K-Patents PR-03 User Manual
Page 51
51
51
51
51
5 Startup, configuration and calibration adjustment
45
35
40
45
50
55
60
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
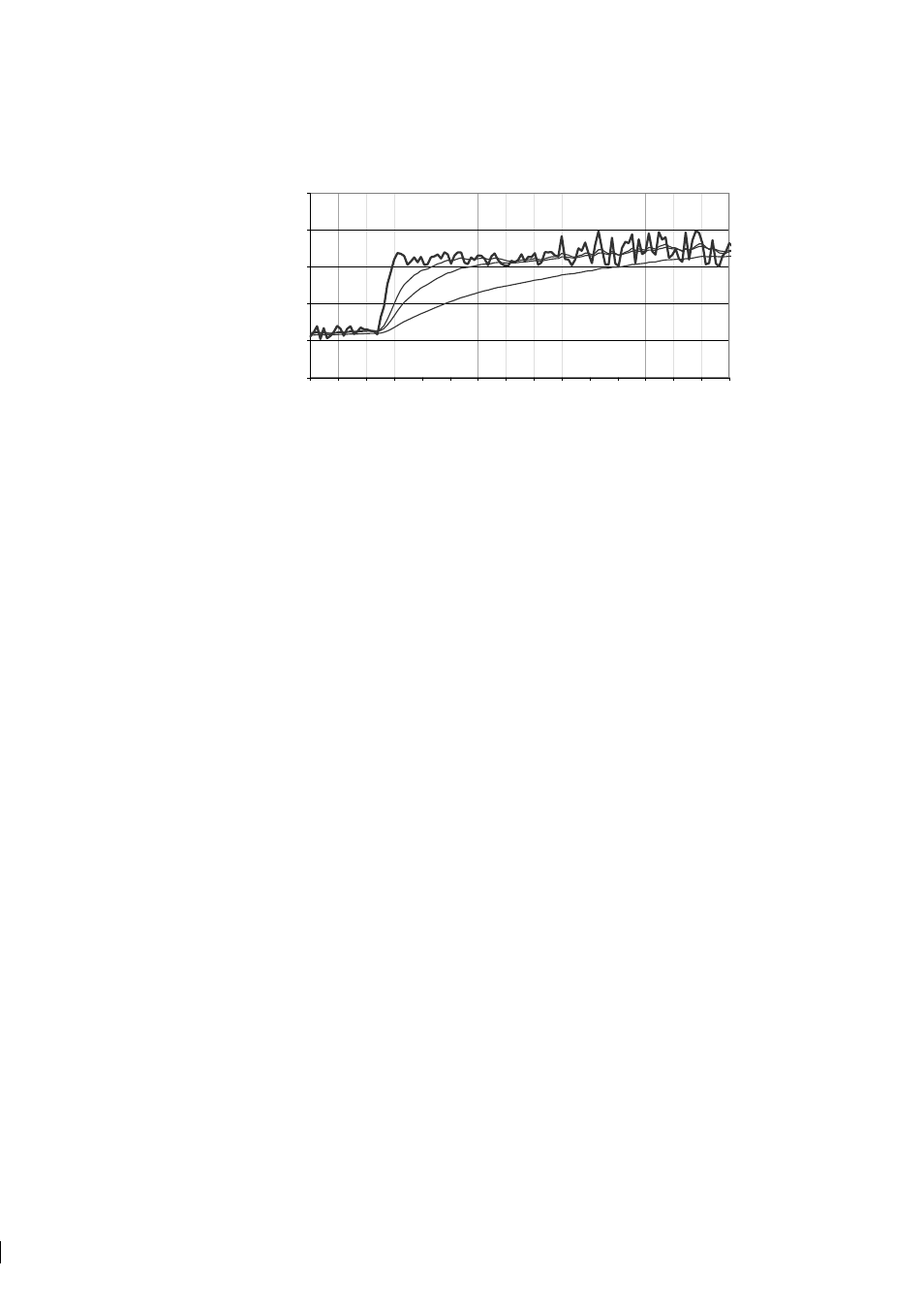
100 110 120 130 140 150
Time [s]
CONC%
Undamped
5 s
10 s
30 s
Figure 5.14
Effect of damping time on measurement
5.10.6 Field calibration
The most accurate calibration is made under normal process conditions using your standard laboratory
determinations of sample concentration. K-Patents provides a field calibration service that optimizes the
calibration constants based on the data supplied.
You should systematically record calibrating data on the Calibration data report (page 109, also available
at www.kpatents.com and by email at [email protected]). When you have completed the Calibration data
report, you have to fax it to either K-Patents headquarters or your local K-Patents representative. A computer
analysis of the data will be made at K-Patents and optimal calibration data will be sent to you to be entered
in the IT-R.
For a complete report you need 10–15 valid data points (see below). A data point is of use for calibration
only when the diagnostic message is Normal
operation
. If prism wash is employed, do not take
samples during the wash. A data point is useful even if the concentration value is outside the range of the
output current.
Each data point consists of:
LAB%
Sample concentration determined by the user.
From IT-R display:
(see Section 5.3)
CONC%
Measurement in concentration units
TEST
Number of photocells on the light side of the optical image (= primary measurement)
TEMP
Process temperature measurement in centigrades
Accurate calibration is only achieved if the sample is taken correctly and the data points are recorded
carefully and only when the message is Normal operation. Pay special attention to following details:
− The sampling valve and the refractometer should be installed close to each other in the process.
−
Warning!
Wear protective clothing appropriate to your process when operating the sampling
!
valve and handling the sample.
− Run the sample before starting to collect data points to avoid sampling old process liquid that
has remained in the sampling valve.
− Read the values CONC%, TEST and TEMP in the IT-R’s display at exactly the same time with
sampling.
− Use a tight container for the sample to avoid evaporation.