Bpdu tunneling configuration, Introduction to bpdu tunneling, Background – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 117
106
BPDU tunneling configuration
Introduction to BPDU tunneling
As a Layer 2 tunneling technology, BPDU tunneling enables Layer 2 protocol packets from
geographically dispersed customer networks to be transparently transmitted over specific tunnels across
a service provider network.
Background
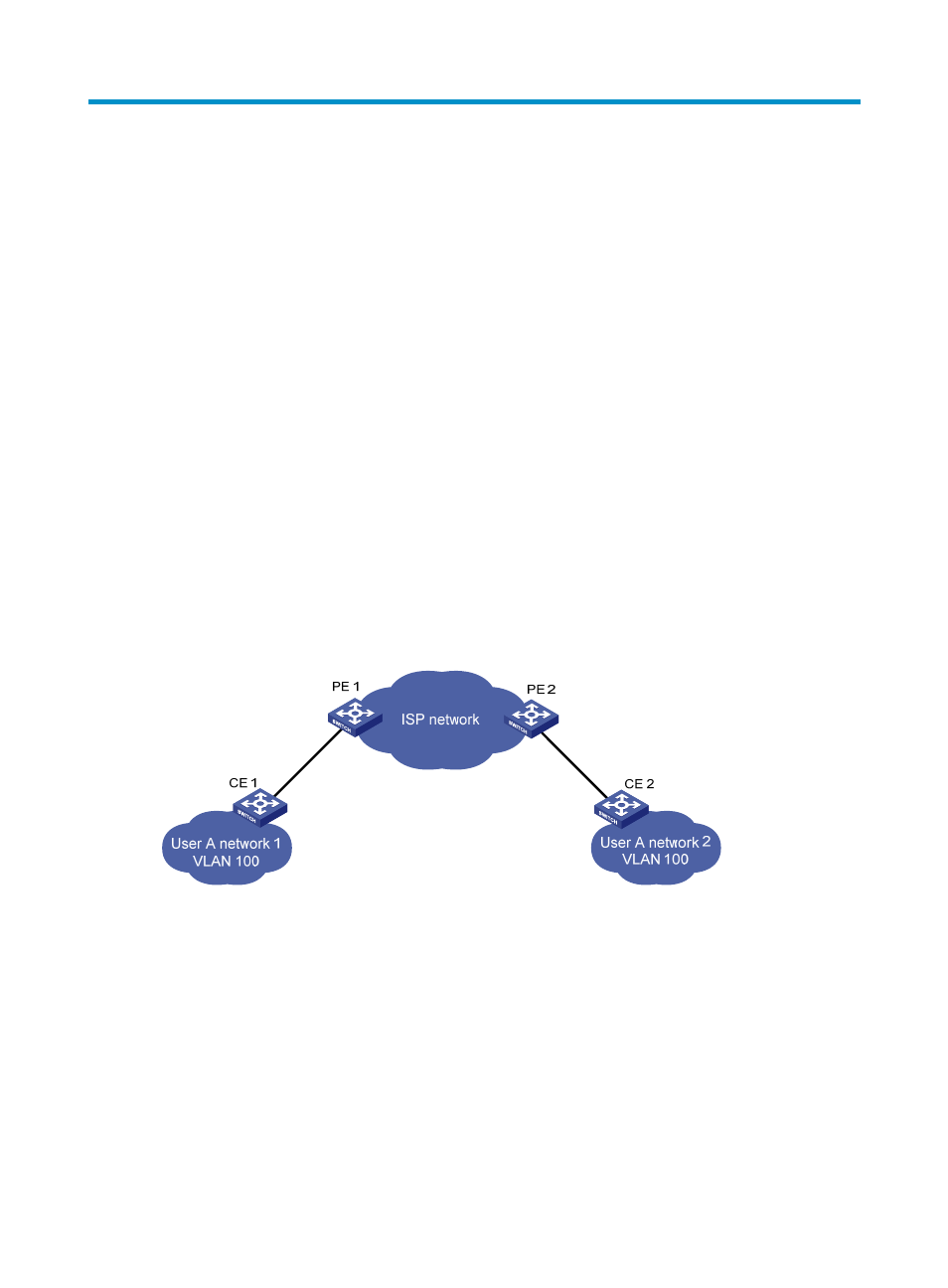
Dedicated lines are used in a service provider network to build user-specific Layer 2 networks. As a result,
a user network consists of parts located at different sides of the service provider network. As shown in
, the devices for User A are CE 1 and CE 2, both of which belong to VLAN 100. User A’s
network is divided into network 1 and network 2, which are connected by the service provider network.
When a Layer 2 protocol (for example, STP) runs on both network 1 and network 2, the Layer 2 protocol
packets must be transmitted over the service provider network to implement Layer 2 protocol calculation
(for example, spanning tree calculation). When receiving a Layer 2 protocol packet, the PEs cannot
determine whether the packet is from the user network or the service provider network, and must deliver
the packet to the CPU for processing. In this case, the Layer 2 protocol calculation in User A’s network is
mixed with that in the service provider network, and the user network cannot implement independent
Layer 2 protocol calculation.
Figure 31 BPDU tunneling application scenario
BPDU tunneling addresses this problem. With BPDU tunneling, Layer 2 protocol packets from customer
networks can be transparently transmitted over the service provider network in the following workflow:
1.
After receiving a Layer 2 protocol packet from CE 1, PE 1 encapsulates the packet, replaces its
destination MAC address with a specific multicast MAC address, and forwards the packet to the
service provider network.
2.
The encapsulated Layer 2 protocol packet (called bridge protocol data unit, BPDU) is forwarded
to PE 2 at the other end of the service provider network, which de-encapsulates the packet, restores
the original destination MAC address of the packet, and then sends the packet to CE 2.
H3C devices support BPDU tunneling for the following protocols:
•
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
•
Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP)