Gvrp configuration, Introduction to gvrp, Garp – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 172: How garp works, Garp messages
161
GVRP configuration
The Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) provides a generic framework for devices in a
switched LAN, such as end stations and switches, to register and deregister attribute values. The GARP
VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) is a GARP application that registers and deregisters VLAN attributes.
GVRP uses the operating mechanism of GARP to maintain and propagate dynamic VLAN registration
information for GVRP devices on the network.
Introduction to GVRP
GARP
GARP provides a mechanism that allows participants in a GARP application to distribute, propagate,
and register—with other participants in a LAN—the attributes specific to the GARP application, such as
VLAN or multicast address attributes.
How GARP works
Each port that participates in a GARP application (GVRP, for example) is a GARP participant.
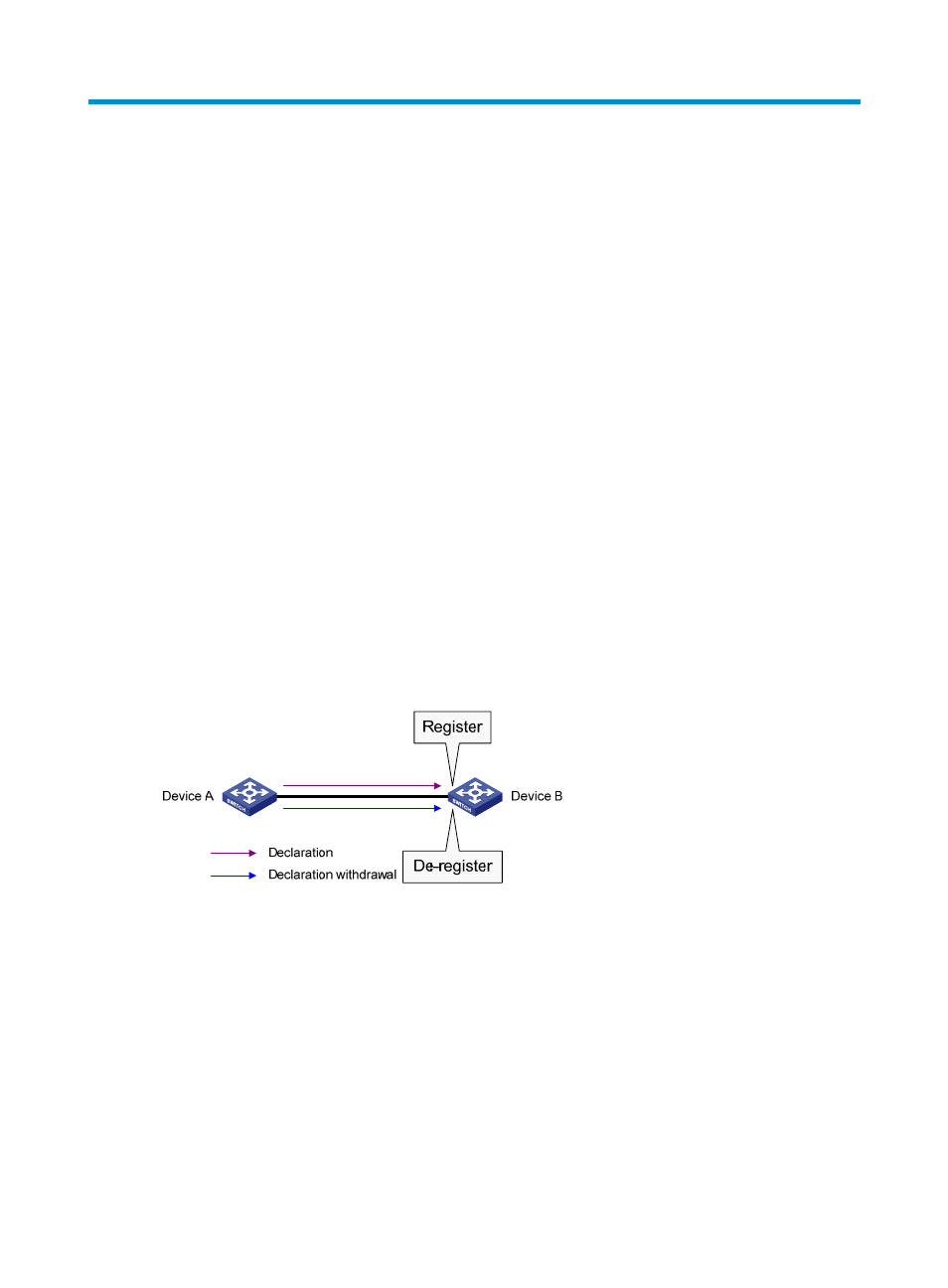
GARP enables GARP participants to propagate attribute values throughout the switched LAN. As shown
in
, a GARP participant registers and deregisters its attribute values with other GARP
participants by sending and withdrawing declarations, and registers and deregisters the attribute values
of other participants according to the declarations and withdrawals that it has received.
Figure 51 How GARP works
For example, a GVRP-enabled port registers and deregisters VLAN in the following cases.
•
When the port receives a VLAN attribute declaration, it registers the VLAN attribute and joins the
VLAN.
•
When the port receives a VLAN withdrawal, it deregisters the VLAN and leaves the VLAN.
GARP messages
A GARP participant exchanges information with other GARP participants by sending GARP messages:
Join, Leave, and LeaveAll. As a GARP application, GVRP also uses GARP messages for information
exchange.
1.
Join messages