H3C Technologies H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 151
141
You can configure an aging timer for the voice VLAN. The system will remove the port from the voice
VLAN when the aging timer expires if no voice packet is received on the port during the aging timer.
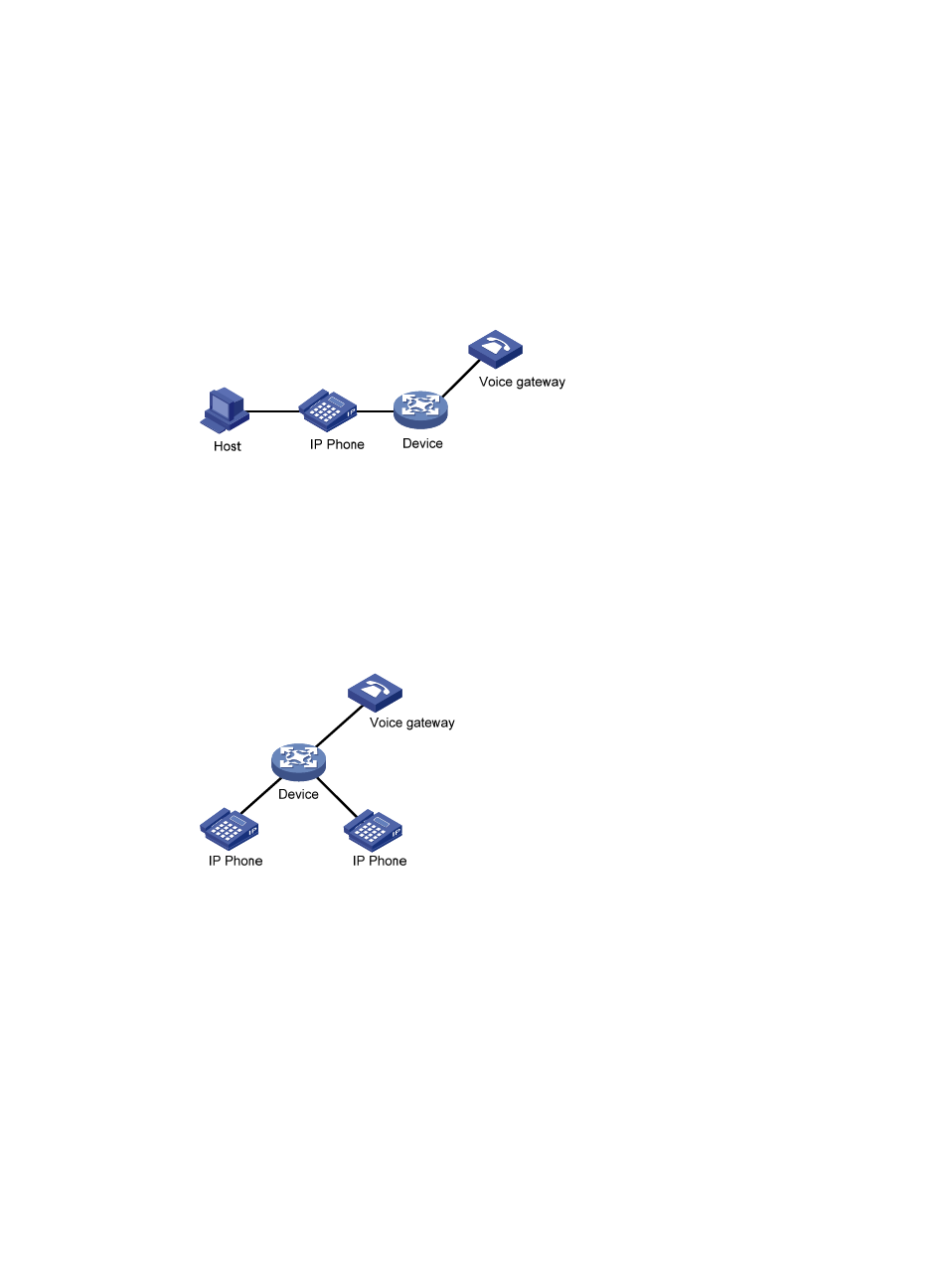
Assigning ports to and removing ports from a voice VLAN are automatically performed. Automatic
mode is suitable for scenarios where PCs and IP phones connected in series access the network
through the device and ports on the device transmit both voice traffic and data traffic at the same
time, as shown in
. When the voice VLAN works normally, if the system reboots, the
system reassigns ports in automatic voice VLAN assignment mode to the voice VLAN after the
reboot, ensuring that existing voice connections can work normally. In this case, voice traffic
streams do not trigger port assignment to the voice VLAN.
Figure 138 PCs and IP phones connected in series access the network
•
Manual mode—You must assign the port to a voice VLAN manually. Then, the system matches the
source MAC addresses in the packets against the OUI addresses. If a match is found, the system
issues ACL rules and configures the packet precedence. In this mode, assigning ports to and
removing ports from a voice VLAN are performed manually. Manual mode is suitable for scenarios
where only IP phones access the network through the device, and ports on the device transmit only
. In this mode, ports assigned to a voice VLAN transmit voice
traffic exclusively, which prevents the impact of data traffic on the transmission of voice traffic.
Figure 139 Only IP phones access the network
Both modes forward tagged packets according to their tags.
and
list the
configurations required for ports of different link types to support tagged or untagged voice traffic sent
from IP phones when different voice VLAN assignment modes are configured.
If the port that receives tagged voice traffic from an IP phone is configured with 802.1X authentication
and a guest VLAN, assign different VLAN IDs to the voice VLAN, the PVID of the accessing port, and the
802.1X guest VLAN.
When IP phones send untagged voice traffic, the voice traffic receiving ports on must operate in manual
voice VLAN assignment mode. To implement the voice VLAN feature, you must configure the PVID of
each receiving port as the voice VLAN. As a result, you cannot implement 802.1X authentication.