Self-defined option configuration example, Configuring dns, Overview – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 81: Static domain name resolution, Dynamic domain name resolution
68
9B
Configuring DNS
80B
Overview
Domain Name System (DNS) is a distributed database used by TCP/IP applications to translate domain
names into IP addresses. With DNS, you can use easy-to-remember domain names in some applications
and let the DNS server translate them into correct IP addresses.
DNS services can be static or dynamic. After a user specifies a name, the device checks the local static
name resolution table for an IP address. If no IP address is available, it contacts the DNS server for
dynamic name resolution, which takes more time than static name resolution. To improve efficiency, you
can put frequently queried name-to-IP address mappings in the local static name resolution table.
226B
Static domain name resolution
Static domain name resolution means setting up mappings between domain names and IP addresses.
You can find IP addresses of the corresponding domain names in the static domain resolution table when
you use applications such as Telnet.
227B
Dynamic domain name resolution
353B
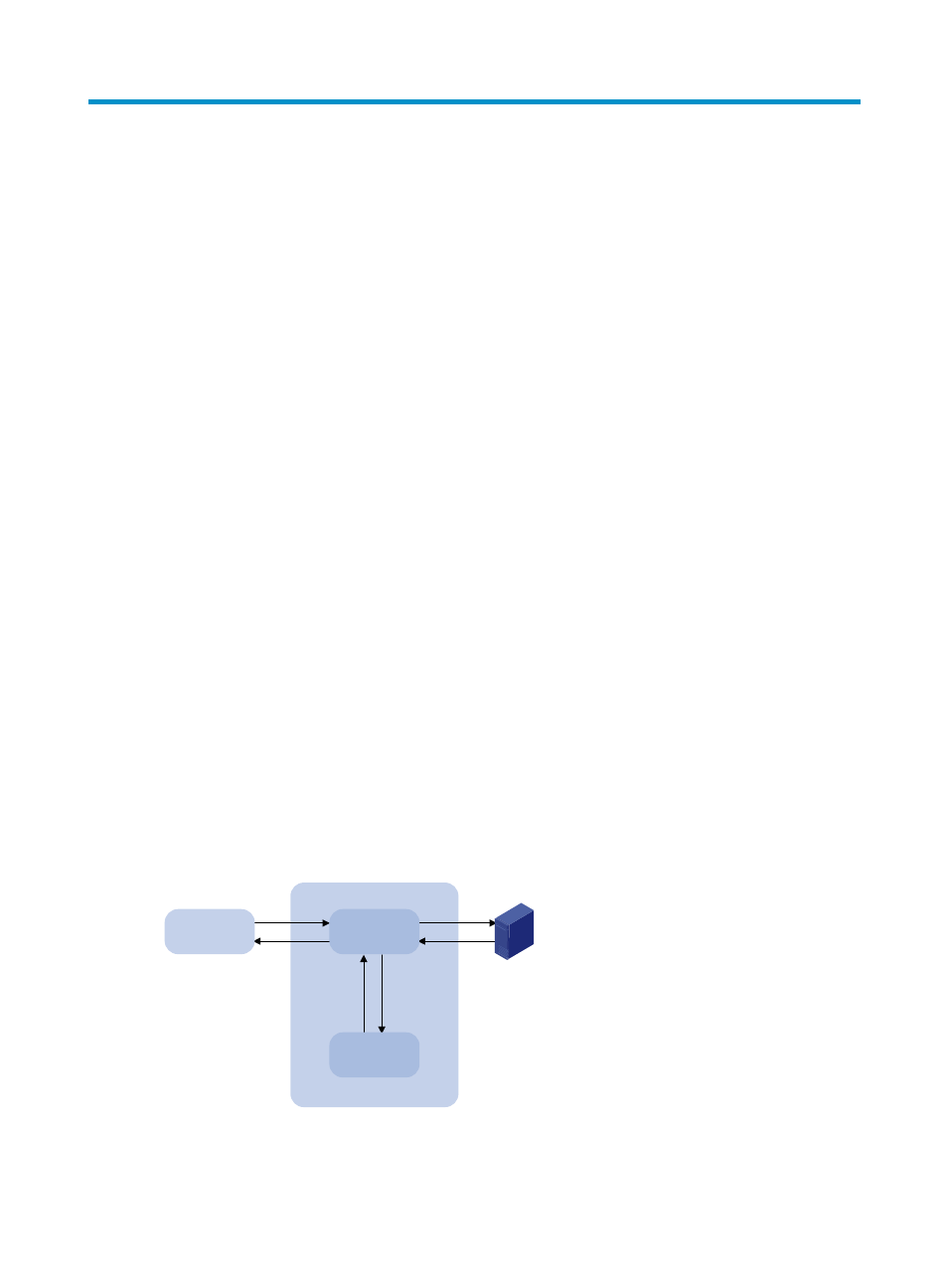
Resolution process
1.
A user program sends a name query to the resolver of the DNS client.
2.
The DNS resolver looks up the local domain name cache for a match. If the resolver finds a match,
it sends the corresponding IP address back. If not, it sends a query to the DNS server.
3.
The DNS server looks up the corresponding IP address of the domain name in its DNS database.
If no match is found, the server sends a query to other DNS servers. This process continues until a
result, whether successful or not, is returned.
4.
After receiving a response from the DNS server, the DNS client returns the resolution result to the
user program.
Figure 27 Dynamic domain name resolution
724H
Figure 27
shows the relationship between the user program, DNS client, and DNS server.
Request
Response
Response
Request
Save
Read
DNS client
DNS server
Resolver
Cache
User
program