Bpdu tunneling for pvst configuration example, Network requirements – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 122
111
[PE1] vlan 2
[PE1-vlan2] quit
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port access vlan 2
# Disable STP on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and then enable BPDU tunneling for STP on it.
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo stp enable
[PE1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] bpdu-tunnel dot1q stp
2.
Configure PE 2.
# Configure the destination multicast MAC address for BPDUs as 0x0100-0CCD-CDD0.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] bpdu-tunnel tunnel-dmac 0100-0ccd-cdd0
# Create VLAN 2 and assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to VLAN 2.
[PE2] vlan 2
[PE2-vlan2] quit
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port access vlan 2
# Disable STP on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and then enable BPDU tunneling for STP on it.
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] undo stp enable
[PE2-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] bpdu-tunnel dot1q stp
BPDU tunneling for PVST configuration example
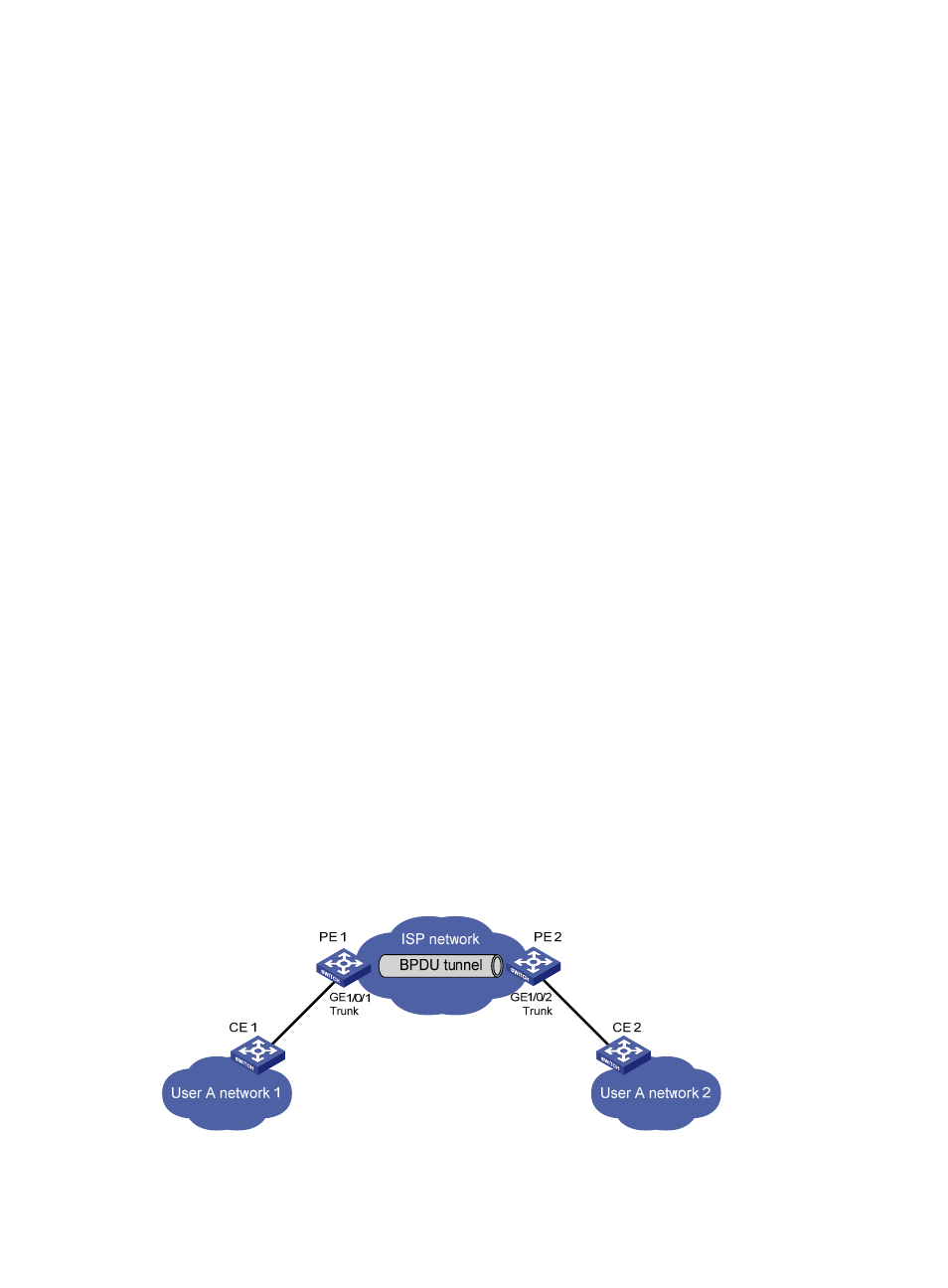
Network requirements
As shown in
:
•
CE 1 and CE 2 are edge devices on the geographically dispersed network of User A. PE 1 and PE
2 are edge devices on the service provider network.
•
All ports that connect service provider devices and customer devices and those that interconnect
service provider devices are trunk ports and allow packets of any VLAN to pass through.
•
PVST is enabled for VLANs 1 through 4094 on User A’s network.
After the configuration, CE 1 and CE 2 must implement consistent PVST calculation across the service
provider network, and the destination multicast MAC address carried in BPDUs must be
0x0100-0CCD-CDD0.
Figure 34 Network diagram for configuring BPDU tunneling for PVST