Yaskawa Varispeed-686SS5 CIMR-SSA User Manual
Page 67
68
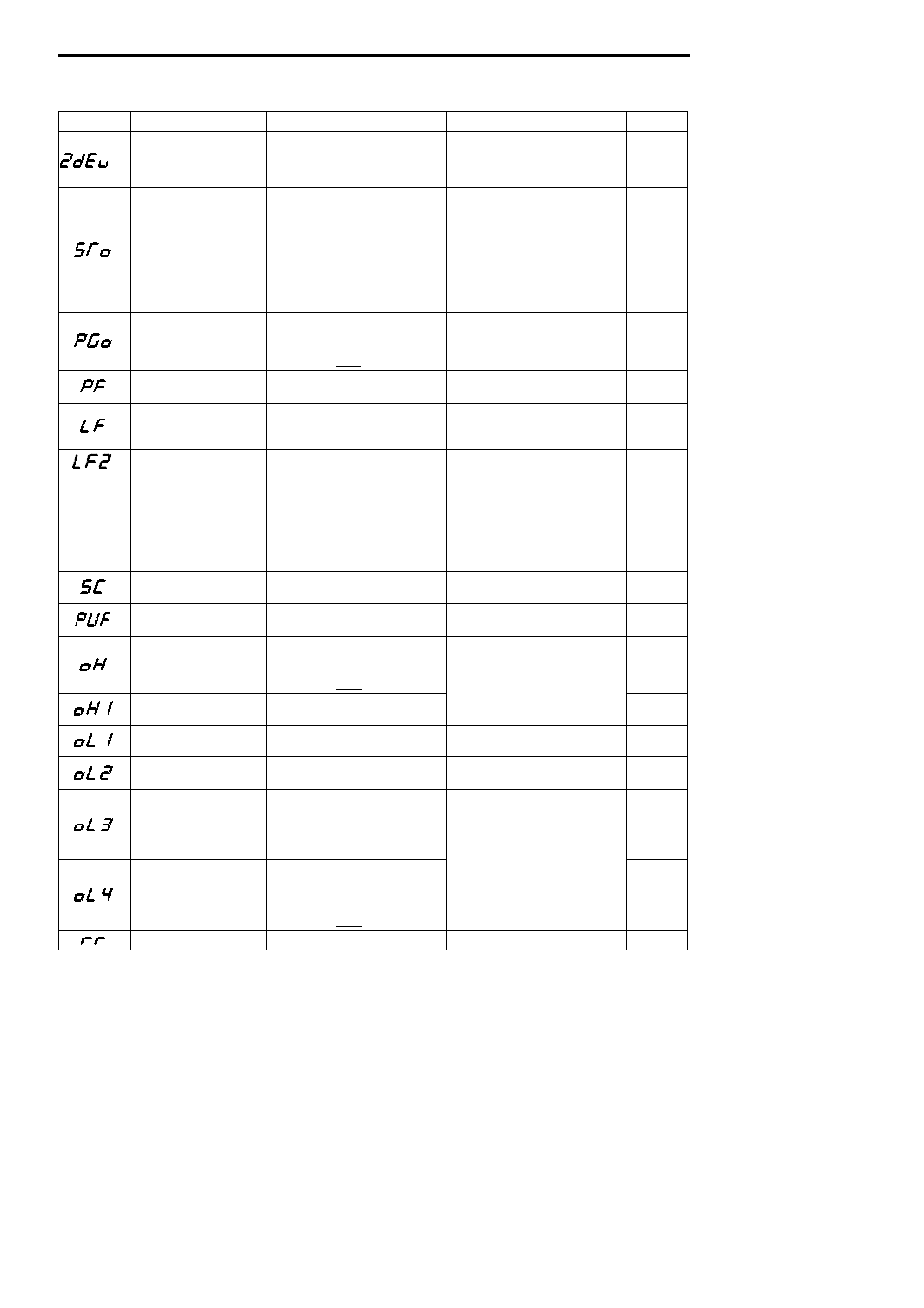
Table 31
Fault Diagnosis and Corrective Actions (Cont’d)
Fault Display
Description
Details
Corrective Action
Rank*
*2 Phase Z pulse fault (ZdEV)
• Excessive speed deviation caused by
phase Z error detection
• Malfunction caused by phase Z pulse
error or noise
• Check the PG wiring cable and connec-
tor.
• Readjust the zero-pulse.
A
Step out (STO)
Control is disabled by step out.
• Check the motor constants. (Refer to
page 44.)
• Set the constant induced voltage
(E1-13) to a value that is 10% less than
that of Ke on the nameplate.
• Check the operating temperature of
the motor.
• Decrease ASR gain (C5-01).
• Decrease accel time (C1-01).
A
PG open circuit (PGO)
The PG line is broken.
Detection time: F1-13
The inverter operates according to the set-
ting of constant F1-02.
• Check the PG line.
• Check the condition of the motor lock or
the load.
B
Excessive ripple in DC bus bar
voltage (PF)
• Inverter input voltage has open-phase.
• Large unbalance in input voltage.
• Check the line voltage.
• Re-tighten the input terminal screws.
A
Load open-phase (LF)
Inverter output has open-phase.
*3
• Check the output wiring.
• Check the motor impedance.
• Re-tighten the input terminal screws.
A
*4
Output current unbalance (LF2) A large unbalance occurred in the output
current because of one of the following
causes.
• The inverter output wiring is faulty.
• ASR gain setting is incorrect.
• Failure occurred with parts on the output
side of the inverter.
• Motor is faulty.
(Unbalanced impedance in motor)
• Check the output wiring.
• Re-tighten the input terminal screws.
• Check the disconnection of the motor
coil.
• Decrease ASR proportional (p) gain 1
(C5-01).
• Replace the inverter.*5
• Replace the motor.*5
A
Load short-circuit (SC)
Inverter output (load) is short-circuited.
• Check the motor coil resistance.
• Check the motor insulation.
A
Fuse blown (PUF)
• Main transistor was broken.
• DC circuit fuse was blown.
Check for damaged transistor, load side
short-circuit, grounding, etc.
A
Inverter overheat alarm (OH)
The transistor heatsink temperature
exceeded the allowable value (95°C).
The inverter operates according to the set-
ting of constant L8-03.
• Check the heatsink and the ambient tem-
perature.
• Check the filter and the fan
B
Inverter overheat (OH1)
The transistor heatsink temperature
exceeded the allowable value (105°C).
• Check the filter and the fan.
A
Motor overload (OL1)
Inverter output exceeded the motor
overload level.
Reduce the load.
A
Inverter overload (OL2)
Inverter output exceeded the inverter
overload level.
• Reduce the load.
• Extend the acceleration time.
A
Overtorque detection 1 (OL3)
Torque exceeded overtorque detection
level 1 (L6-02).
Detection time: L6-03
The inverter operates according to the set-
ting of constant L6-01.
Check the load
B
Overtorque detection 2 (OL4)
Torque exceeded overtorque detection
level 2 (L6-05).
Detection time: L6-06
The inverter operates according to the set-
ting of constant L6-04.
Check the load.
B
Braking transistor fault (RR)
The braking transistor has failed.
Replace the inverter.
A
(Cont’d)