Configuring multicast vlans, Overview – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 85
76
Configuring multicast VLANs
Overview
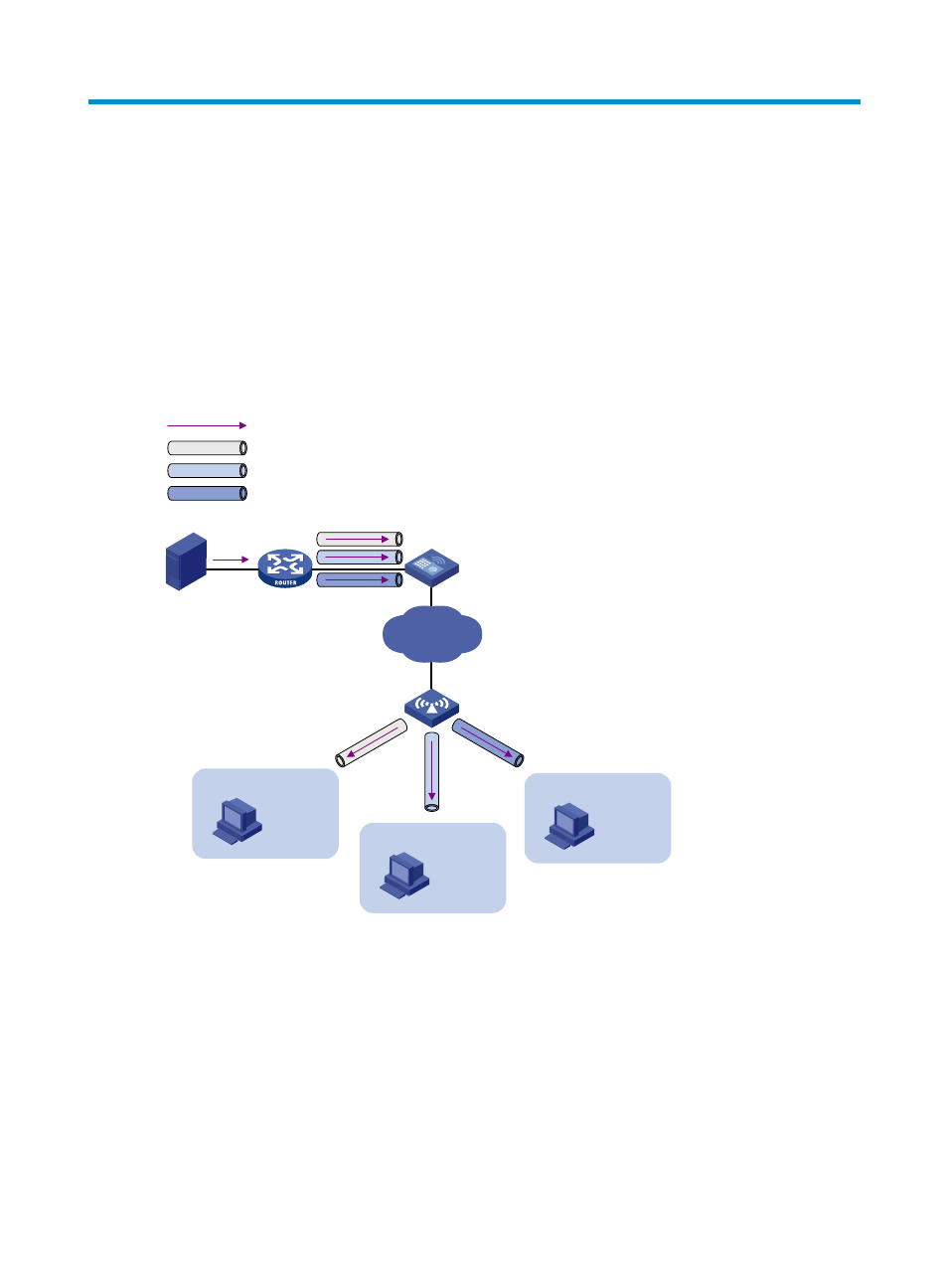
In the traditional multicast programs-on-demand mode shown in
, when hosts (Host A, Host B
and Host C) that belong to different VLANs require multicast programs-on-demand service, the Layer 3
device, Router A, must forward a separate copy of the multicast traffic in each user VLAN to the Layer 2
device, AC. This results in not only waste of network bandwidth but also extra burden on the Layer 3
device.
Figure 17 Multicast transmission without multicast VLAN
The multicast VLAN feature configured on the Layer 2 device is the solution to this issue. With the
multicast VLAN feature, the Layer 3 device replicates the multicast traffic only in the multicast VLAN
instead of making a separate copy of the multicast traffic in each user VLAN. This saves network
bandwidth and lessens the burden on the Layer 3 device.
The multicast VLAN feature can be implemented in a port-based multicast VLAN.
As shown in
, Host A, Host B, and Host C are in different user VLANs. All the user ports (ports
with attached hosts) on the AC are hybrid ports. On the AC, configure VLAN 10 as a multicast VLAN,
assign all the user ports to VLAN 10, and enable IGMP snooping in the multicast VLAN and all user
VLANs.
Source
VLAN 2
VLAN 3
VLAN 4
AC
Receiver
Host A
Receiver
Host B
Receiver
Host C
Router A
IGMP querier
IP network
AP
Multicast packets
VLAN 2
VLAN 3
VLAN 4