Exploring the gsm snmp agent, Icontrol mibs – Grass Valley iControl V.4.43 User Manual
Page 520
iControl and SNMP
Exploring the GSM SNMP Agent
510
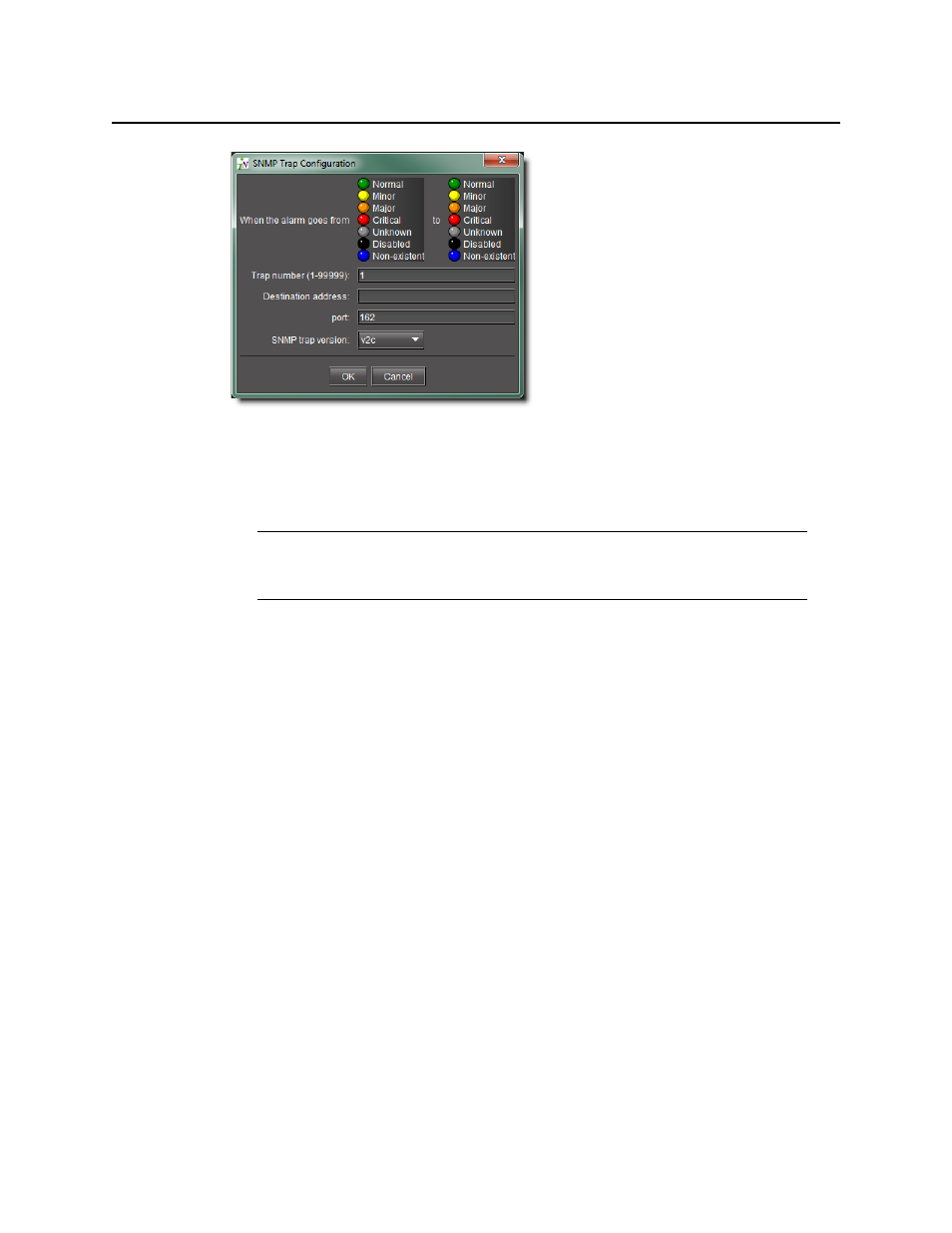
Figure 8-122
6. In the Admin tab of the General status managers window, an entry labelled SNMP trap
sender appears (with an associated SNMP Manager address) in the Global actions list.
7. Close the window.
Exploring the GSM SNMP Agent
In order to be able to establish useful communications between the GSM SNMP agent and a
third party SNMP manager, it is important to understand some of the agent’s implementation
details, such as its MIB structures and syntax.
iControl MIBs
OIDs specific to Miranda and to the iControl GSM SNMP agent and traps can be resolved to a
textual convention using two Management Information Base (MIB) files available from
Miranda Technologies Inc.:
GSM‐MIB.mib
and
MIRANDA‐MIB.mib
.
The root file is
MIRANDA‐MIB.mib
, which contains:
• the root level definition for
GSM‐MIB.mib
• an enumeration of all the different types of alarms that can be reported by an iControl
GSM SNMP agent. This enumeration covers most of the alarms reported by all Miranda
Densité and Imaging series cards. The textual convention for this enumeration is
GsmTraps. Some examples of alarm types are: black detect, freeze detect, and audio silence.
• an enumeration of the different states of an alarm (e.g. error, warning, ok).
The GSM-MIB.mib file describes the GSM alarm table and the traps variable bindings. GSM trap
numbers are configurable by the user, which results in the creation of a custom MIB based on
the configuration of the GSM SNMP trap actions.
Note: The SNMP OIDs specific to Miranda devices and to the iControl GSM agent
and traps are contained in MIB files (
GSM‐MIB.mib
and the
MIRANDA‐MIB.mib
)
available from Miranda Technical Support (see