Lfib, Control plane and forwarding plane, Mpls network architecture – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 13
2
LSR
A router that performs MPLS forwarding is a label switching router (LSR).
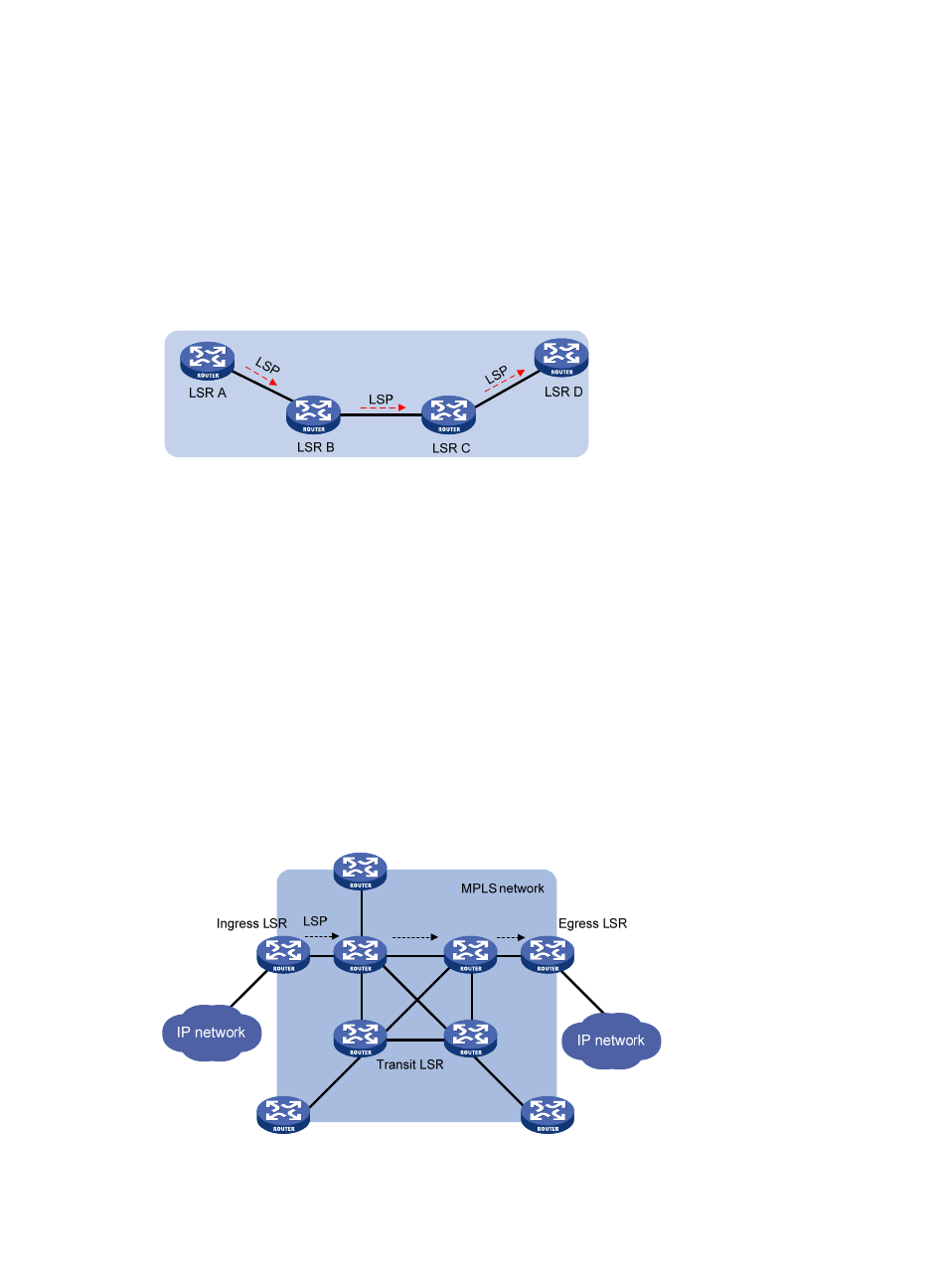
LSP
A label switched path (LSP) is the path along which packets of a FEC travel through an MPLS network.
An LSP is a unidirectional packet forwarding path. Two neighboring LSRs are called the "upstream LSR"
and "downstream LSR" along the direction of an LSP. In
Figure 2
, LSR B is the downstream LSR of LSR A,
and LSR A is the upstream LSR of LSR B.
Figure 2 Label switched path
LFIB
The Label Forwarding Information Base (LFIB) on an MPLS network functions like the Forwarding
Information Base (FIB) on an IP network. When an LSR receives a labeled packet, it searches the LFIB to
obtain information for forwarding the packet, such as the label operation type, the outgoing label value,
and the next hop.
Control plane and forwarding plane
An MPLS node consists of a control plane and a forwarding plane.
•
Control plane—Assigns labels, distributes FEC-label mappings to neighbor LSRs, creates the LFIB,
and establishes and removes LSPs.
•
Forwarding plane—Forwards packets according to the LFIB.
MPLS network architecture
Figure 3 MPLS network architecture