General cabling requirements, Minimum curvature radius of cables, Minimum curvature radius of fibers – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 149: Prerequisites
141
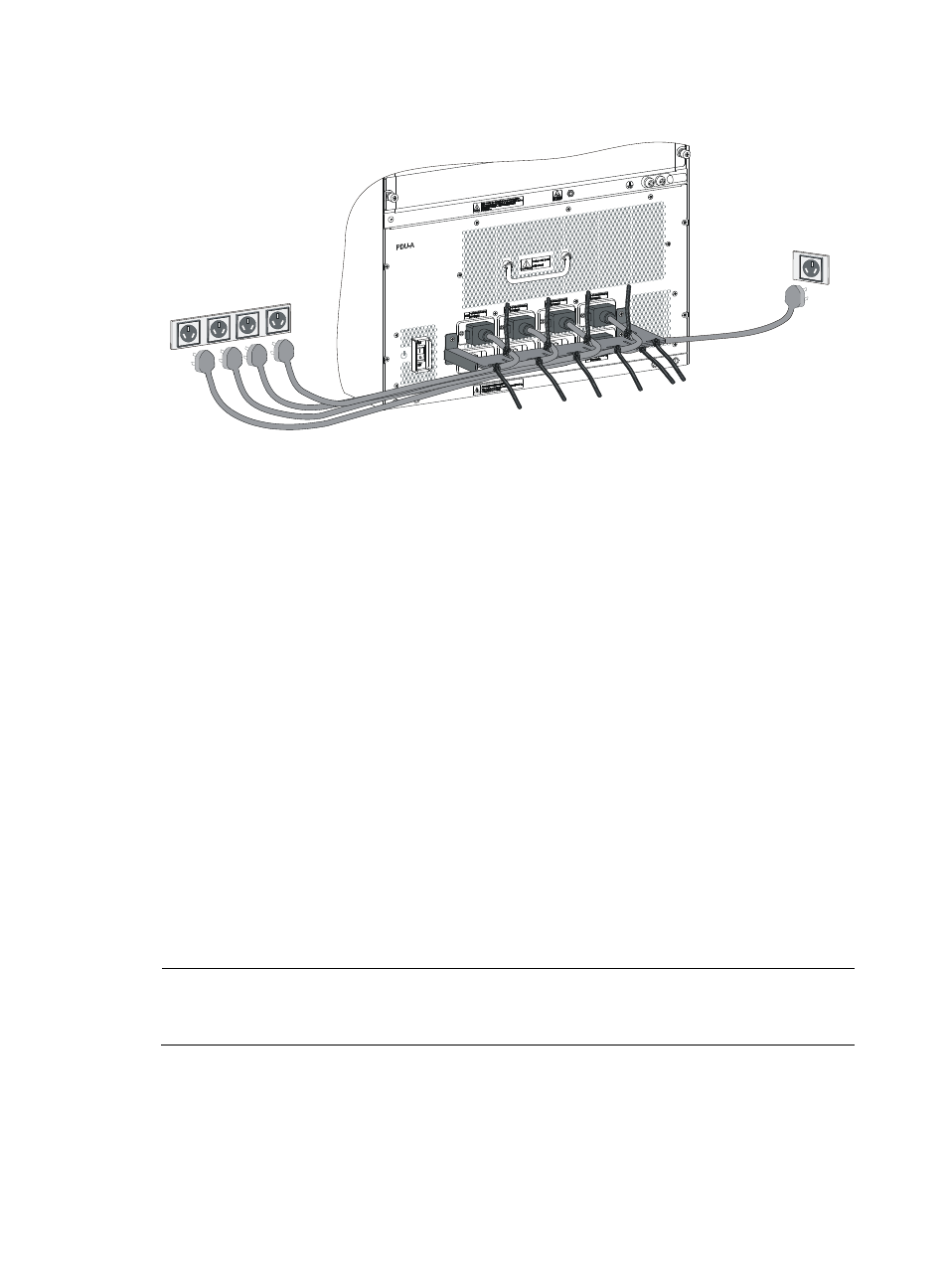
Figure 93 Routing and bundling power cords on the S12510-X AC switch
General cabling requirements
Minimum curvature radius of cables
•
The curvature radius of an attached power cord, communication cable, or ribbon cable should be
a minimum of five times the cable's outer diameter. If the cable is frequently bent, plugged and
unplugged, the curvature radius should be a minimum of seven times the cable's outer diameter.
•
The curvature radius of an ordinary attached coaxial cable should be a minimum of seven times of
the cable's outer diameter. If the coaxial cable is frequently bent, plugged and unplugged, the
curvature radius should be a minimum of 10 times the cable's outer diameter.
•
The curvature radius of a high-speed cable (for example, SFP+ DAC cable) should be a minimum
of five times of the cable's outer diameter. If the coaxial cable is frequently bent, plugged and
unplugged, the curvature radius should be a minimum of 10 times the cable's outer diameter.
Minimum curvature radius of fibers
•
When the fiber is wrapped up around the cabling plate, the diameter of the cabling plate should
be a minimum of 25 times the fiber's diameter.
•
When the fiber is being moved, the curvature radius of the fiber should be a minimum of 20 times
the fiber's diameter.
•
When the fiber is attached, the curvature radius of the fiber should be a minimum of 10 times the
fiber's diameter.
NOTE:
The fiber's diameter refers to the outer diameter of the fiber jacket. Typically, the diameter of a single-core
fiber is 0.9 mm (0.04 in), 2.0 mm (0.08 in), or 3.0 mm (0.12 in).
Prerequisites
Label cables before you route or bundle them.