Tunneling, Nat-pt – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 170
157
•
Automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6 tunneling—A point-to-multipoint link. Both ends of the tunnel use
IPv4-compatible IPv6 addresses. The address format is 0:0:0:0:0:0:a.b.c.d/96, where a.b.c.d is
the IPv4 address of the tunnel destination. This mechanism simplifies tunnel establishment.
Automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6 tunnels have limitations because IPv4-compatible IPv6 addresses
must use globally unique IPv4 addresses.
•
6to4 tunneling
{
Ordinary 6to4 tunneling—A point-to-multipoint automatic tunnel. It is used to connect multiple
isolated IPv6 networks over an IPv4 network. The destination IPv4 address of a 6to4 tunnel is
embedded in the destination 6to4 address of packets. This mechanism enables the device to
automatically get the tunnel destination address, simplifying tunnel establishment.
The 6to4 address format is 2002:abcd:efgh:subnet number::interface ID/64, where 2002 is
the fixed IPv6 address prefix, and abcd:efgh represents a 32-bit globally unique IPv4 address
in hexadecimal notation. For example, 1.1.1.1 can be represented by 0101:0101. The IPv4
address identifies a 6to4 network (an IPv6 network where all hosts use 6to4 addresses). The
border router of a 6to4 network must have the IPv4 address abcd:efgh configured on the
interface connected to the IPv4 network. The subnet number identifies a subnet in the 6to4
network. The subnet number::interface ID uniquely identifies a host in the 6to4 network.
6to4 tunneling uses an IPv4 address to identify a 6to4 network. This method overcomes the
limitations of automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6 tunneling.
{
6to4 relay—Connects a 6to4 network to an IPv6 network that uses an IP prefix other than
2002::/16. A 6to4 relay router is a gateway that forwards packets from a 6to4 network to an
IPv6 network.
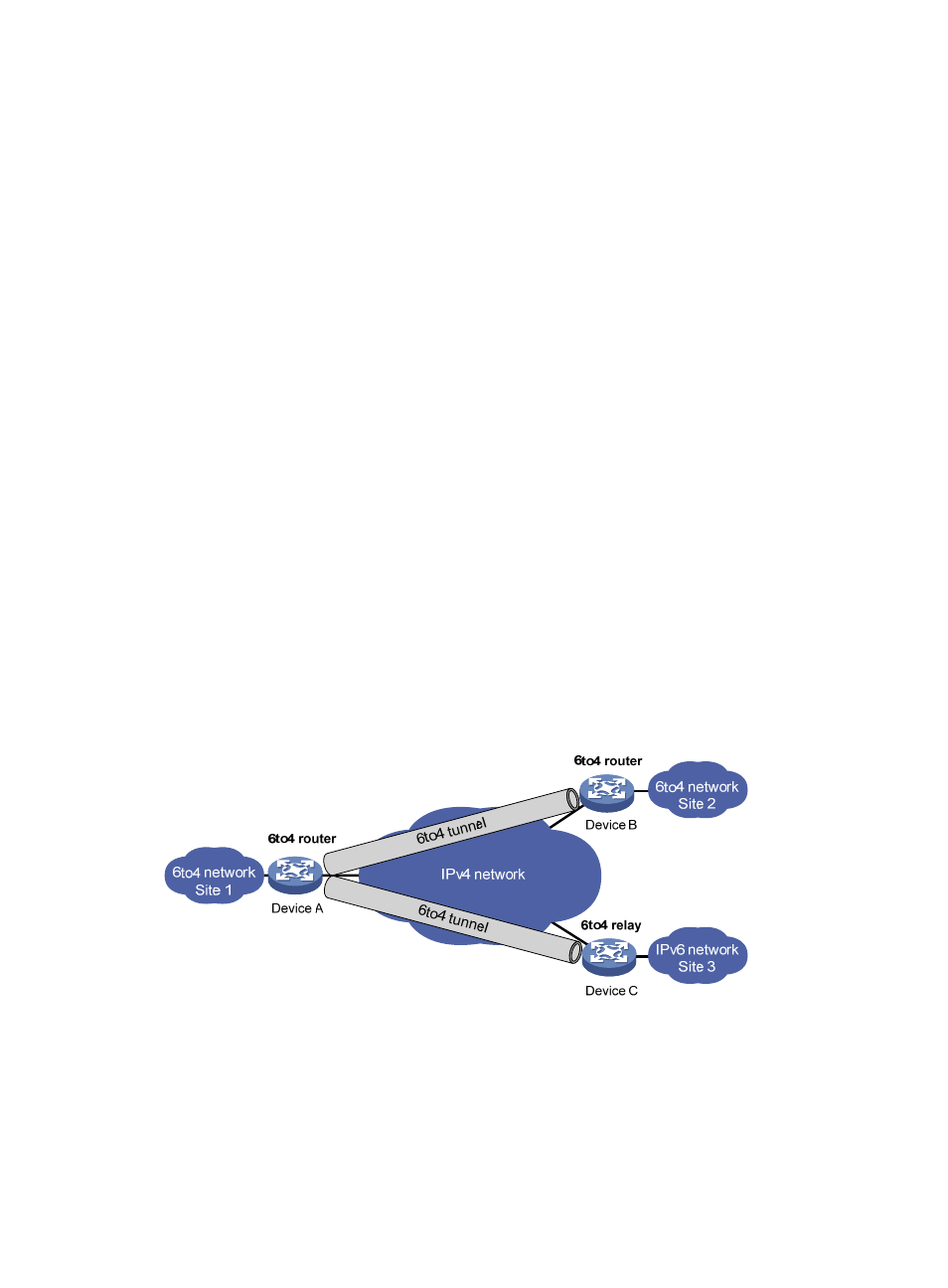
As shown in
799H
Figure 64
, 6to4 network Site 1 communicates with IPv6 network Site 3 over a
6to4 tunnel. Configure a static route on the border router (Device A) in the 6to4 network. The
next-hop address must be the 6to4 address of the 6to4 relay router (Device C). Device A
forwards all packets destined for the IPv6 network over the 6to4 tunnel, and Device C then
forwards them to the IPv6 network.
Figure 64 Principle of 6to4 tunneling and 6to4 relay
•
ISATAP tunneling—An ISATAP tunnel is a point-to-multipoint automatic tunnel. It provides a solution
to connect an IPv6 host to an IPv6 network over an IPv4 network.
The destination addresses of IPv6 packets and the IPv6 addresses of tunnel interfaces are all ISATP
addresses. The ISATAP address format is prefix:0:5EFE:abcd:efgh. The 64-bit prefix is a valid IPv6
unicast address prefix. The abcd:efgh segments represent a 32-bit IPv4 address, which identifies
the tunnel destination but does not require global uniqueness.