PLANET GSW-1602SF User Manual
Page 82
User’s Manual of GSW-1602SF / GSW-2404SF
STP Port States
The BPDUs take some time to pass through a network. This propagation delay can result in topology changes where a port
that transitioned directly from a Blocking state to a Forwarding state could create temporary data loops. Ports must wait for
new network topology information to propagate throughout the network before starting to forward packets. They must also
wait for the packet lifetime to expire for BPDU packets that were forwarded based on the old topology. The forward delay
timer is used to allow the network topology to stabilize after a topology change. In addition, STP specifies a series of states
a port must transition through to further ensure that a stable network topology is created after a topology change.
Each port on a switch using STP exists is in one of the following five states:
Blocking
– the port is blocked from forwarding or receiving packets
Listening
– the port is waiting to receive BPDU packets that may tell the port to go back to the blocking state
Learning – the port is adding addresses to its forwarding database, but not yet forwarding packets
Forwarding
– the port is forwarding packets
Disabled
– the port only responds to network management messages and must return to the blocking state
first
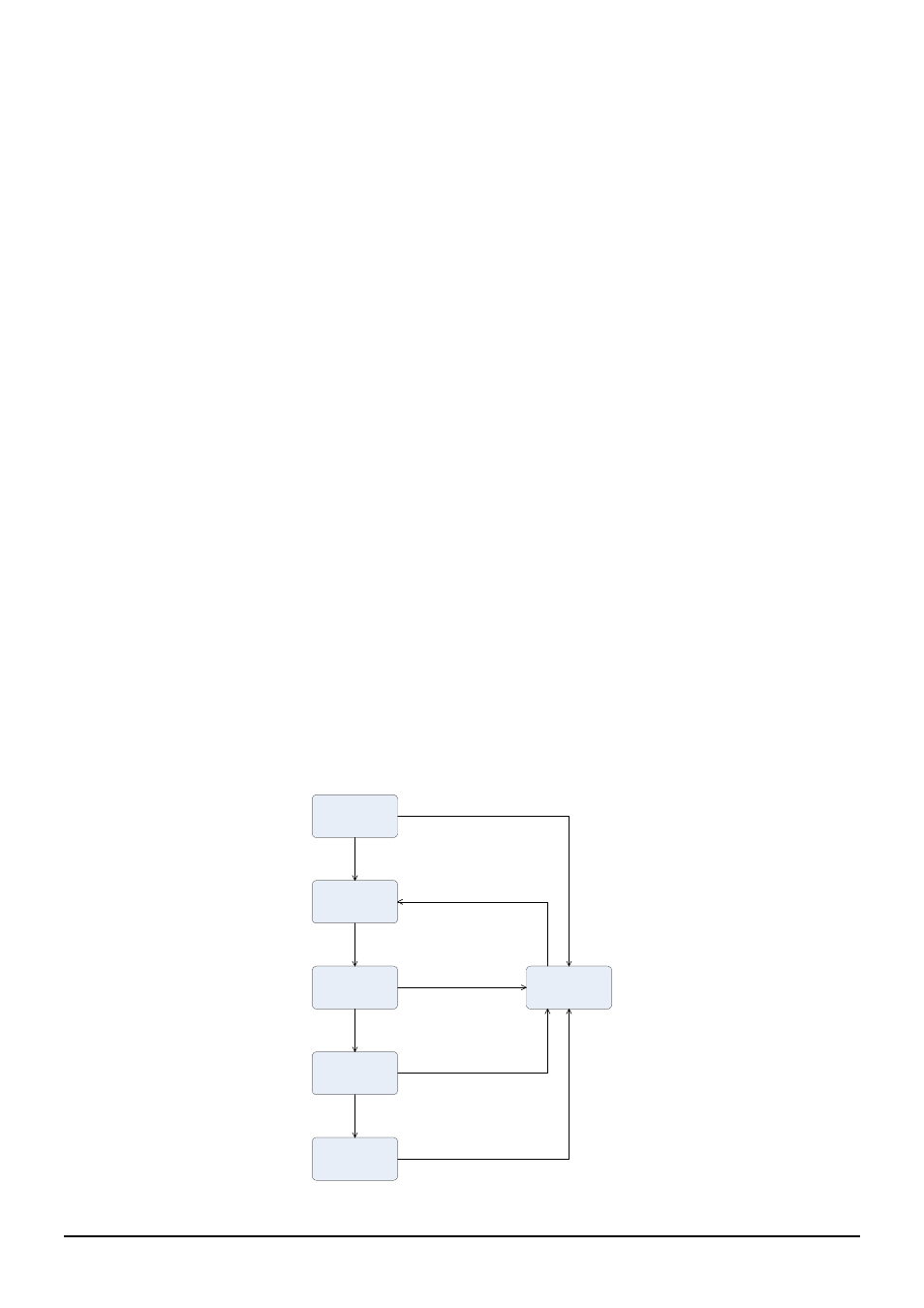
A port transitions from one state to another as follows:
From initialization (switch boot) to blocking
From blocking to listening or to disabled
From listening to learning or to disabled
From learning to forwarding or to disabled
From forwarding to disabled
From disabled to blocking
Switch
Blocking
Listening
Learning
Forwarding
Disable
STP Figure
STP Port State Transitions
-76-