Ripng packet format, Basic format, Rte format – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 177
166
•
Next hop address—IPv6 address of a neighbor along the path to the destination
•
Egress interface—Outbound interface that forwards IPv6 packets
•
Metric—Cost from the local router to the destination
•
Route time—Time that elapsed since a route entry is last changed. Each time a route entry is
modified, the routing time is set to 0.
RIPng packet format
Basic format
A RIPng packet consists of a header and multiple route table entries (RTEs). The maximum number of RTEs
in a packet depends on the IPv6 MTU of the sending interface.
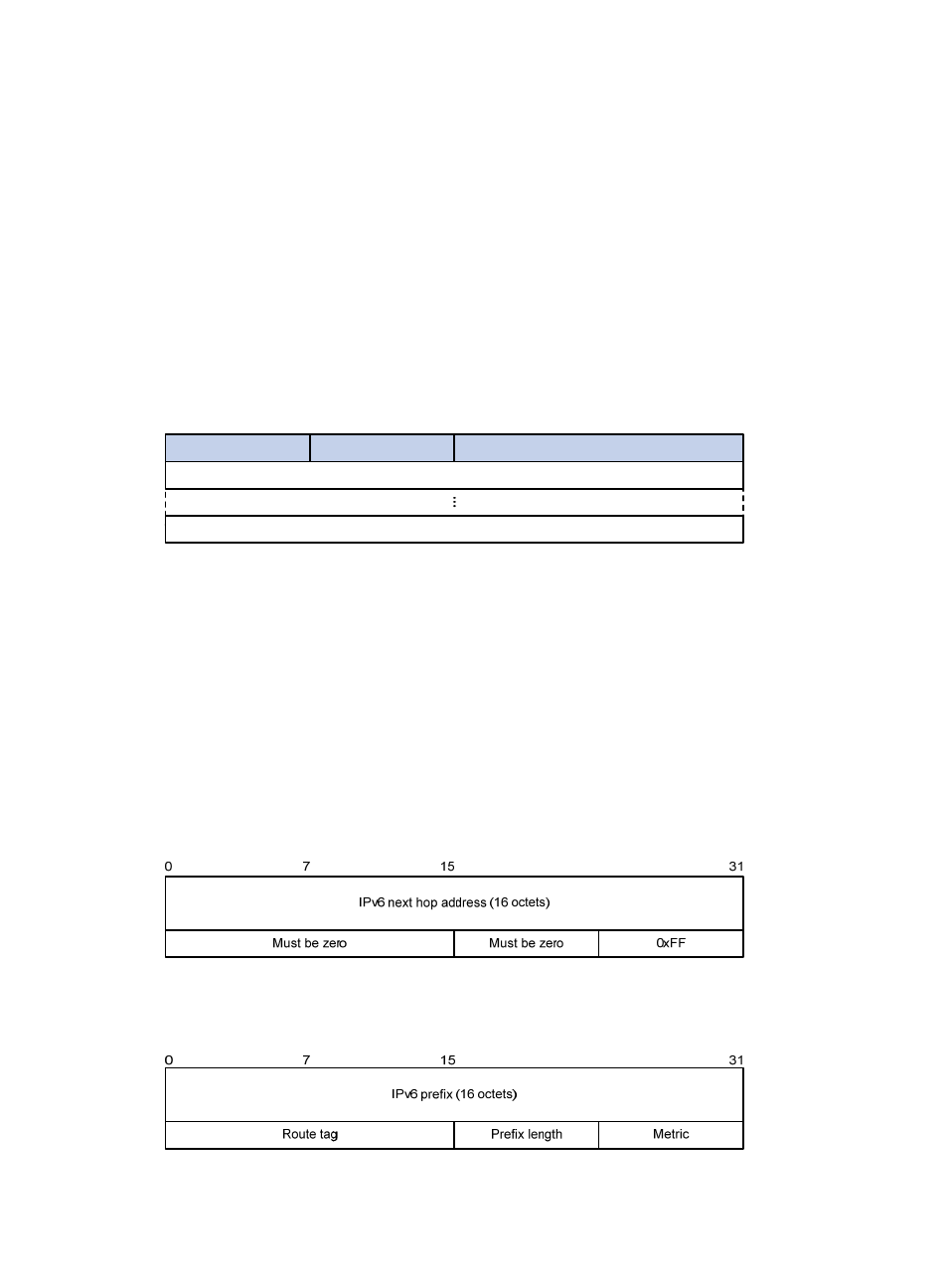
Figure 58 RIPng basic packet format
Packet header description:
•
Command: Type of message. 0x01 indicates Request, 0x02 indicates Response.
•
Version: Version of RIPng. It can only be 0x01 now.
•
RTE: Route table entry, 20 bytes for each entry.
RTE format
The following are types of RTEs in RIPng:
•
Next hop RTE—Defines the IPv6 address of a next hop
•
IPv6 prefix RTE—Describes the destination IPv6 address, route tag, prefix length and metric in the
RIPng routing table.
Figure 59 Next hop RTE format
IPv6 next hop address is the IPv6 address of the next hop.
Figure 60 IPv6 prefix RTE format
Command
Route table entry 1 (20 octets)
Version
Must be zero
Route table entry n (20 octets)
0
7
15
31