H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 88
75
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms
--- host.com ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
234B
Dynamic domain name resolution configuration example
358B
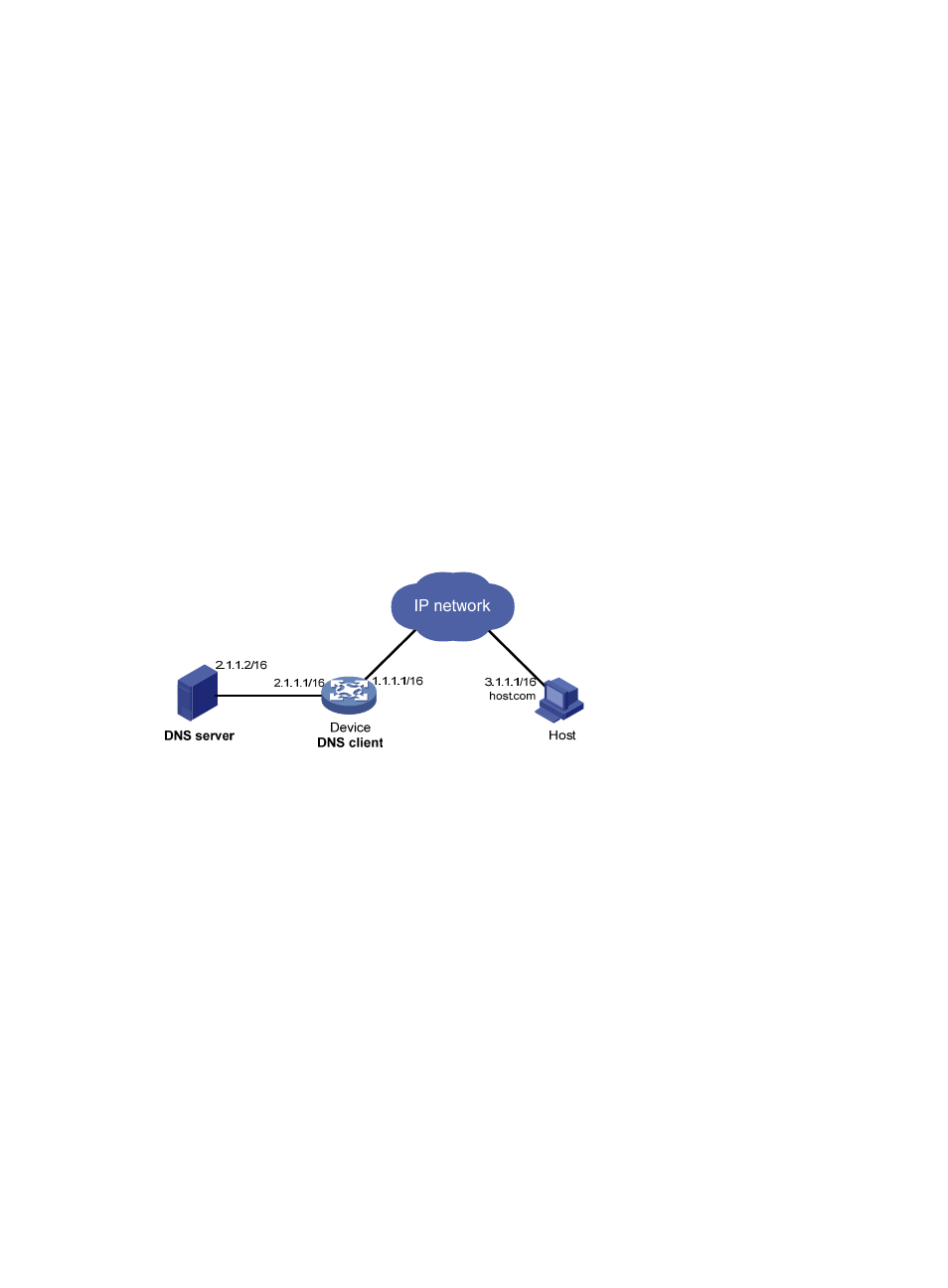
Network requirements
As shown in
735H
Figure 31
, the device wants to access the host by using an easy-to-remember domain name
rather than an IP address, and to request the DNS server on the network for an IP address by using
dynamic domain name resolution. The IP address of the DNS server is 2.1.1.2/16 and the DNS server has
a com domain, which stores the mapping between domain name host and IP address 3.1.1.1/16.
Configure dynamic domain name resolution and the domain name suffix com on the device that serves
as a DNS client so that the device can use domain name host to access the host with the domain name
host.com and the IP address 3.1.1.1/16.
Figure 31 Network diagram
359B
Configuration procedure
Before performing the following configuration, make sure that the device and the host can reach each
other, and that the IP addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in
736H
Figure 31
.
This configuration may vary with DNS servers. The following configuration is performed on a PC running
Windows Server 2000.
1.
Configure the DNS server:
a.
Select Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > DNS.
The DNS server configuration page appears, as shown in
737H
Figure 32
.
b.
Right-click Forward Lookup Zones, select New Zone, and then follow the wizard to create a
new zone named com.