Basic concepts in igmp snooping, Igmp snooping related ports – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 11
2
Basic concepts in IGMP snooping
IGMP snooping related ports
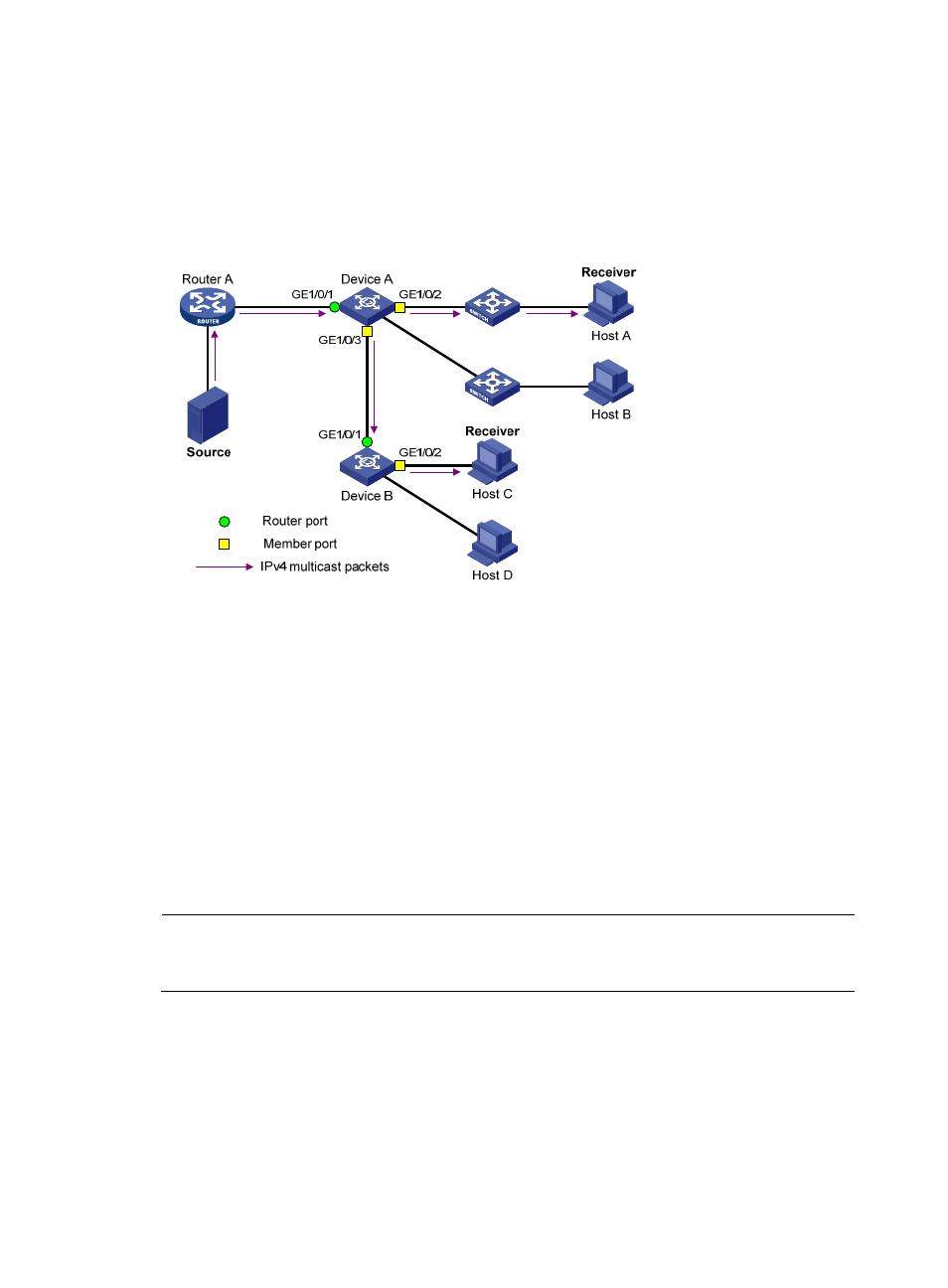
As shown in
, Router A connects to the multicast source, IGMP snooping runs on Device A and
Device B, and Host A and Host C are receiver hosts (multicast group members).
Figure 2 IGMP snooping related ports
The following describes the ports involved in IGMP snooping, as shown in
:
•
Router port—Layer 3 multicast device-side port. Layer 3 multicast devices include designated
routers (DRs) and IGMP queriers. In
, GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device A and Device B are
router ports. The Layer 2 device registers all its local router ports in its router port list.
Do not confuse the "router port" in IGMP snooping with the "routed interface" commonly known as
the "Layer 3 interface." The router port in IGMP snooping is the Layer 2 interface.
•
Member port—Multicast receiver-side port. In
, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and
GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 of Device A and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 of Device B are member ports. The
Layer 2 device registers all the member ports on the local device in its IGMP snooping forwarding
table.
Unless otherwise specified, router ports and member ports in this document include static and dynamic
ports.
NOTE:
An IGMP-snooping-enabled Layer 2 device deems that all its ports on which IGMP general queries with
the source IP address other than 0.0.0.0 or PIM hello messages are received are dynamic router ports.
Compared with a common Layer 2 device, an AC has wireless interfaces. The port roles on the access
controller in
are described as follows:
•
Router port—GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on the access controller leads the device toward the multicast
source, so GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 is a router port.
•
Member port—GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on the access controller connects to a multicast receiver, so
GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 is a member port. In addition, after an AP joins an ESS, the access
controller creates a virtual Layer 2 interface WLAN-DBSS corresponding to that ESS. As shown