Configuring ldp loop detection, Ldp configuration task list – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 38
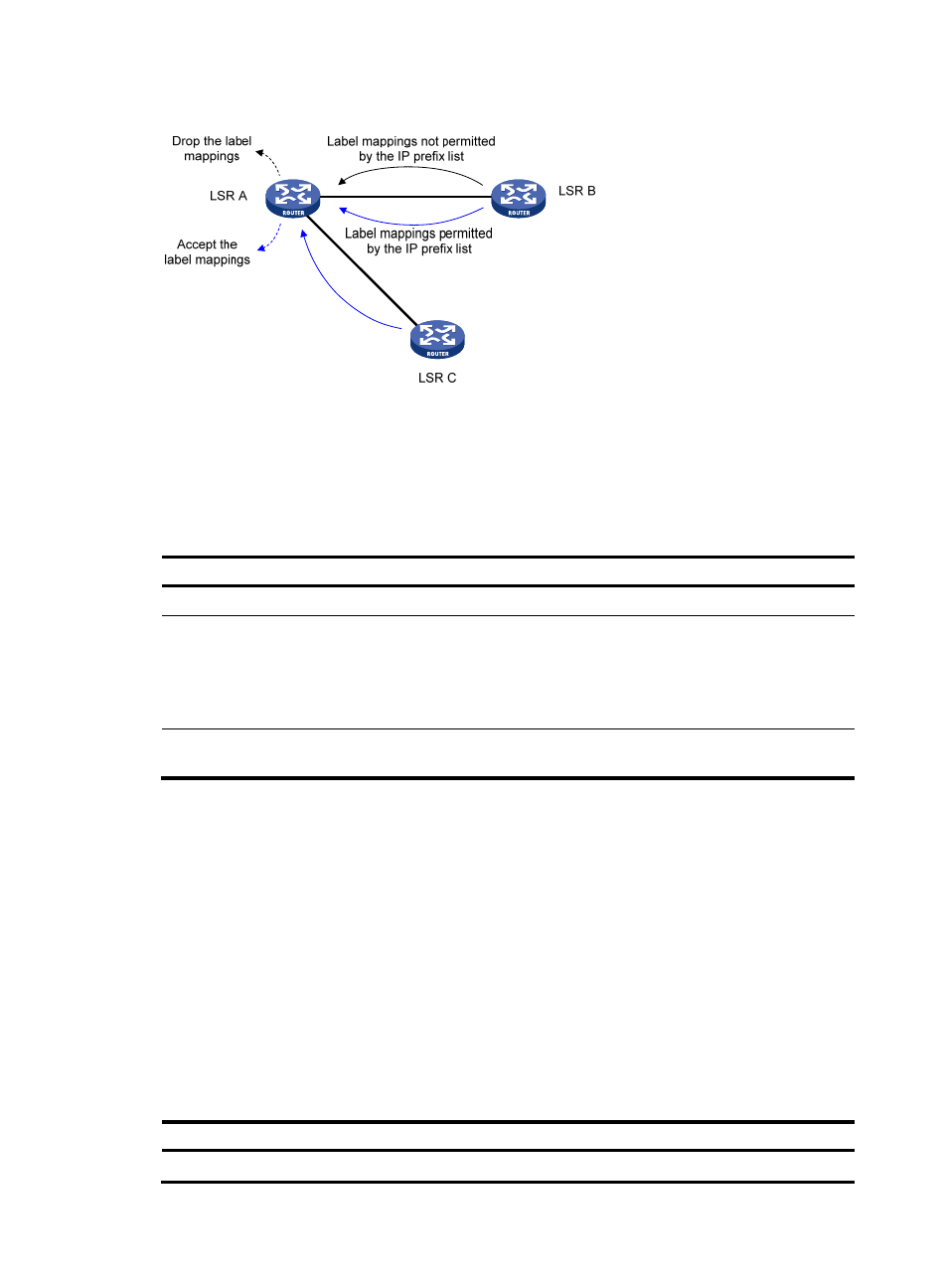
27
Figure 15 Label acceptance control diagram
A label advertisement policy on an LSR and a label acceptance policy on its upstream LSR can achieve
the same purpose. H3C recommends using the label advertisement policy to reduce network load.
You must create an IP prefix list before you configure a label acceptance policy. For information about IP
prefix list configuration, see Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide.
To configure a label acceptance policy:
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Enter LDP view or enter
LDP-VPN instance view.
•
Enter LDP view:
mpls ldp
•
Enter LDP-VPN instance view:
a.
mpls ldp
b.
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
N/A
3.
Configure a label
acceptance policy.
accept-label peer peer-lsr-id prefix-list
prefix-list-name
By default, LDP accepts all label
mappings.
Configuring LDP loop detection
LDP detects and terminate LSP loops in the following ways:
•
Maximum hop count—LDP adds a hop count in a label request or label mapping message. The
hop count value increments by 1 on each LSR. When the maximum hop count is reached, LDP
considers that a loop has occurred and terminates the establishment of the LSP.
•
Path vector—LDP adds LSR ID information in a label request or label mapping message. Each LSR
checks whether its LSR ID is contained in the message. If not, the LSR adds its own LSR ID into the
message. If yes, the LSR considers that a loop has occurred and terminates LSP establishment. In
addition, when the number of LSR IDs in the message reaches the path vector limit, LDP also
considers that a loop has occurred and terminates LSP establishment.
To configure LDP loop detection:
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
Do
no
t filter
labe
l
m
ap
ping
s