Displaying and maintaining the dhcp relay agent, Configuring ddns, Overview – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 93: Ddns application
80
10B
Configuring DDNS
89B
Overview
DNS provides only the static mappings between domain names and IP addresses. When the IP address
of a node changes, your access to the node fails.
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) can dynamically update the mappings between domain names
and IP addresses for DNS servers to direct you to the latest IP address mapping to a domain name.
DDNS is supported by only IPv4 DNS, and is used to update the mappings between domain names and
IPv4 addresses.
238B
DDNS application
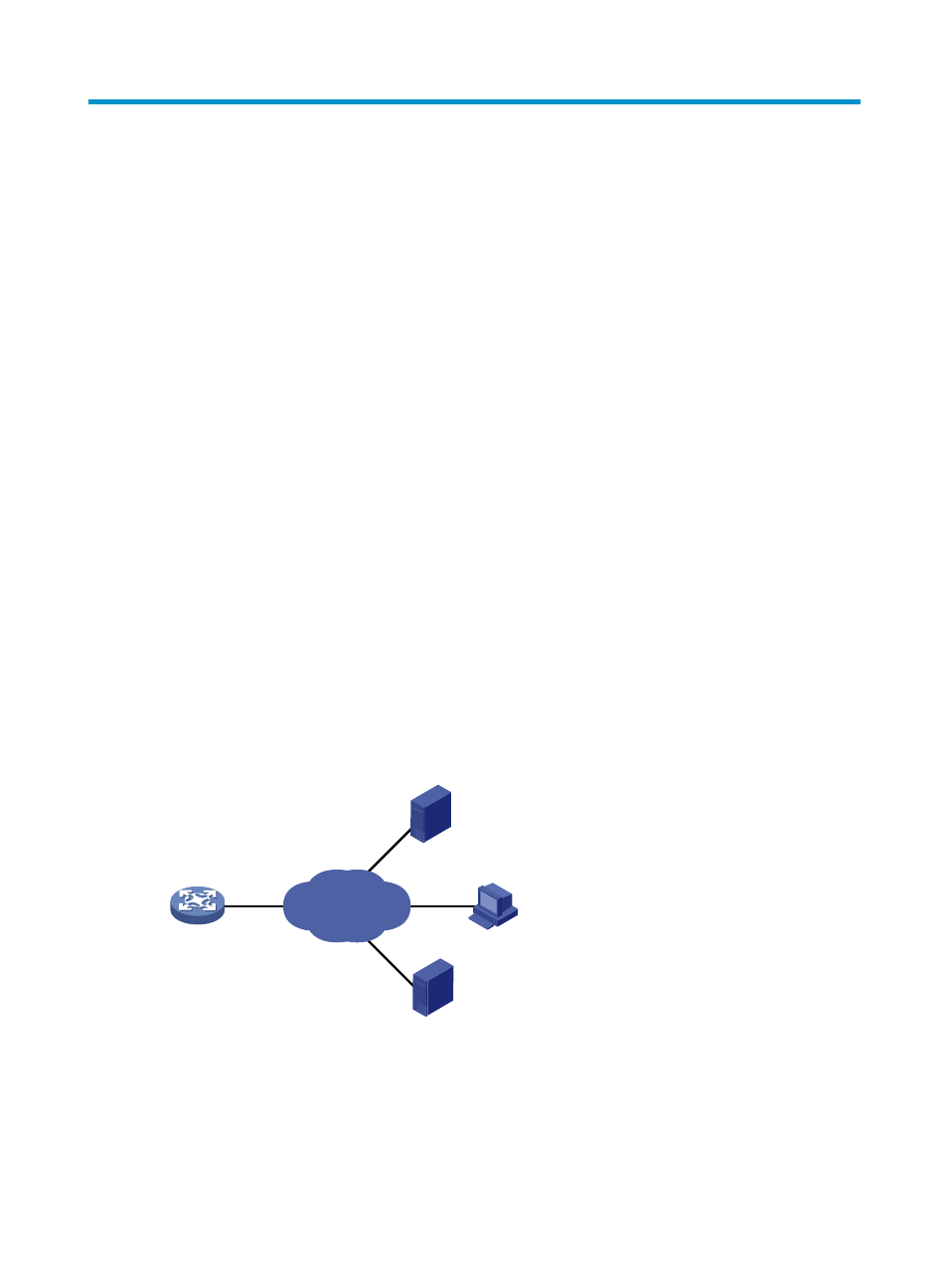
As shown in
741H
Figure 36
, DDNS works on the client-server model.
•
DDNS client—A device that needs to update the mapping between the domain name and the IP
address dynamically on the DNS server when the client's IP address changes. An Internet user
typically uses the domain name to access an application layer server such as an HTTP server or an
FTP server. When its IP address changes, the application layer server runs as a DDNS client that
sends a request to the DDNS server for updating the mapping between the domain name and the
IP address.
•
DDNS server—Informs the DNS server of latest mappings. When receiving the mapping update
request from a DDNS client, the DDNS server tells the DNS server to re-map the domain name and
the IP address of the DDNS client. Therefore, the Internet users can use the same domain name to
access the DDNS client even if the IP address of the DDNS client has changed.
Figure 36 DDNS application
With the DDNS client configured, a device can dynamically update the latest mapping between its
domain name and IP address on the DNS server through DDNS servers.
HTTP server
DDNS client
DDNS server
DNS server
IP network
HTTP client