Discussion – Grass Valley NV9000-SE v.5.0 User Manual
Page 429
411
NV9000-SE Utilities
User’s Guide
•
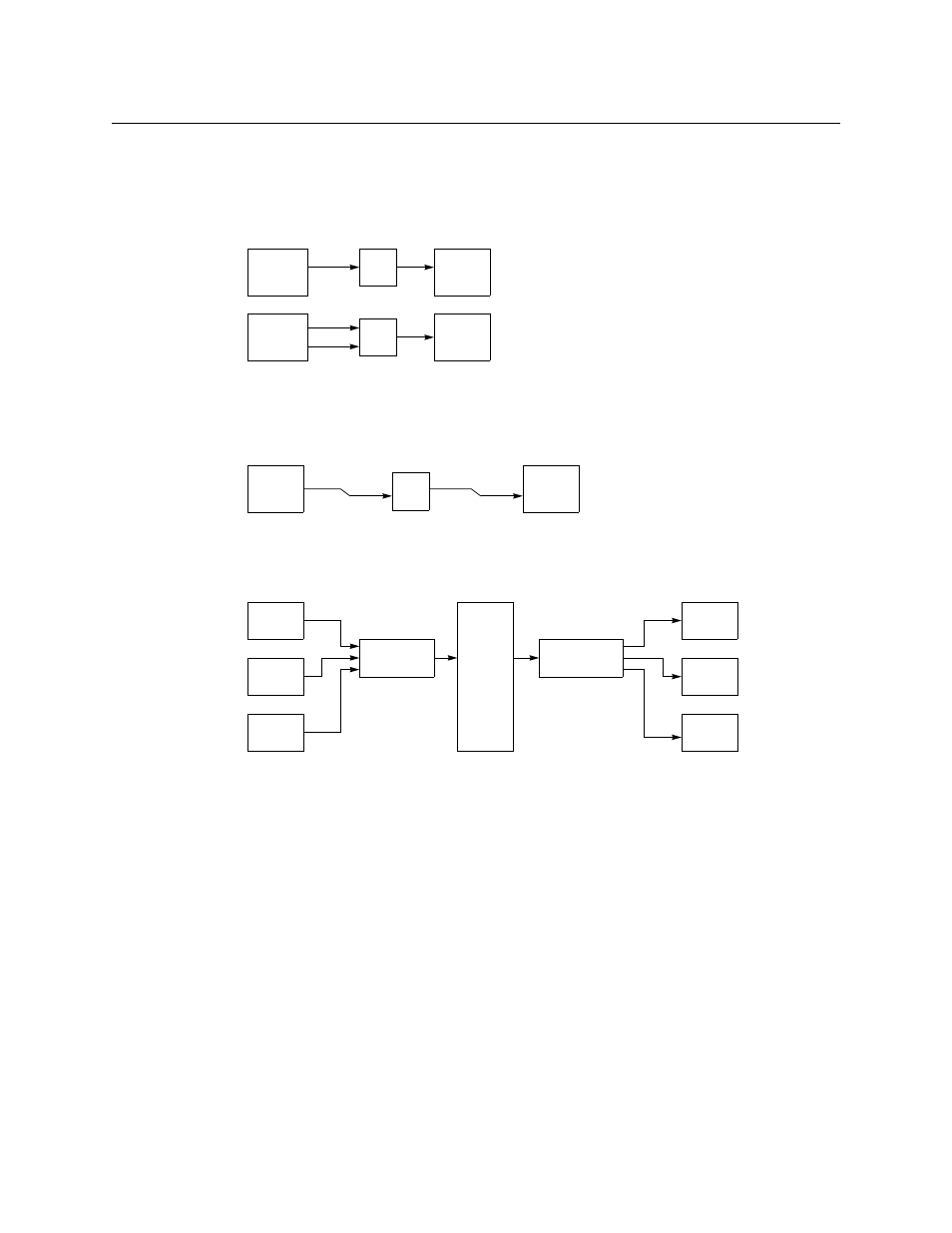
Case B: format conversions.
In this case, tielines use intermediate devices to connect router matrices of different types.
Here, analog signals are converted to digital signals along tielines:
With tielines, it is possible to take an analog source to a digital output (in one take on a single
control panel).
•
Case C: up- or down-conversion:
•
Case D: embedding or disembedding.
In this example, a tieline connects multiple ports at one end and a single port at the other
end:
Discussion
These are the main reasons for tielines:
•
Switch a source on one router to a destination on another router.
•
Connect routers in separate locations.
•
Expand smaller routers.
•
(Commonly) to perform signal conversions.
•
(Commonly) to perform audio embedding or disembedding.
•
Create signal delays (for audio).
These are the specific benefits of defining tielines:
•
Only a single press of a take button is required.
•
Tielines for a take are obtained from a pool of tielines defined in the NV9000 configuration.
Ports are not committed to particular tielines. Takes using tielines (as needed) are transpar-
ent to the operator as long as the system controller does not run out of tieline ports.
Digital
System
L
A/D
SD
Router
AES
Router
tielines
Analog
System
A/D
R
Analog
Video
Router
Analog
Audio
Router
tielines
Up
Conv.
HD
Router
SD
Router
Embedder
SD
AES
1/2
AES
3/4
tielines
(some
router)
SD
Disembedder
AES
1/2
AES
3/4
tielines