4 xml diagram legend, 1 element symbols, 1 examples – Doremi DSV-J2 User Manual
Page 64
15.4 XML Diagram Legend
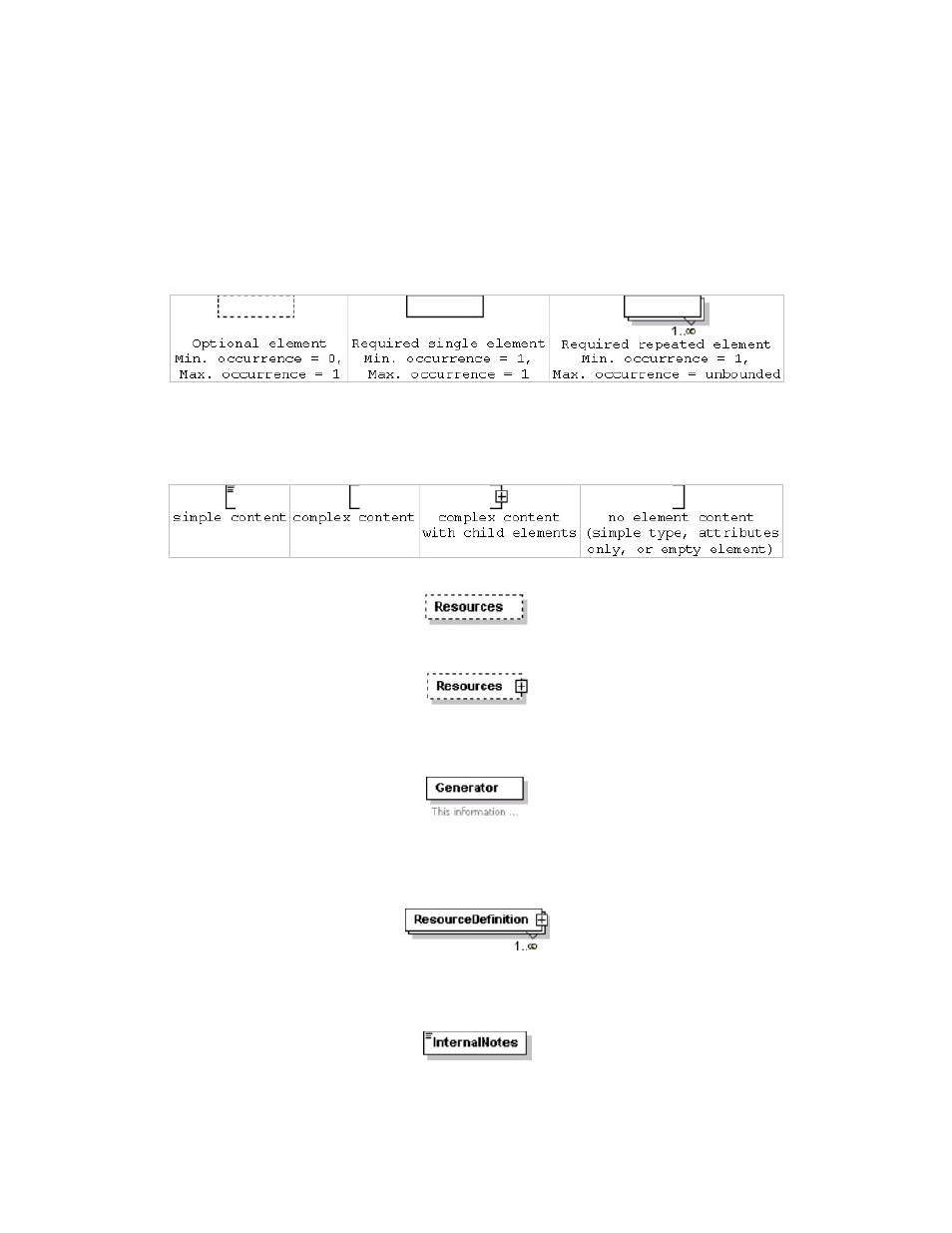
The following provides a legend for notation used in diagrams depicting XML structures.
15.4.1Element symbols
In the schema design diagrams presented above in this document, only the elements are
drawn. Attributes are not visible. The cardinality of the element (0..1, 1 exactly, 0..n, 1..n) is
indicated by the border of the elements. Optional elements are drawn with a dashed line,
required elements with a solid line. A maximum occurrence greater one is indicated by a double
border.
The content model of elements is symbolized on the left and right side of the element boxes.
The left side indicates whether the element contains a simple type (text, numbers, dates, etc.) or
a complex type (further elements). The right side of the element symbol indicates whether it
contains child elements or not:
15.4.1.1 Examples
Optional single element without child elements. Minimum Occurrence = 0, Maximum
Occurrence = 1, content = complex.
As above, but with child elements. The plus at the right side indicates the presence of one or
more undisplayed child elements.
Mandatory single element. Minimum Occurrence = 1, Maximum Occurrence = 1, content =
complex, no child elements (i.e., this denotes an empty element). The gray or green text below
the element displays the xml-schema annotation associated with the element.
Mandatory multiple element containing child elements (content = complex). This element must
occur at least once (Minimum Occurrence = 1) and may occur as often as desired (Maximum
Occurrence = unbounded).
Mandatory single element with containing simple content (e.g. text) or mixed complex content
(e.g. text with xhtml markup). Minimum Occurrence = 1, Maximum Occurrence = 1, type =
DSV.OM.000391.DRM
Page 64 of 68
Version 1.3
Doremi Labs