2 linear interpolation (mvs), 1) overview, 2) format – Yaskawa MP2000 Series: User's Manual for Motion Programming User Manual
Page 157: Caution
8 Command Reference
8.2.2 Linear Interpolation (MVS)
8-50
8.2.2 Linear Interpolation (MVS)
(1) Overview
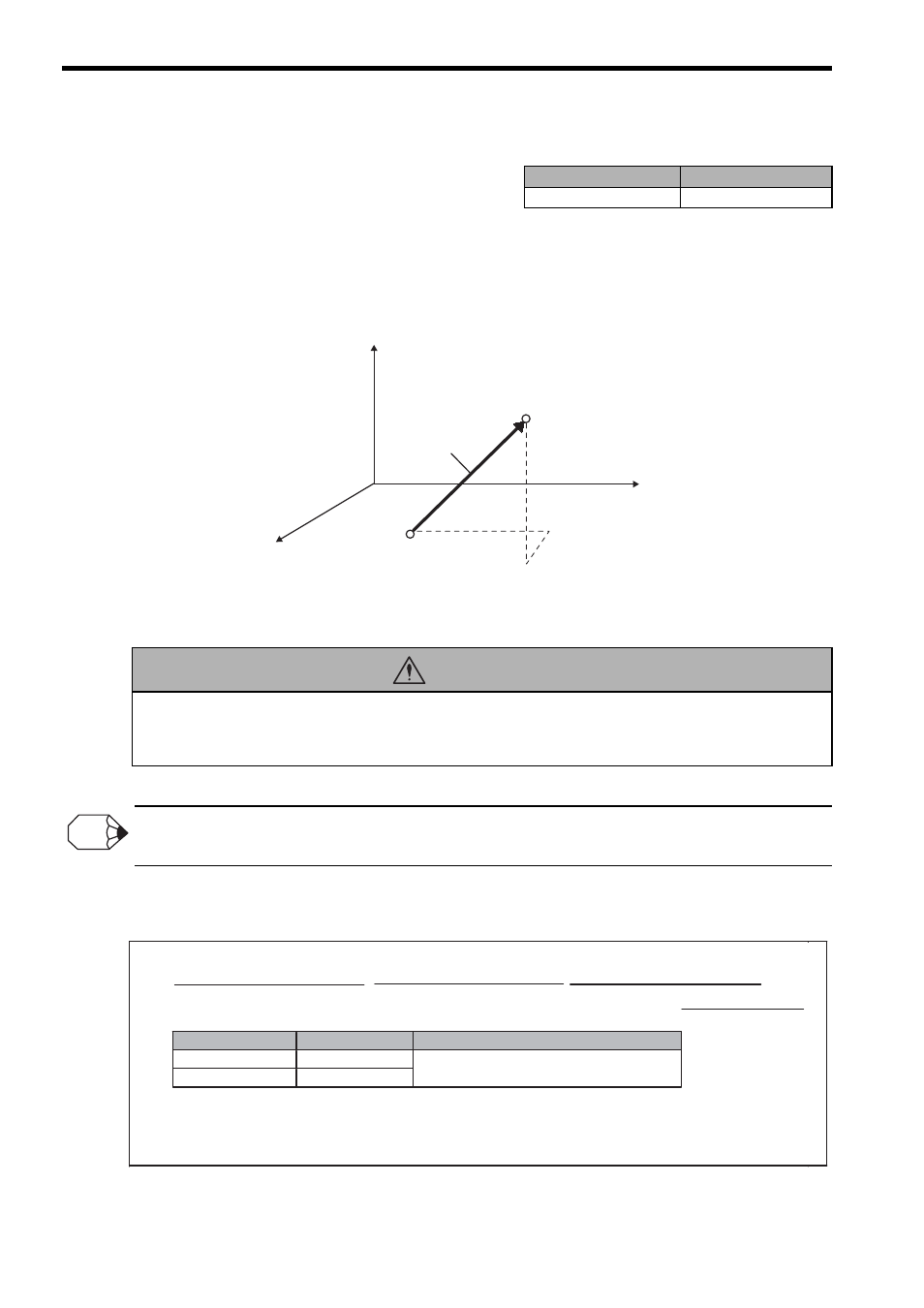
The Linear Interpolation command (MVS) moves each axis on a straight line from the program current position
to the end position at the specified interpolation feed speed. Up to 16 axes can be moved simultaneously. Any
axis not specified in the command will not be moved.
Fig. 8.27 Movement Path with MVS Command
For axis movement with the MVS command, an in-position check is not automatically executed. Use the PFN command to
execute an in-position check if required.
(2) Format
Motion Programs
Sequence Programs
Applicable
Not applicable
• Linear Interpolation (MVS) can be executed for either linear axes or rotary axes. If rotary axes are included,
however, the linear interpolation path will not be in straight line. When programming, be sure to check the
path to make sure that there are no tools or other obstacles in the way of the workpiece.
Failure to carry out this check may result in damage to equipment, serious personal injury, or even death.
[Logical axis 2]
[Logical axis 1]
[Logical axis 3]
Logical axis 3
Logical axis 2
Logical axis 1
Interpolation
feed speed
(Composite
speed)
End position
Program
current position
CAUTION
INFO
...
Unit
Usable Data
Reference position
Reference unit
Interpolation feed speed
Reference units/min
Directly designated value
Double integer type register (Indirect designation)
Note: The interpolation feed speed can be omitted.
MVS [Logical axis name 1] Reference position [Logical axis name 2] Reference position [Logical axis name 3] Reference position
F
Interpolation feed speed ;
Item