Dns spoofing – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 83
70
A DNS proxy operates as follows:
1.
A DNS client considers the DNS proxy as the DNS server, and sends a DNS request to the DNS
proxy. The destination address of the request is the IP address of the DNS proxy.
2.
The DNS proxy searches the local static domain name resolution table and dynamic domain name
resolution cache after receiving the request. If the requested information is found, the DNS proxy
returns a DNS reply to the client.
3.
If the requested information is not found, the DNS proxy sends the request to the designated DNS
server for domain name resolution.
4.
After receiving a reply from the DNS server, the DNS proxy records the IP address-to-domain name
mapping and forwards the reply to the DNS client.
With no DNS server or route to a DNS server, the DNS proxy does not forward DNS requests or answer
requests from the DNS clients.
229B
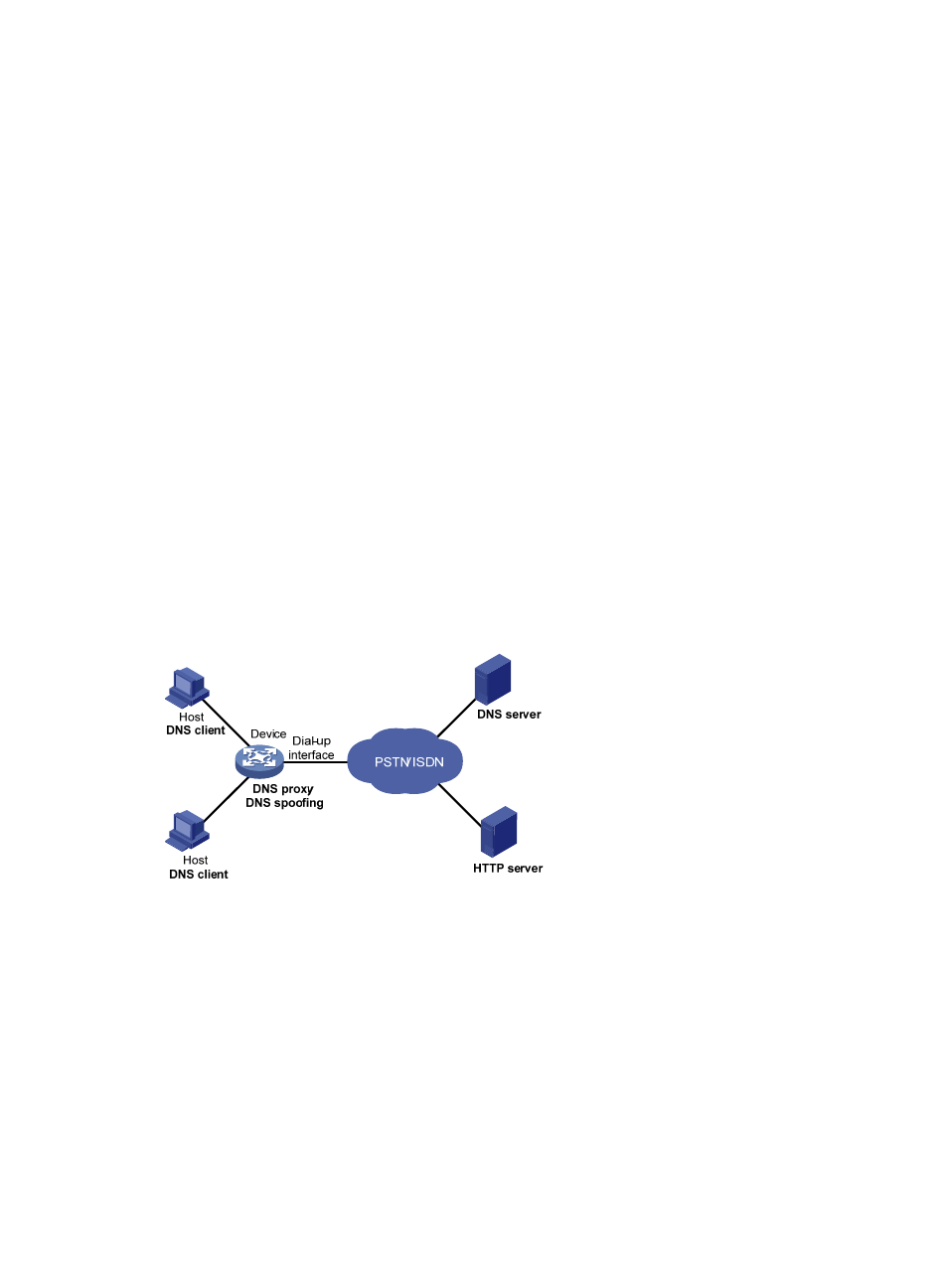
DNS spoofing
DNS spoofing is applied to the dial-up network, as shown in
726H
Figure 29
.
•
The device connects to the PSTN/ISDN network through a dial-up interface and triggers the
establishment of a dial-up connection only when packets are to be forwarded through the dial-up
interface.
•
The device serves as a DNS proxy and is specified as a DNS server on the hosts. After the dial-up
connection is established through the dial-up interface, the device dynamically obtains the DNS
server address through DHCP or other autoconfiguration mechanisms.
Figure 29 DNS spoofing application
DNS spoofing enables the DNS proxy to send a spoofed reply with a configured IP address even if it
cannot reach the DNS server because no dial-up connection is available. Without DNS spoofing, the
proxy does not answer or forward a DNS request if it cannot find a local matching DNS entry or reach
the DNS server.
In the network as shown in
727H
Figure 29
, a host accesses the HTTP server in following these steps:
1.
The host sends a DNS request to the device to resolve the domain name of the HTTP server into an
IP address.
2.
Upon receiving the request, the device searches the local static and dynamic DNS entries for a
match. If the dial-up connection has not been established, the device does not know the DNS
server address, or the DNS server address configured on the device is not reachable, the device
spoofs the host by replying a configured IP address. The TTL of the DNS reply is 0. The device must
have a route to the IP address with the dial-up interface as the output interface.