Troubleshooting dhcp server configuration, Symptom, Analysis – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 82: Solution, Dns proxy
69
The DNS client is made up of the resolver and cache. The user program and DNS client can run on the
same device or different devices, but the DNS server and the DNS client usually run on different devices.
Dynamic domain name resolution allows the DNS client to store latest mappings between domain names
and IP addresses in the dynamic domain name cache. The DNS client does not need to send a request
to the DNS server for a repeated query next time. The aged mappings are removed from the cache, and
latest entries are required from the DNS server. The DNS server decides how long a mapping is valid,
and the DNS client gets the aging information from DNS responses.
354B
DNS suffixes
The DNS client holds a list of suffixes which the user sets. The resolver can use the list to supply the missing
part of incomplete names.
For example, a user can configure com as the suffix for aabbcc.com. The user only needs to type aabbcc
to obtain the IP address of aabbcc.com because the resolver adds the suffix and delimiter before passing
the name to the DNS server.
•
If there is no dot (.) in the domain name (for example, aabbcc), the resolver considers this a host
name and adds a DNS suffix before the query. If no match is found after all the configured suffixes
are used, the original domain name (for example, aabbcc) is used for the query.
•
If there is a dot (.) in the domain name (for example, www.aabbcc), the resolver directly uses this
domain name for the query. If the query fails, the resolver adds a DNS suffix for another query.
•
If the dot (.) is at the end of the domain name (for example, aabbcc.com.), the resolver considers
it an FQDN and returns the query result, successful or failed. The dot at the end of the domain name
is considered a terminating symbol.
The device supports static and dynamic DNS client services.
If an alias is configured for a domain name on the DNS server, the device can resolve the alias into the
IP address of the host.
228B
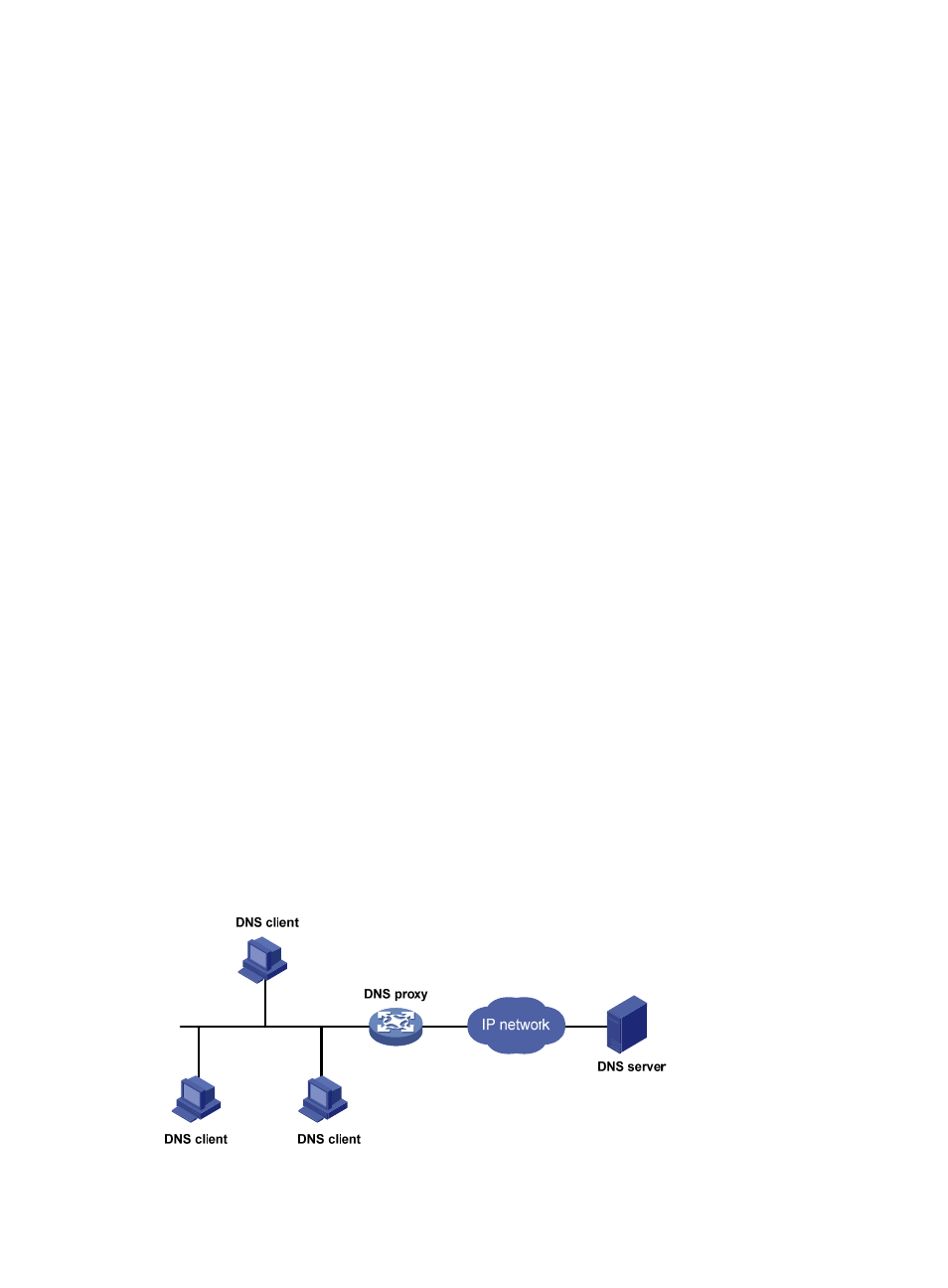
DNS proxy
A DNS proxy forwards DNS requests and replies between DNS clients and a DNS server.
As shown in
725H
Figure 28
, a DNS client sends a DNS request to the DNS proxy, which forwards the request
to the designated DNS server, and conveys the reply from the DNS server to the client.
The DNS proxy simplifies network management. When the DNS server address is changed, you can
change the configuration on only the DNS proxy instead of on each DNS client.
Figure 28 DNS proxy application