2 port authentication – Signamax Managed Hardened PoE Industrial DIN-rail Mount Switch User Manual
Page 42
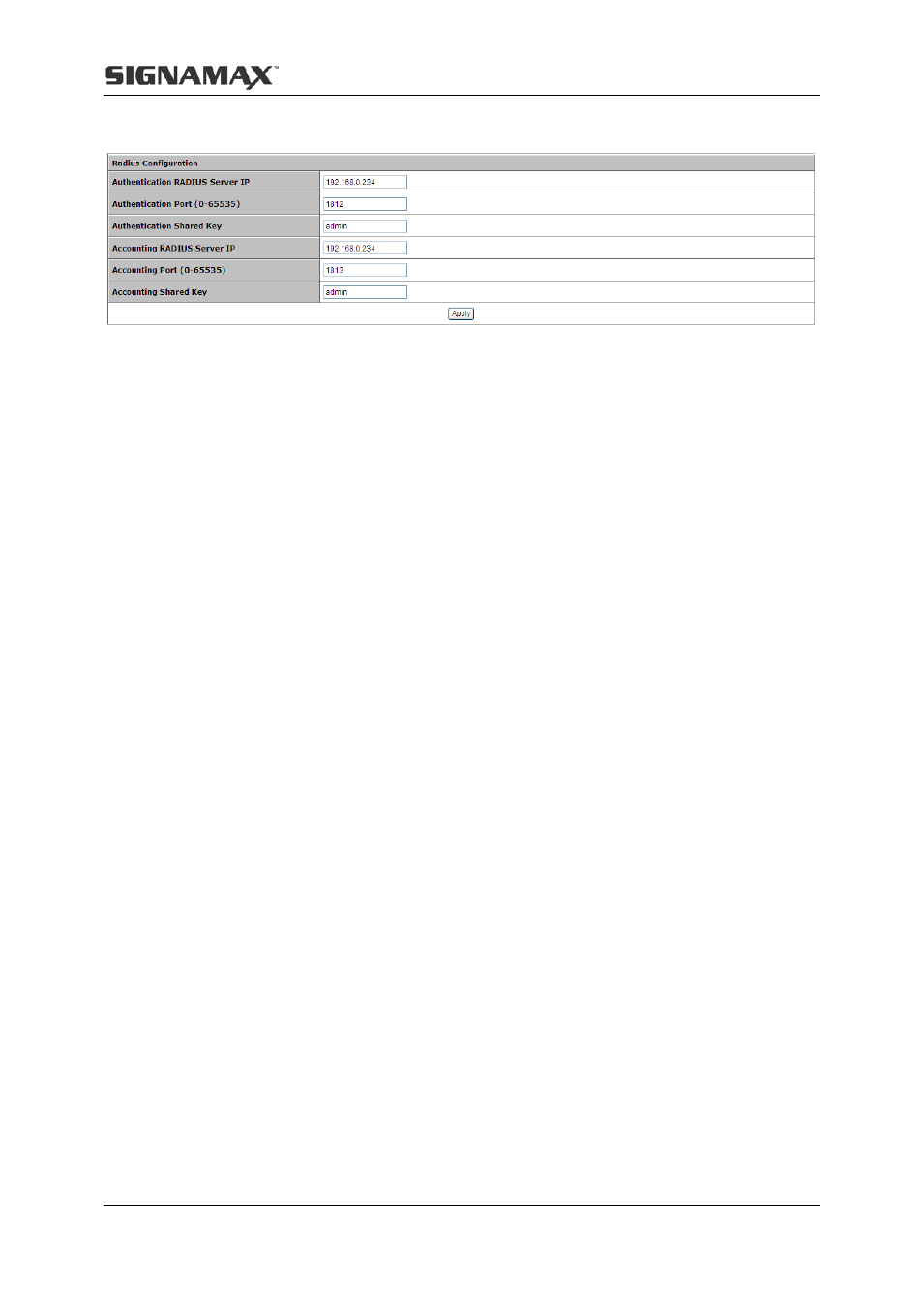
8 Security
37
shared key.
8.2 Port Authentication
IEEE 802.1x authentication system uses extensible authentication protocol (EAP) to
exchange information between supplicant systems and the authentication servers. When a
supplicant system passes the authentication, the authentication server passes the
information about the supplicant system to the authenticator system. The authenticator
system in turn determines the state (authorized or unauthorized) of the controlled port
according to the instructions (accept or reject) received from the RADIUS server.
802.1x Authentication Procedure:
A supplicant system launches an 802.1x client to initiate an access request by sending
an EAPoL-start packet to the switch, with its user name and password provided. The
802.1x client program then forwards the packet to the switch to start the authentication
process.
Upon receiving the authentication request packet, the switch sends an
EAP-request/identity packet to ask the 802.1x client for the user name.
The 802.1x client responds by sending an EAP-response/identity packet to the switch
with the user name contained in it. The switch then encapsulates the packet in a RADIUS
Access-Request packet and forwards it to the RADIUS server.
Upon receiving the packet from the switch, the RADIUS server retrieves the user name
from the packet, finds the corresponding password by matching the user name in its
database, encrypts the password using a randomly-generated key, and sends the key to
the switch through an RADIUS access-challenge packet. The switch then sends the key
to the 802.1x client.
Upon receiving the key (encapsulated in an EAP-request/MD5 challenge packet) from
the switch, the client program encrypts the password of the supplicant system with the
key and sends the encrypted password (contained in an EAP-response/MD5 challenge
packet) to the RADIUS server through the switch. (Normally, the encryption is
irreversible.)
The RADIUS server compares the received encrypted password (contained in a RADIUS
access-request packet) with the locally-encrypted password. If the two match, it will then