Maintenance point – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 27
18
An MA serves a VLAN. Packets sent by the MPs in an MA carry the relevant VLAN tag. An MP can
receive packets sent by other MPs in the same MA.
Maintenance point
An MP is configured on a port and belongs to an MA. MPs fall into two types: maintenance association
end points (MEPs) and maintenance association intermediate points (MIPs).
•
MEP
Each MEP is identified by an integer called a “MEP ID”. The MEPs of an MD define the range and
boundary of the MD. The MA and MD that a MEP belongs to define the VLAN attribute and level of the
packets sent by the MEP. MEPs fall into inward-facing MEPs and outward-facing MEPs.
The level of a MEP determines the levels of packets that the MEP can process. The packets transmitted
from a MEP carry the level of the MEP. A MEP forwards packets at a higher level and processes packet
of its level or lower. The processing procedure is specific to packets in the same VLAN. Packets of
different VLANs are independent.
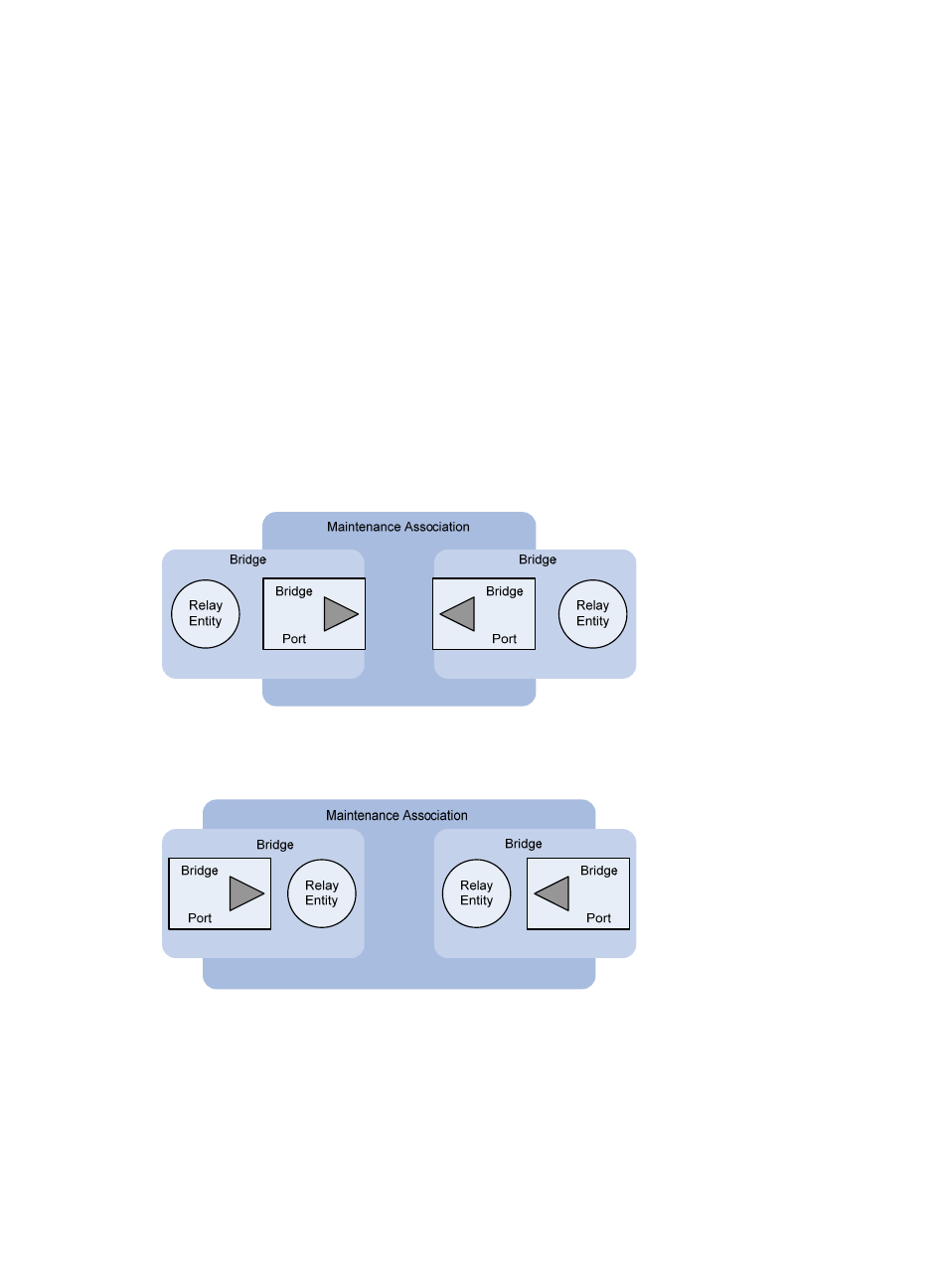
The direction of a MEP (outward-facing or inward-facing) determines the position of the MD relative to the
port.
Figure 4 Outward-facing MEP
As shown in
, an outward-facing MEP sends packets to its host port.
Figure 5 Inward-facing MEP
As shown in
, an inward-facing MEP does not send packets to its host port. Rather, it sends
packets to other ports on the device.
•
MIP
A MIP is internal to an MD. It cannot send CFD packets actively. However, it can handle and respond to
CFD packets. The MA and MD to which a MIP belongs define the VLAN attribute and level of the packets
received.