Class e, Private network ip addresses, Network address translation (nat) – Comtech EF Data SLM-5650A Vipersat User Manual
Page 94: Subnets, Class e . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . a-8, Subnets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . a-8, Figure a-5 nat router example
IP Addressing
A-8
Vipersat SLM-5650A User Guide
Class E
• 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
• Reserved for experimental use and limited broadcast
Private Network IP Addresses
RFC 1918 defines blocks of addresses for use on private networks:
• 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
• 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
• 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
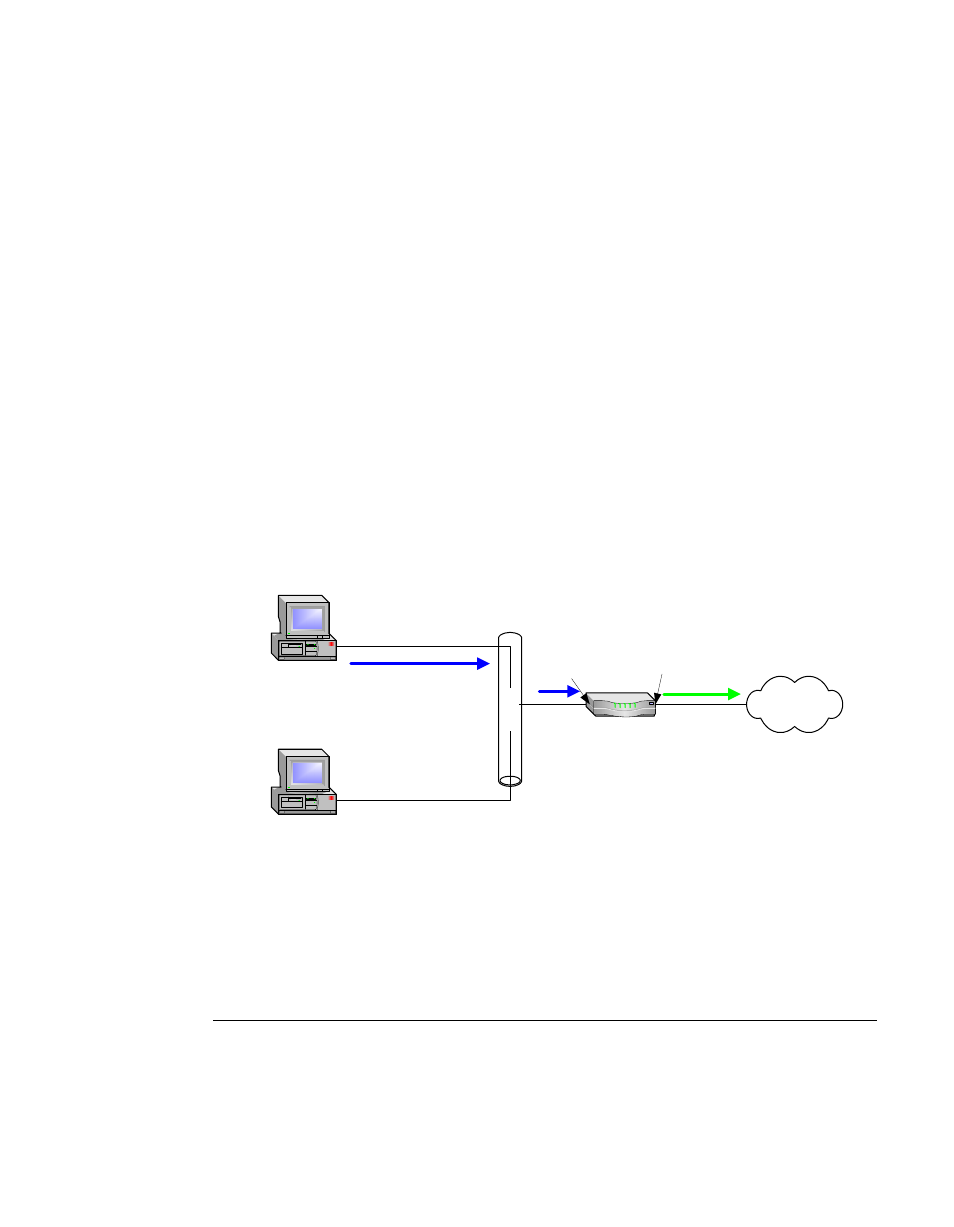
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Private networks can only connect to the public Internet by using a Network
Address Translation (NAT) device (a router, for example) or a proxy server
which has been assigned a public IP address. These network devices use a
public IP address to request information from the Internet on behalf of the
private IP addressed devices on the associated private network.
Figure A-5 NAT Router Example
This use of private addresses helps to conserve public IP addresses.
Subnets
Subnets can be defined as the further segmentation of the InterNIC assigned
Network ID IP address. The amount and type of subnetting performed by the
organization is determined by the network layout.
E
thernet
Host 1
Host 2
NAT Router
Internet
192.168.0.2
192.168.0.3
192.168.0.1
Public IP