Altera FIR Compiler User Manual
Page 51
Chapter 4: Functional Description
4–9
FIR Compiler
© May 2011
Altera Corporation
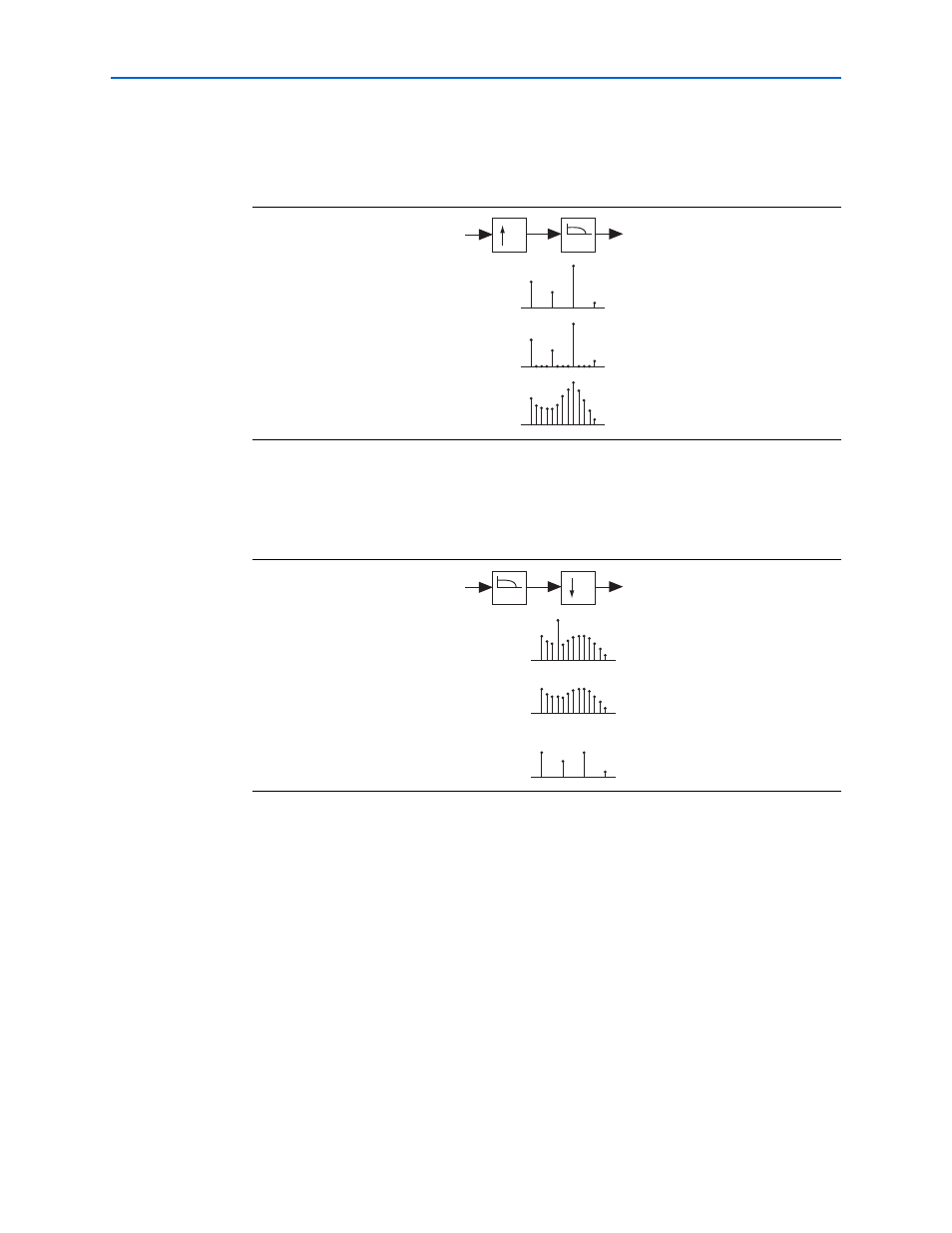
Mathematically, when a signal is interpolated, zeros are inserted between data points
and the data is then filtered to remove spectral components that were not present in
the original signal (
To decimate a signal, a low-pass filter is applied, which removes spectral components
that will not be present at the low sample rate. After filtering, appropriate sample
values are taken (
The FIR Compiler generates interpolation and decimation filters by combining high-
and low-level optimization techniques.
Using the high-level optimization technique, the FIR Compiler processes the data
from a polyphase decomposed filter. The polyphase decomposition breaks a single
filter into several smaller filters, which results in the following:
■
When using an interpolation filter, zero-stuffed data does not need to be
computed; potentially saving resources (
■
When using a decimation filter, output data—which is discarded during
downsampling—is never computed, again potentially saving resources
(
Using the low-level optimization technique, the polyphase decomposed filter is
implemented using a multichannel, multiple coefficient set structure with an
appropriate wrapper.
Figure 4–7. Signal Interpolation
Figure 4–8. Signal Decimation
N
Input
Data
After
Zero
Stuffing
After
Low-Pass
Filtering
LPF
Input
Output
M
Input
Data
Filtered
Data
Decimated
Data
LPF
Input
Output