Traffic forwarding and flooding – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 295
284
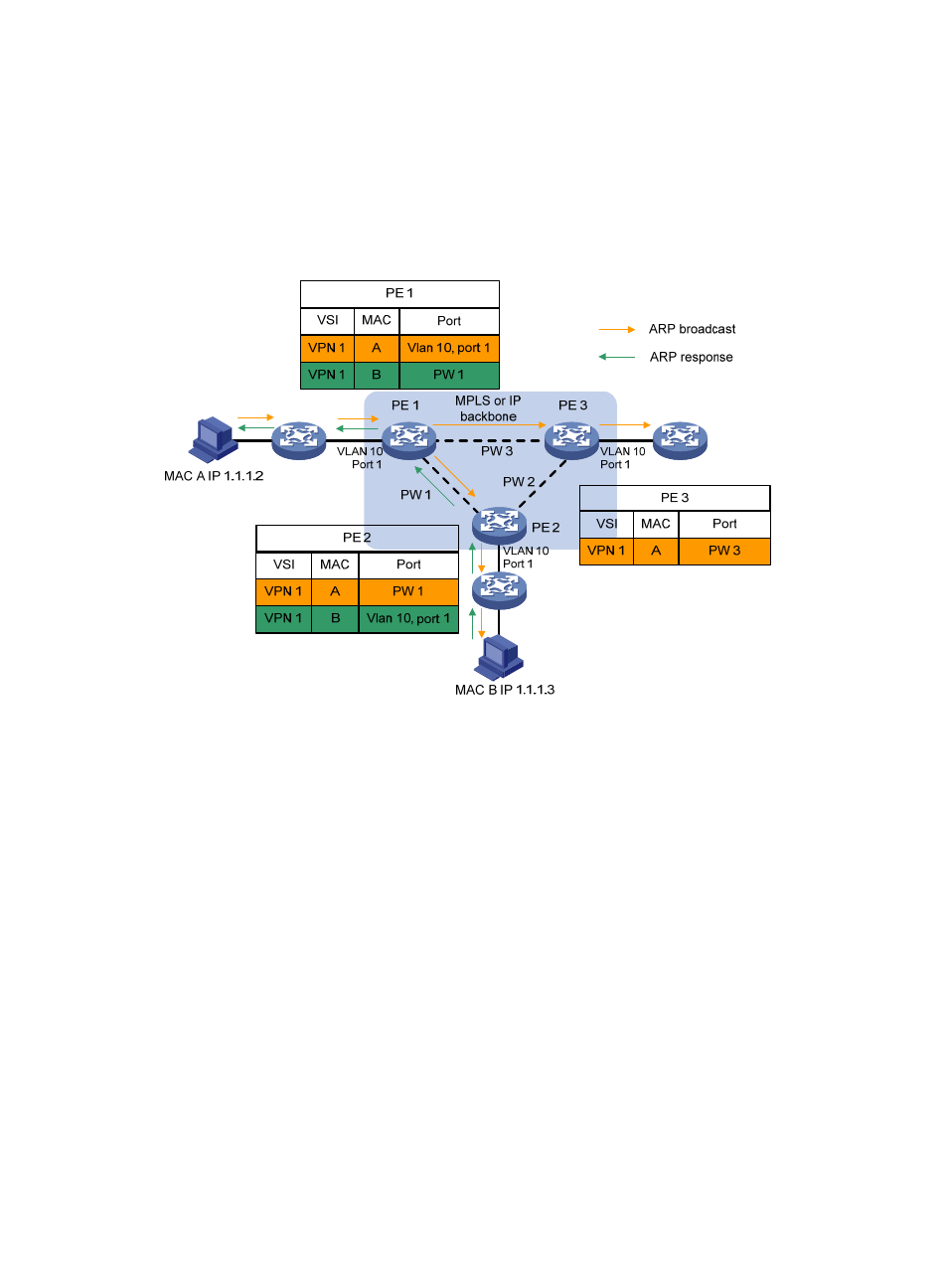
If the source MAC address of a packet from a CE does not exist in the MAC address table, the PE
learns the source MAC address on the AC connected to the CE.
•
Learning the source MAC addresses of remote sites connected through PWs:
A VSI regards a PW as a logical Ethernet interface. If the source MAC address of a packet
received from a PW does not exist in the MAC address table, the PE learns the source MAC
address on the PW of the VSI.
Figure 75 Source MAC address learning on a PE
If no packet is received from a MAC address before the aging timer expires, VPLS deletes the MAC
address to save MAC address table resources.
When an AC or a PW goes down, the PE deletes MAC addresses on the AC or PW and sends an LDP
address withdrawal message to notify all other PEs in the VPLS instance to delete those MAC addresses.
Traffic forwarding and flooding
Unicast traffic forwarding and flooding:
After a PE receives a unicast packet from an AC, the PE searches the MAC address table of the VSI bound
to the AC to determine how to forward this packet.
•
If a match is found, the PE forwards the packet according to the matching entry. If the outgoing
interface in the entry is a PW, the PE inserts the PW label to the packet, adds the public tunnel
header to the packet, and then forwards the packet to the remote PE over the PW. If the outgoing
interface in the entry is a local interface, the PE directly forwards the packet to the local interface.
•
If no match is found, the PE floods the packet to all other ACs and PWs in the VSI.
After a PE receives a unicast packet from a PW, the PE searches the MAC address table of the VSI bound
to the PW to determine how to forward this packet.
•
If a match is found, the PE forwards the packet through the egress interface in the matching entry.
•
If no match is found, the PE floods the packet to all ACs in the VSI.