Fixed pre-trigger with post-trigger stop event, No pre-trigger, infinite post-trigger, Fixed pre-trigger with infinite post-trigger – Measurement Computing USB-2527 User Manual
Page 33: Counter inputs, Mapped channels
USB-2527 User's Guide
Functional Details
33
Fixed pre-trigger with post-trigger stop event
In this mode, you set the number of pre-trigger readings to acquire. The acquisition continues until a stop-
trigger event occurs.
No pre-trigger, infinite post-trigger
In this mode, no pre-trigger data is acquired. Instead, data is acquired beginning with the trigger event, and is
terminated when you issue a command to halt the acquisition.
Fixed pre-trigger with infinite post-trigger
You set the amount of pre-trigger data to acquire. Then, the system continues to acquire data until the program
issues a command to halt acquisition.
Counter inputs
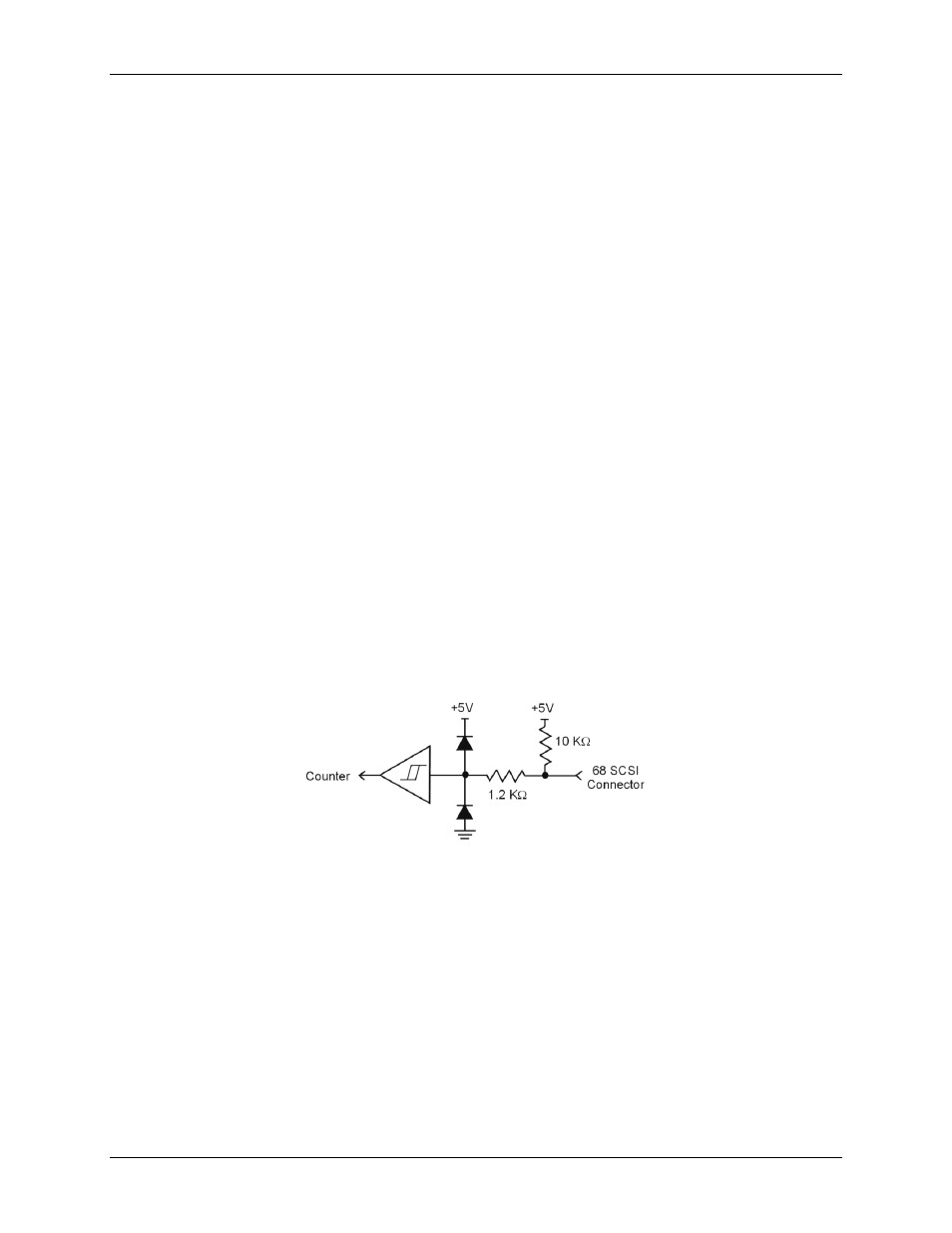
Four 32-bit counters are built into the USB-2527. Each counter accepts frequency inputs up to 20 MHz.
USB-2527 counter channels can be configured as standard counters or as multi-axis quadrature encoders.
The counters can concurrently monitor time periods, frequencies, pulses, and other event driven incremental
occurrences directly from pulse-generators, limit switches, proximity switches, and magnetic pick-ups.
Counter inputs can be read asynchronously under program control, or synchronously as part of an analog or
digital scan group.
When reading synchronously, all counters are set to zero at the start of an acquisition. When reading
asynchronously, counters may be cleared on each read, count up continually, or count until the 16 bit or 32 bit
limit has been reached. See the counter mode descriptions below.
Figure 13. Typical USB-2527 counter channel
Mapped channels
A mapped channel is one of four counter input signals that can get multiplexed into a counter module. The
mapped channel can participate with the counter's input signal by gating the counter, latching the counter, and
so on. The four possible choices for the mapped channel are the four counter input signals (post-debounce).
A mapped channel can be used to:
gate the counter
decrement the counter
latch the current count to the count register
Usually, all counter outputs are latched at the beginning of each scan within the acquisition. However, you can
use a second channel—known as the mapped channel—to latch the counter output.