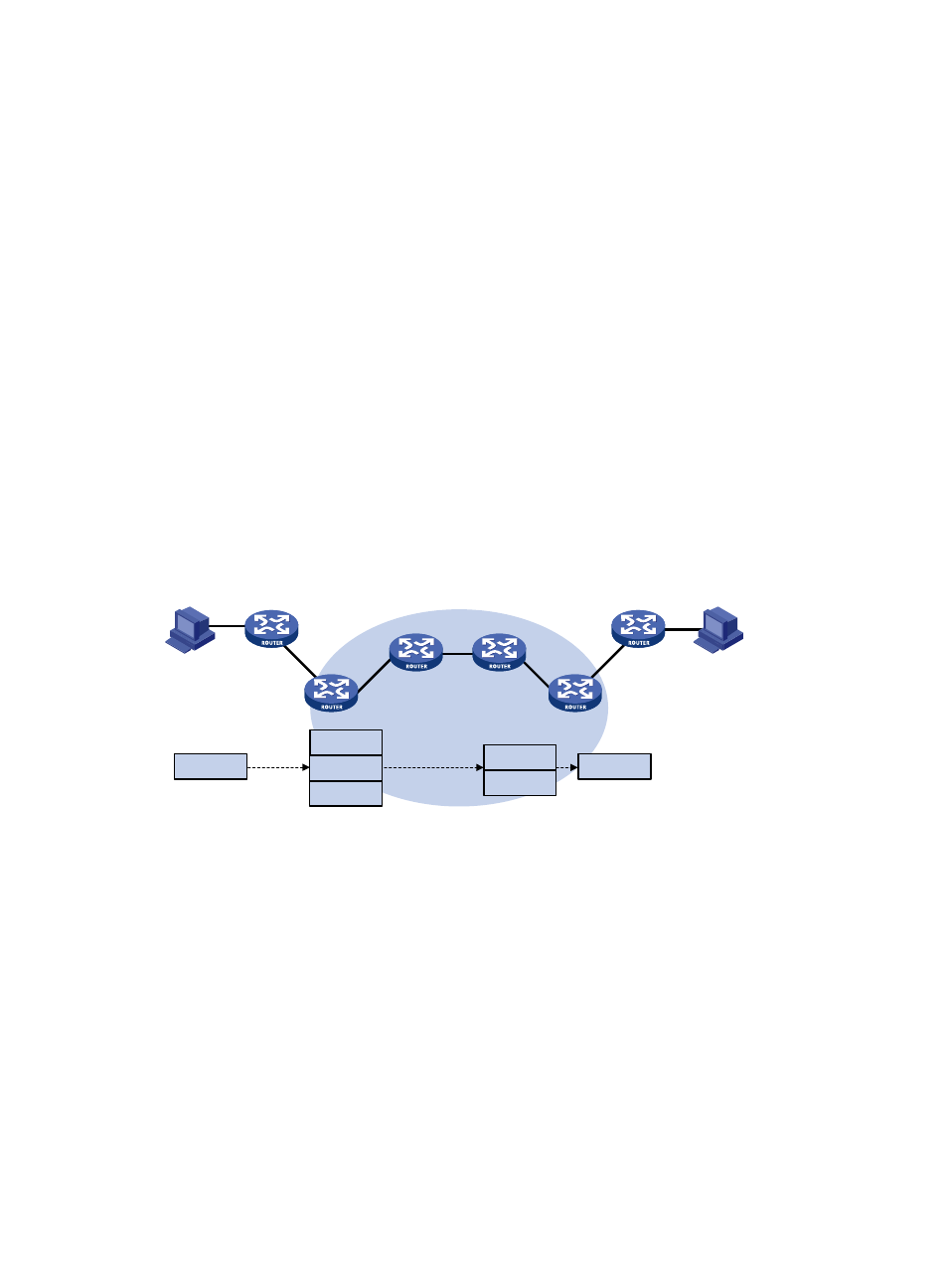
Figure 31 VPN packet forwarding
As shown in
, a VPN packet is forwarded from Site 1 to Site 2 by using the following process:
1.
Site 1 sends an IP packet with the destination address 1.1.1.2. CE 1 transmits the packet to PE 1.
2.
PE 1 finds the matching VPN route based on the inbound interface and destination address of the
packet, labels the packet with both the inner label and the outer tag, and forwards the packet to
the public tunnel.
3.
P devices forward the packet to PE 2 by the outer tag. The outer tag is removed from the packet at
the penultimate hop.
4.
PE 2 finds the matching VPN route according to the inner label and destination address of the
packet, and then forwards the packet out of the interface to CE 2.
5.
CE 2 transmits the packet to the destination through IP forwarding.
When two sites of a VPN are connected to the same PE, the PE directly forwards packets between the two
sites through the VPN routing table without adding any tag or label.
CE 1
Site 1
PE 1
P
P
PE 2
CE 2
Site 2
2.1.1.1/24
1.1.1.2/24
1.1.1.2
1.1.1.2
Inner label
Outer tag
1.1.1.2
Inner label
1.1.1.2
MPLS network